Configure SSO using OIDC
This page shows how to generally configure single sign-on (SSO) to authenticate to the account console and Databricks workspaces using OIDC. For a demo of configuring OIDC SSO with Okta, see Secure Your Databricks Access with OIDC SSO.
For an overview of single sign-on in the account, see Configure SSO in Databricks.
Enable SSO using OIDC
To prevent getting locked out of Databricks during single sign-on testing, Databricks recommends keeping the account console open in a different browser window. You can also configure emergency access with security keys to prevent lockout. See Emergency access to prevent lockouts.
-
As an account admin, log in to the account console and click Security.
-
Click the Authentication tab.
-
Next to Authentication, click Manage.
-
Choose Single sign-on with my identity provider.
-
Click Continue.
-
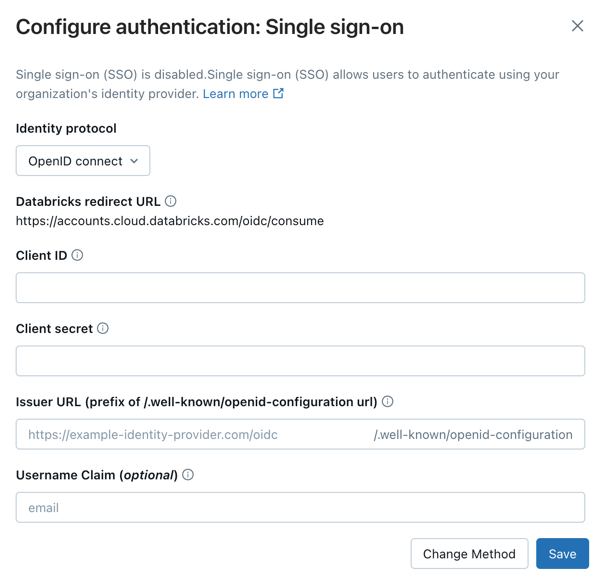
Under Identity protocol, select OpenID Connect.
-
Copy the value in the Databricks Redirect URL field.
-
Go to your identity provider and create a new client application (web), entering the Databricks Redirect URL value in the appropriate field in the identity provider configuration interface.
Your identity provider should have documentation to guide you through this process.
-
Copy the client ID, client secret, and OpenID issuer URL generated by the identity provider for the application.
-
Client ID is the unique identifier for the Databricks application you created in your identity provider. This is sometimes referred to as the Application ID.
-
Client secret is a secret or password generated for the Databricks application that you created. It is used to authorize Databricks with your identity provider.
-
Issuer URL is the prefix of the URL at which your identity-provider's OpenID Configuration Document can be found. That OpenID Configuration Document must found be in
{issuer-url}/.well-known/openid-configuration.Remove the
/.well-known/openid-configurationending from the URL. You can specify query parameters by appending them to the issuer URL, for example{issuer-url}?appid=123.
-
-
Return to the Databricks account console Authentication tab and enter values you copied from the identity provider application to the Client ID, Client secret, and OpenID issuer URL fields.
-
Optionally, enter a Username claim if you want to use a claim other than
emailas users' Databricks usernames. See your identity provider's documentation for specific information on claim values.
-
Click Save.
-
Click Test SSO to validate that your SSO configuration is working properly.
-
Click Enable SSO to enable single sign-on for your account.
-
Test account console login with SSO.
-
Grant all account users access to the Databricks application in your identity provider. You might need to modify the access permissions for the application.
Configure unified login and add users to Databricks
After you configure SSO, Databricks recommends that you configure unified login and add users to your account using SCIM provisioning.
-
Configure unified login
Unified login allows you to use the account console SSO configuration in your Databricks workspaces. If your account was created after June 21, 2023 or you did not configure SSO before December 12, 2024, unified login is enabled on your account for all workspaces and it cannot be disabled. To configure unified login, see Enable unified login.
-
Add users to Databricks
-
Enable JIT provisioning
Databricks recommends enabling JIT to automatically add users to Databricks when they first log in using SSO. JIT provisioning is on by default for accounts created after May 1, 2025 when SSO is configured. See Automatically provision users (JIT).
-
Configure SCIM provisioning
Databricks recommends using SCIM provisioning to sync users and groups automatically from your identity provider to your Databricks account. SCIM streamlines onboarding a new employee or team by using your identity provider to create users and groups in Databricks and give them the proper level of access. See Sync users and groups from your identity provider using SCIM.
-
Troubleshooting OIDC SSO
The following table lists OIDC error codes that might be encountered during SSO authentication. Each entry provides the error code, machine-readable error name, a detailed explanation, and recommended next steps for troubleshooting. Use this information to quickly identify and resolve OIDC authentication issues in your workspace.
Error Code | Explanation | Next steps |
|---|---|---|
| A generic login error occurred. | Obtain the request ID to identify which requests failed. |
| The | Check the IdP configuration to ensure the |
| The | Inspect your network traffic to verify if the nonce expired or if the cookie missing. |
| Databricks could not retrieve metadata from the OIDC configuration. The IdP's issuer URL is used to look up endpoints required for the OIDC flow. | Ensure that |
| The IdP did not return an authorization code. Databricks needs this code to redeem for an ID token in the next step. | Check that your IdP supports the OIDC authorization code flow ( |
| This typically occurs when the client secret is incorrect or expired. It might also happen if the IdP returns any non-200 response. | Ensure the client secret is valid. |
| The authorization code was received from the IdP, but the subsequent token exchange did not return the expected ID token. After receiving the authorization code, the next step in the OIDC flow is to obtain the ID token. | Check the IdP configuration. You also can manually test the OIDC flow to verify that codes and tokens are returned. |
| Similar to | Check the IdP configuration. You also can manually test the OIDC flow to verify that codes and tokens are returned. |
| The IdP did not send the email claim in the ID token. This might be due to the use of a custom claim. | Verify if a custom claim is used, and ensure it is properly configured. |
| A generic login error occurred. | Obtain the request ID to identify which requests failed. |