Configure AI Gateway on model serving endpoints
A new AI Gateway experience is available in Beta. The new AI Gateway is the enterprise control plane for governing LLM endpoints and coding agents with enhanced features. See AI Gateway (Beta).
In this article, you learn how to configure AI Gateway on a model serving endpoint.
Requirements
- A Databricks workspace in a region where model serving is supported. See Model serving features availability.
- A model serving endpoint. You can use one of the preconfigured pay-per-token endpoints on your workspace or do the following:
- To create an endpoint for external models, complete steps 1 and 2 of Create an external model serving endpoint.
- To create an endpoint for provisioned throughput, see Provisioned throughput Foundation Model APIs.
- To create an endpoint for a custom model, see Create an endpoint.
Configure AI Gateway using the UI
In the AI Gateway section of the endpoint creation page, you can individually configure AI Gateway features. See Supported features for which features are available on external model serving endpoints and provisioned throughput endpoints.
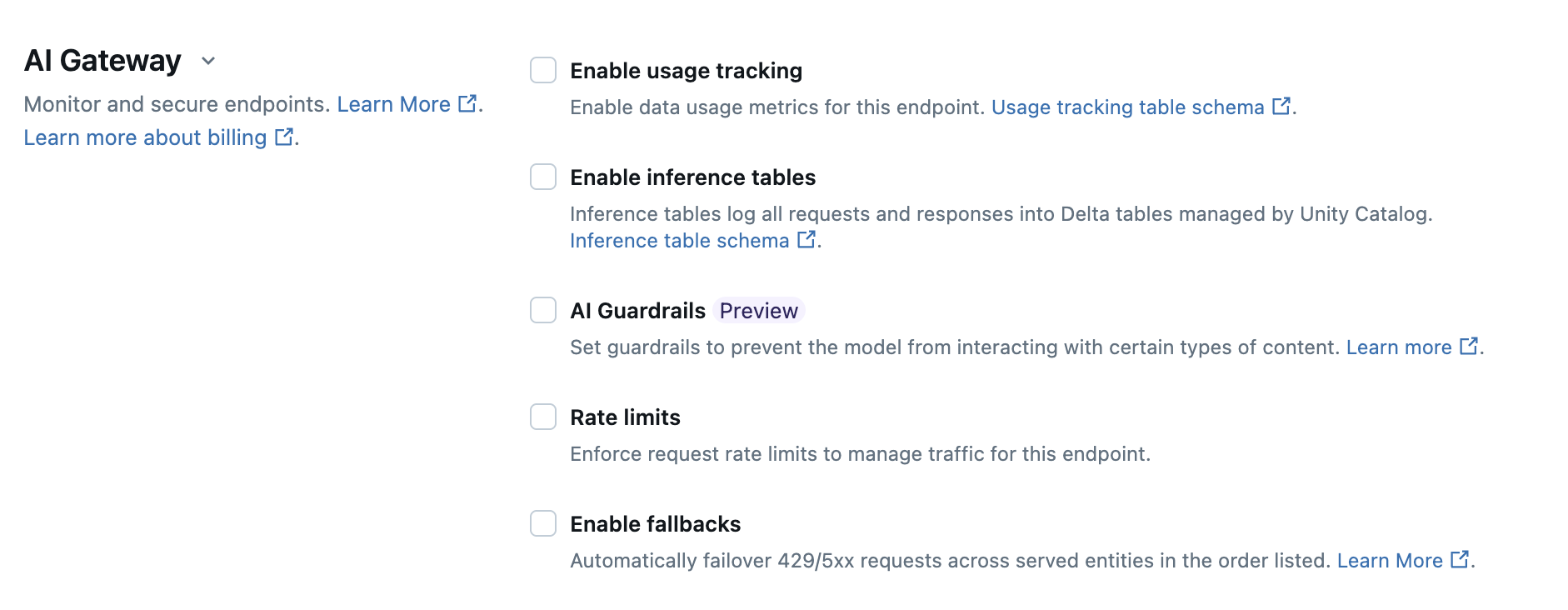
The following table summarizes how to configure AI Gateway during endpoint creation using the Serving UI. If you prefer to do this programmatically, see the Notebook example.
