Deploy a Databricks app
After you create and develop your Databricks app, deploy it to make it accessible in the Databricks workspace. Deployment builds your app, installs dependencies, and runs it using the configuration defined in your project files. You can deploy apps using the Databricks UI or the Databricks CLI.
If you create an app from a template, Databricks deploys it automatically when you first create it. However, you can still re-deploy it later after you make changes. See Create a Databricks app from a template.
Deployment logic
Databricks Apps supports deploying applications that use either Python, Node.js, or a combination of both. This allows for flexible architectures, such as a Node.js frontend with a Python backend.
During deployment, the build process checks for a package.json file at the root of your app directory to determine whether Node.js is used. If present, it includes Node-specific build steps alongside Python steps. The deployment logic follows this pattern:
If package.json is present:
- Run
npm install - Run
pip install -r requirements.txt(if it exists) - Run
npm run build(if abuildscript is defined inpackage.json) - Run the command specified in
app.yaml, ornpm run startif no command is specified
If no command is specified in app.yaml, Databricks executes npm run start, even if the app includes Python code. To run both Python and Node.js processes, define a custom start script that uses a tool like concurrently to launch both. For example: concurrently "npm run start:node" "python my_app.py".
If package.json is not present:
- Run
pip install -r requirements.txt(if it exists) - Run the command specified in
app.yaml, orpython <my-app>.pyif no command is specified
Prepare for deployment
Before you deploy your app, verify that your project includes the necessary components:
- Main script - Your entry point file, such as
app.pyorapp.js. - Optional
app.yamlfile - If your app requires a custom command or environment variables, include anapp.yamlfile to configure execution. See Configure Databricks app execution withapp.yaml. - Dependencies - Make sure all dependencies are available. See Manage dependencies for a Databricks app.
- Secrets or environment values - If you use the
envsection inapp.yaml, verify that the referenced secrets or external sources are correctly configured and accessible. See Add resources to a Databricks app.
In addition, make sure the app service principal has access to the source code folder.
Choose a deployment source
You can deploy Databricks apps from the following sources:
- Workspace folder - Upload app files to a workspace folder and deploy from there. This is the standard deployment method.
- Git repository - Configure a Git repository for an app and deploy directly without uploading files to the workspace. The app reads code from the configured Git reference (branch, tag, or commit) each time you deploy. All major Git providers are supported, including GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket. For a full list of supported providers, see Connect your Git provider to Databricks.
You can switch between workspace and Git sources for the same app at any time.
Deploy the app
The following sections describe how to deploy from a workspace folder or directly from a Git repository.
Deploy from a workspace folder
- Databricks UI
- Databricks CLI
To deploy an app from the Databricks UI:
- Upload the app files to your Databricks workspace. For instructions, see Import a file.
- Click
Compute in the sidebar.
- Go to the Apps tab and click the link to your app in the Name column.
- Click Deploy and select the folder in your workspace where you uploaded the app files.
- Click Select, then Deploy.
- Review the configuration and click Deploy.
To deploy an app using the CLI:
-
Open a terminal and navigate to the directory that contains your app files.
-
Upload your app files to the Databricks workspace using the
synccommand. Replace the path with the workspace location where you want to upload the files.Bashdatabricks sync --watch . /Workspace/Users/my-email@org.com/my-appThe
--watchflag keeps the sync process running and automatically uploads changes when you modify files locally. To exclude specific files or directories from syncing, add them to a.gitignorefile in your local app directory. Common files to exclude arenode_modules/,.env,__pycache__/,.DS_Store, and any large data files or build artifacts. -
Verify the upload by viewing the files in your workspace. Click
Workspace in the sidebar and navigate to the directory you created for your app.
-
Deploy the app by running the following command. Replace the app name and source code path with your values.
Bashdatabricks apps deploy my-app-name \
--source-code-path /Workspace/Users/my-email@org.com/my-appThe CLI displays deployment progress and confirms when the app is running.
Deploy from a Git repository
This feature is in Beta. If an admin disables the feature, existing apps deployed from Git continue to run, but you can't redeploy or restart them until you re-enable the preview or remove the repository from the app.
To deploy an app from a Git repository, add the repository at the app level, then specify the Git reference when you deploy it. Your Git repository must contain the app files, including app.yaml, dependencies, and entry point. All major Git providers are supported, including GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket.
To configure and deploy an app from Git:
- Upload your app files to a Git repository.
- From your Databricks workspace, click
Compute in the sidebar.
- Go to the Apps tab and either select an existing app to edit or click Create app.
- In the Configure Git repository step, enter the Git repository URL (for example,
https://github.com/org/repo) and select a Git provider. - Click Create app or Save to return to the app details page.
- For private repositories, the app's service principal must have a Git credential configured. On the app details page, click Configure Git credential. Alternatively, edit the app and add the credential in the Configure Git repository step. You must have
CAN MANAGEpermissions on the app to add a Git credential. For instructions for each provider, see Connect your Git provider to Databricks.
For security, Databricks deletes all Git credentials associated with the app's service principal when you change the deployment source (from Git to workspace or workspace to Git) or when you change the Git repository. Changing only the Git reference doesn't delete credentials. After changing the deployment source or repository, you must reconfigure the Git credential to deploy from Git again.
App creators automatically receive CAN MANAGE permissions on the service principal only when the Git deployment Beta feature is enabled. If you created an app while the feature was disabled, you might not have permission to add a Git credential.
Service principals support one Git credential per provider. Updating a credential, such as through the account console, replaces the existing credential for that provider and affects all apps using that service principal with that provider.
Then, deploy the app:
- On the app details page, click Deploy.
- Select From Git.
