Data lakehouse architecture: Databricks well-architected framework
This set of articles provides principles and best practices for implementing and operating a lakehouse using Databricks.
Databricks well-architected framework for the lakehouse
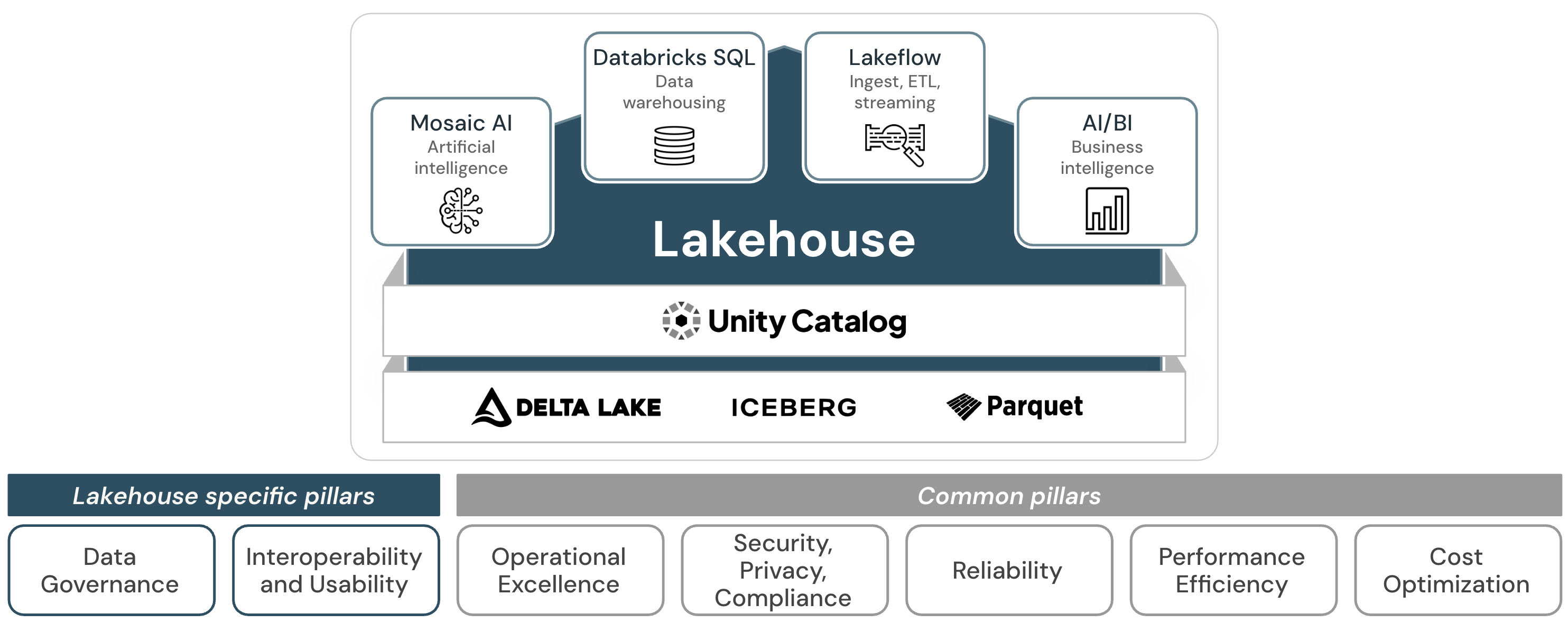
The well-architected lakehouse consists of seven pillars that describe different areas of concern for the implementation of a data lakehouse in the cloud.
Pillars shared with cloud frameworks
The following five pillars align with the pillars in the AWS Well-Architected Framework:
For the five shared pillars, the principles and best practices of the cloud framework still apply. The well-architected lakehouse extends these with lakehouse-specific principles and best practices.
-
- Operational excellence
- All operations processes that keep the lakehouse running in production.
-
- Security, privacy, and compliance
- Protection for the Databricks application, customer workloads, and customer data from threats.
-
- Reliability
- The ability of a system to recover from failures and continue to function.
-
- Performance efficiency
- The ability of a system to adapt to changes in load.
-
- Cost optimization
- Managing costs to maximize the value delivered.
Lakehouse-specific pillars
The following two pillars address concerns unique to lakehouse architecture:
-
- Data and AI governance
- The oversight to ensure that data and AI bring value and support your business strategy.
-
- Interoperability and usability
- The ability of the lakehouse to interact with users and other systems.
The two lakehouse-specific pillars warrant additional context:
Data and AI governance
The lakehouse unifies data warehousing and AI use cases on a single platform. This eliminates the data silos that traditionally separate data engineering, analytics, BI, data science, and machine learning.
A unified governance solution simplifies data management by consolidating governance controls into a single processing layer. This approach minimizes data copies and improves your ability to maintain compliance and detect potential breaches.
Interoperability and usability
An integrated lakehouse provides a consistent user experience for all personas and workloads. This consistency reduces training and onboarding costs while improving collaboration between functions. In contrast, assembling separate data tools can lead to high implementation costs, inconsistent user experiences, and limited collaboration capabilities.
Organizations adopt multi-cloud strategies for various reasons, including mergers, acquisitions, or independent business unit decisions. A multi-cloud lakehouse delivers a unified user experience across all cloud providers. This reduces system proliferation and lowers the skill requirements for employees working with data.
Modern business processes require systems to work together across organizational boundaries. The lakehouse supports secure data flow between internal and external partners' systems, enabling effective collaboration in networked business environments.