Feature | How to enable | Details |
|---|---|---|
Usage tracking | Select Enable usage tracking to enable tracking and monitoring of data usage metrics. |
|
Payload logging | Select Enable inference tables to automatically log requests and responses from your endpoint into Delta tables managed by Unity Catalog. |
|
| ||
Rate limits | Select Rate limits to manage and specify the number of queries per minute (QPM) or tokens per minute (TPM) that your endpoint can support.
|
|
Traffic splitting | In the Served entities section, specify the percentage of traffic you want to be routed to specific models. To configure traffic splitting on your endpoint programmatically, see Serve multiple external models to an endpoint. |
|
Fallbacks | Select Enable fallbacks in the AI Gateway section to send your request to other served models on the endpoint as a fallback. |
|
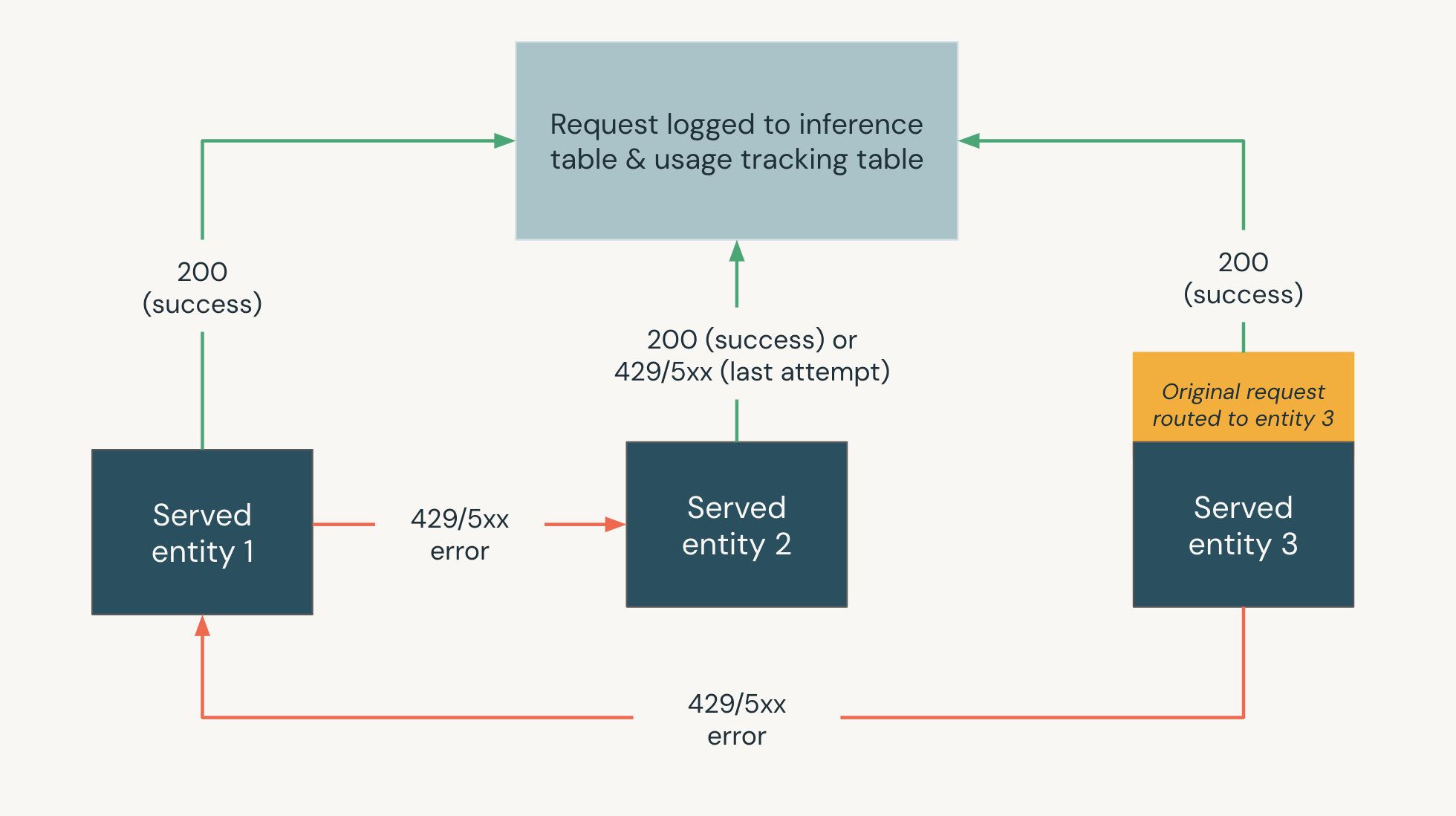
The following diagram shows a fallbacks example where,
- Three served entities are served on a model serving endpoint.
- The request is originally routed to Served entity 3.
- If the request returns a 200 response, the request was successful on Served entity 3 and the request and its response are logged to the usage tracking and payload logging tables of the endpoint.
- If the request returns a 429 or 5xx error on Served entity 3, the request falls back to the next served entity on the endpoint, Served entity 1.
- If the request returns a 429 or 5xx error on Served entity 1, the request falls back to the next served entity on the endpoint, Served entity 2.
- If the request returns a 429 or 5xx error on Served entity 2, the request fails since this is the maximum number of fall back entities. The failed request and the response error are logged to the usage tracking and payload logging tables.
Configure AI Guardrails in the UI
This feature is in Public Preview.
The following table shows how to configure supported guardrails.