- For Git reference, enter the branch name, tag, or commit SHA (for example,
main,v1.0.0, or a commit hash). - For Reference type, specify the type of reference, such as a branch, tag, or commit.
- Click Deploy.
For branch or tag references, Databricks deploys the most recent commit from that branch or tag. For commit SHA references, Databricks always deploys that specific commit. If the service principal's Git credential is invalid or expired, the deployment fails.
Post-deployment behavior
After deployment completes, Databricks starts your app based on the defined command in your app.yaml file or defaults to running python app.py. The app details page shows the current status and provides access to logs, deployment history, and environment information.
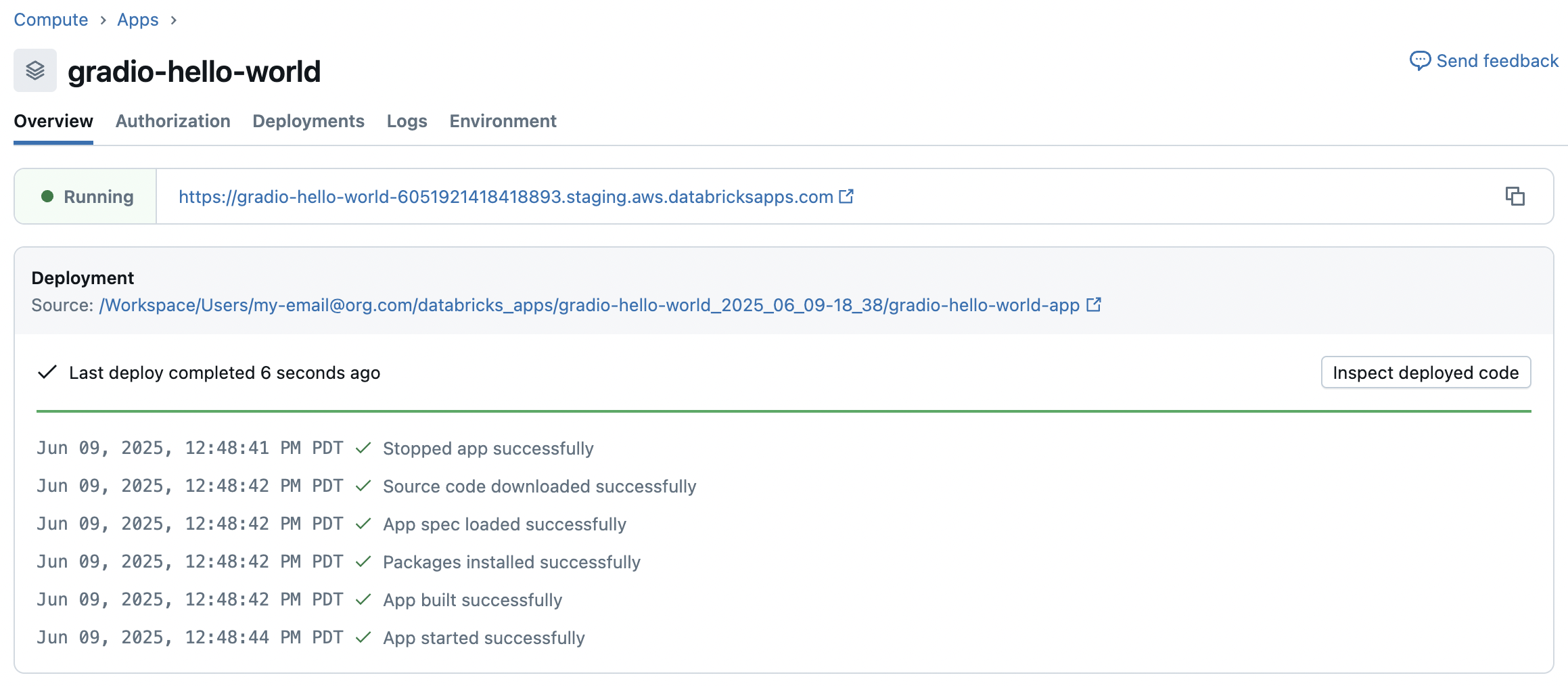
To view the deployed app's output, click the app link.
Go to the Logs tab for debugging and runtime monitoring. See Logging and Monitoring for Databricks Apps.
Update or redeploy the app
Redeploy your app after making changes to source code or configuration. Redeploying applies your latest updates without recreating the app. You can redeploy from either the workspace or Git repository at any time.
Redeploy from a workspace folder
To redeploy from a workspace folder:
- Update your app files in the workspace folder.
- Select the app and click Deploy.
- If the source code path changed or you're switching from a Git source, click the arrow next to Deploy and select Deploy using a different source.
Redeploy from a Git repository
To redeploy from a Git repository:
- Push your changes to the Git repository.
- In your Databricks workspace, select your app and click Deploy.
- If the Git reference changed or you're switching from a workspace source, click the arrow next to Deploy and select Deploy using a different source.
To change the Git repository or credential, edit the app configuration. Removing the Git repository from the app enforces deployment from the workspace.
Changing the Git repository or switching between deployment sources (Git and workspace) deletes all Git credentials for the app's service principal. You must reconfigure credentials before deploying from Git again.
Troubleshoot deployment issues
If your app fails to deploy or doesn't run as expected, try the following troubleshooting steps:
- Check logs for error messages or runtime output.
- Validate
app.yamlsyntax and settings. - Verify that secrets and environment variables in the
envsection resolve properly. - Confirm that all required dependencies are included or installed.
For Git repository deployments:
- For private repositories, verify the app's service principal has a Git credential configured.
- Verify the Git repository URL is correct.
- Verify the Git reference (branch, tag, or commit) exists in the repository.