Troubleshoot PostgreSQL ingestion
The PostgreSQL connector for Lakeflow Connect is in Public Preview. Reach out to your Databricks account team to enroll in the Public Preview.
This page describes the common issues with the PostgreSQL connector in Databricks Lakeflow Connect and how to resolve them.
General pipeline troubleshooting
The troubleshooting steps in this section apply to all ingestion pipelines in Lakeflow Connect.
If a pipeline fails while running, click the step that failed and confirm whether the error message provides sufficient information about the nature of the error.
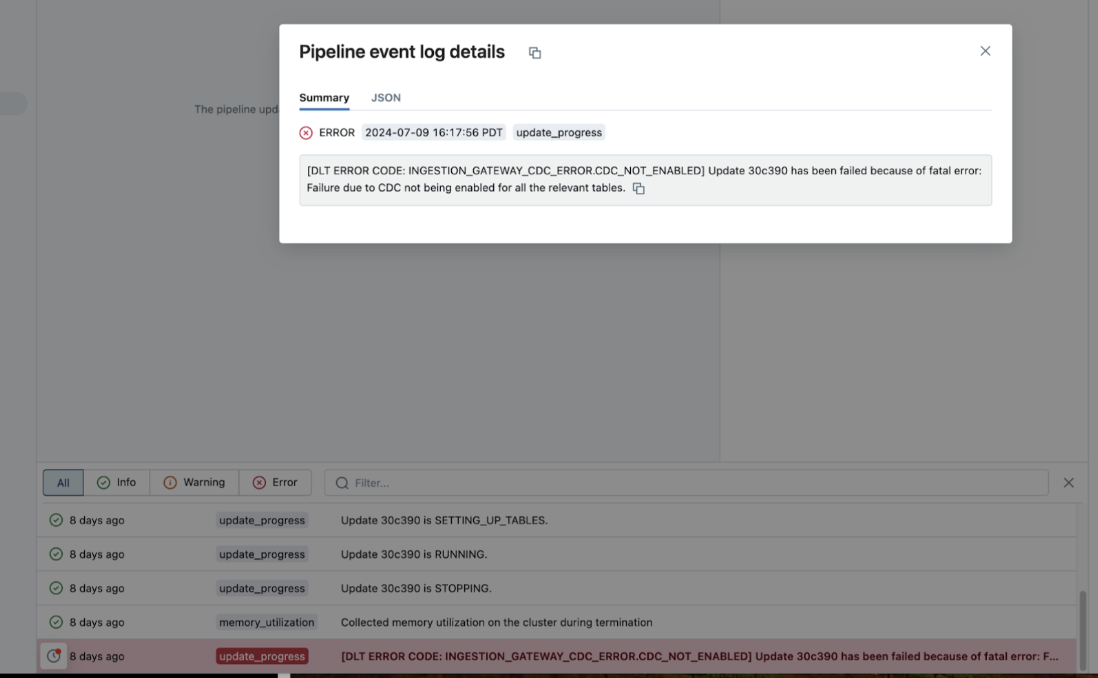
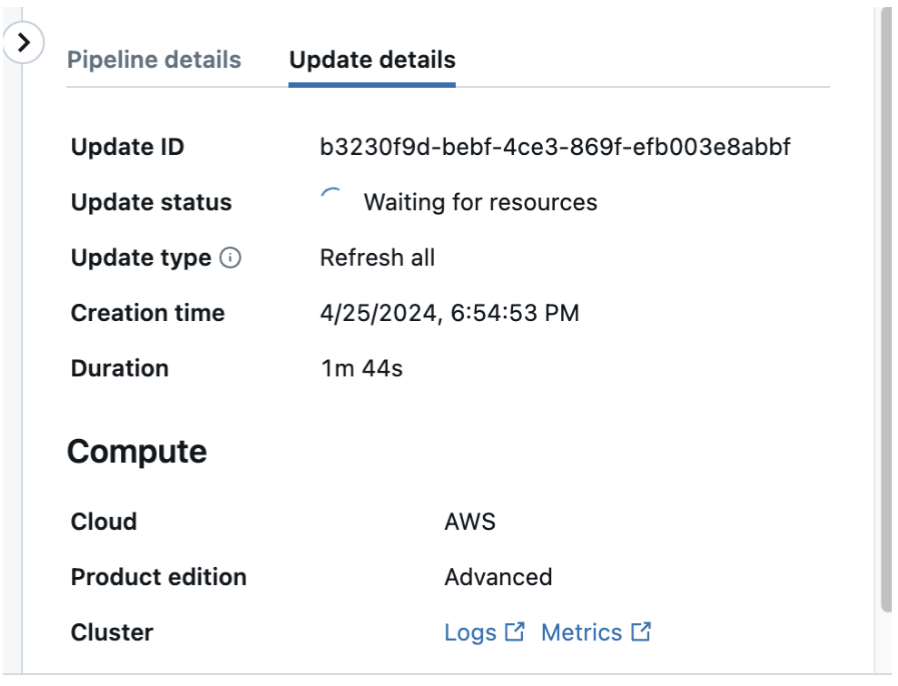
You can also check and download the cluster logs from the pipeline details page by clicking Update details in the right-hand panel, then Logs. Scan the logs for errors or exceptions.
Connector-specific troubleshooting
The troubleshooting steps in this section are specific to the PostgreSQL connector.
Permission errors
If you receive a permission error, verify that the replication user has the necessary privileges. See PostgreSQL database user requirements for the complete list of required privileges.