Guardrail | How to enable |
|---|---|
Safety | Select Safety to enable safeguards to prevent your model from interacting with unsafe and harmful content. |
Personally identifiable information (PII) detection | Select to Block or Mask PII data such as names, addresses, credit card numbers if such information is detected in endpoint requests and responses. Otherwise, select None for no PII detection to occur. |

Usage tracking table schemas
The following sections summarize the usage tracking table schemas for the system.serving.served_entities and system.serving.endpoint_usage system tables.
system.serving.served_entities usage tracking table schema
The system.serving.served_entities usage tracking system table has the following schema:
Column name | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| The unique ID of the served entity. | STRING |
| The customer account ID for Delta Sharing. | STRING |
| The customer workspace ID of the serving endpoint. | STRING |
| The ID of the creator. For pay-per-token endpoints, this is | STRING |
| The name of the serving endpoint. | STRING |
| The unique ID of the serving endpoint. | STRING |
| The name of the served entity. | STRING |
| Type of the entity that is served. Can be | STRING |
| The underlying name of the entity. Different from the | STRING |
| The version of the served entity. | STRING |
| The version of the endpoint configuration. | INT |
| The task type. Can be | STRING |
| Configurations for external models. For example, | STRUCT |
| Configurations for foundation models. For example, | STRUCT |
| Configurations for custom models. For example, | STRUCT |
| Configurations for feature specifications. For example, | STRUCT |
| Timestamp of change for the served entity. | TIMESTAMP |
| Timestamp of entity deletion. The endpoint is the container for the served entity. After the endpoint is deleted, the served entity is also deleted. | TIMESTAMP |
system.serving.endpoint_usage usage tracking table schema
The system.serving.endpoint_usage usage tracking system table has the following schema:
Column name | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| The customer account ID. | STRING |
| The customer workspace id of the serving endpoint. | STRING |
| The user provided request identifier that can be specified in the model serving request body. For custom model endpoints, this is not supported for requests larger than 4MiB. | STRING |
| A Databricks generated request identifier attached to all model serving requests. | STRING |
| The ID of the user or service principal whose permissions are used for the invocation request of the serving endpoint. | STRING |
| The HTTP status code that was returned from the model. | INTEGER |
| The timestamp at which the request is received. | TIMESTAMP |
| The token count of the input. This will be 0 for custom model requests. | LONG |
| The token count of the output. This will be 0 for custom model requests. | LONG |
| The character count of the input string or prompt. This will be 0 for custom model requests. | LONG |
| The character count of the output string of the response. This will be 0 for custom model requests. | LONG |
| The user provided map containing identifiers of the end user or the customer application that makes the call to the endpoint. See Further define usage with | MAP |
| Whether the request is in stream mode. | BOOLEAN |
| The unique ID used to join with the | STRING |
Further define usage with usage_context
When you query an external model with usage tracking enabled, you can provide the usage_context parameter with type Map[String, String]. The usage context mapping appears in the usage tracking table in the usage_context column. The usage_context map size cannot exceed 10 KiB.
{
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is Databricks?"
}
],
"max_tokens": 128,
"usage_context":
{
"use_case": "external",
"project": "project1",
"priority": "high",
"end_user_to_charge": "abcde12345",
"a_b_test_group": "group_a"
}
}
If you're using the OpenAI Python client, you can specify the usage_context by including it in the extra_body parameter.
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(
api_key="dapi-your-databricks-token",
base_url="https://example.staging.cloud.databricks.com/serving-endpoints"
)
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="databricks-claude-sonnet-4-5",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "What is Databricks?"}],
temperature=0,
extra_body={"usage_context": {"project": "project1"}},
)
answer = response.choices[0].message.content
print("Answer:", answer)
Account admins can aggregate different rows based on the usage context to get insights and can join this information with the information in the payload logging table. For example, you can add end_user_to_charge to the usage_context for tracking cost attribution for end users.
Monitor endpoint usage
To monitor endpoint usage, you can join the system tables and inference tables for your endpoint.
Join system tables
This example applies to external, provisioned throughput, pay-per-token, and custom model endpoints.
To join the endpoint_usage and served_entities system tables, use the following SQL:
SELECT * FROM system.serving.endpoint_usage as eu
JOIN system.serving.served_entities as se
ON eu.served_entity_id = se.served_entity_id
WHERE created_by = "\<user_email\>";
Update AI Gateway features on endpoints
You can update AI Gateway features on model serving endpoints that had them previously enabled and endpoints that did not. Updates to AI Gateway configurations take about 20-40 seconds to be applied, however rate limiting updates can take up to 60 seconds.
The following shows how to update AI Gateway features on a model serving endpoint using the Serving UI.
In the Gateway section of the endpoint page, you can see which features are enabled. To update these features, click Edit AI Gateway.

Notebook example
The following notebook shows how to programmatically enable and use Databricks AI Gateway features to manage and govern models from providers. See the PUT /api/2.0/serving-endpoints/{name}/ai-gateway for REST API details.