ERROR: permission denied for table
This error indicates that the replication user does not have SELECT privileges on the specified table. Grant the necessary privileges:
GRANT SELECT ON TABLE schema_name.table_name TO databricks_replication;
ERROR: must be superuser or replication role to use replication slots
This error indicates that the replication user does not have the REPLICATION privilege. Grant the replication role:
-- For standard PostgreSQL
ALTER USER databricks_replication WITH REPLICATION;
-- For AWS RDS/Aurora
GRANT rds_replication TO databricks_replication;
-- For GCP Cloud SQL
ALTER USER databricks_replication with REPLICATION;
Check whether logical replication is enabled
To check whether logical replication is enabled:
SHOW wal_level;
The output should be logical. If it is not, update the wal_level parameter and restart the PostgreSQL server.
For cloud-managed PostgreSQL:
- AWS RDS/Aurora: Set
rds.logical_replicationto1in the parameter group. - Azure Database for PostgreSQL: Enable logical replication in the server parameters.
- GCP Cloud SQL: Set the
cloudsql.logical_decodingflag toon.
Check whether a publication exists
To check whether a publication exists for your tables:
SELECT * FROM pg_publication WHERE pubname = 'databricks_publication';
-- Check which tables are included in the publication
SELECT schemaname, tablename
FROM pg_publication_tables
WHERE pubname = 'databricks_publication';
If the publication does not exist, create it:
CREATE PUBLICATION databricks_publication FOR TABLE schema_name.table_name;
Check replica identity
To check the replica identity setting for a table:
SELECT schemaname, tablename, relreplident
FROM pg_tables t
JOIN pg_class c ON t.tablename = c.relname
WHERE schemaname = 'your_schema' AND tablename = 'your_table';
The relreplident column should show the following values:
ffor FULL replica identity (required for tables without primary keys or TOASTable columns).dfor DEFAULT replica identity (uses primary key).
If the replica identity is not set correctly, update it:
ALTER TABLE schema_name.table_name REPLICA IDENTITY FULL;
Replication slot errors
WAL accumulation and disk space issues
If the ingestion gateway is stopped for an extended period, the replication slot can cause Write-Ahead Log (WAL) files to accumulate, potentially filling up disk space.
To check WAL disk usage:
SELECT pg_size_pretty(pg_wal_lsn_diff(pg_current_wal_lsn(), restart_lsn)) AS retained_wal
FROM pg_replication_slots
WHERE slot_name = 'your_slot_name';
To prevent WAL accumulation:
- Ensure the ingestion gateway runs continuously.
- Monitor replication lag and disk space regularly.
If WAL files have accumulated, you can manually drop the replication slot:
SELECT pg_drop_replication_slot('your_slot_name');
If a replication slot is dropped or becomes invalid, update the pipeline spec with a new slot for that database and run a full refresh.
Timeout while waiting for table token
The ingestion pipeline might time out while waiting for information to be provided by the gateway. This might be due to one of the following reasons:
- You are running an older version of the gateway.
- There was an error generating the necessary information. Check the gateway driver logs for errors.
- The initial snapshot is taking longer than expected. For large tables, consider increasing the pipeline timeout or running the initial load during off-peak hours.
Source table naming conflict
Ingestion pipeline error: "org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.ExtendedAnalysisException: Cannot have multiple queries named `orders_snapshot_load` for `orders`. Additional queries on that table must be named. Note that unnamed queries default to the same name as the table.
This indicates that there is a name conflict due to multiple source tables named orders in different source schemas that are being ingested by the same ingestion pipeline to the same destination schema.
Create multiple gateway-pipeline pairs writing these conflicting tables to different destination schemas.
Incompatible schema changes
An incompatible schema change causes the ingestion pipeline to fail with an INCOMPATIBLE_SCHEMA_CHANGE error. To continue replication, trigger a full refresh of the affected tables.
Incompatible schema changes include the following:
- Changing the data type of a column
- Renaming a column
- Changing the primary key of a table
- Dropping a column that is part of the replica identity
Databricks cannot guarantee that all rows prior to the schema change have been ingested when the ingestion pipeline fails due to an incompatible schema change.
Connection timeout errors
If you receive connection timeout errors, perform the following checks:
- Verify that the firewall rules allow connections from the Databricks workspace.
- Check that the PostgreSQL server is reachable from the Databricks network.
- Ensure that the
pg_hba.conffile allows connections from the Databricks IP range. - Verify that the connection credentials are correct.
SSL/TLS connection errors
If you receive SSL/TLS connection errors, perform the following checks:
-
Verify that the PostgreSQL server supports SSL connections.
-
Check the
sslparameter in the PostgreSQL configuration:SQLSHOW ssl; -
Ensure that the
pg_hba.conffile requires or allows SSL connections for the replication user. -
For cloud-managed databases, verify that SSL is enforced in the server settings.
default auth: cannot configure default credentials
If you receive this error, there is an issue with discovering the current user credentials. Try replacing the following:
w = WorkspaceClient()
with:
w = WorkspaceClient(host=input('Databricks Workspace URL: '), token=input('Token: '))
See Authentication in the Databricks SDK for Python documentation.
PERMISSION_DENIED: You are not authorized to create clusters. Please contact your administrator.
Contact a Databricks account admin to grant you Unrestricted cluster creation permissions.
DLT ERROR CODE: INGESTION_GATEWAY_INTERNAL_ERROR
Check the stdout files in the driver logs for detailed error messages. Common causes include the following:
- Replication slot errors
- Publication configuration issues
- Network connectivity problems
- Insufficient privileges on the source database