Autoscaling
Lakebase Autoscaling is available in the following regions: us-east-1, us-east-2, us-west-2, eu-central-1, eu-west-1, ap-south-1, ap-southeast-1, ap-southeast-2.
Lakebase Autoscaling is the latest version of Lakebase with autoscaling compute, scale-to-zero, branching, and instant restore. For feature comparison with Lakebase Provisioned, see choosing between versions.
Autoscaling dynamically adjusts the amount of compute resources allocated to your Lakebase computes in response to current workload demands. As your application experiences varying levels of activity throughout the day, autoscaling automatically increases compute capacity during peak usage and reduces it during quieter periods, eliminating the need for manual intervention.
This visualization shows how autoscaling works throughout a typical day, with compute resources scaling up or down based on demand to ensure your database has the resources it needs while conserving resources during off-peak times.
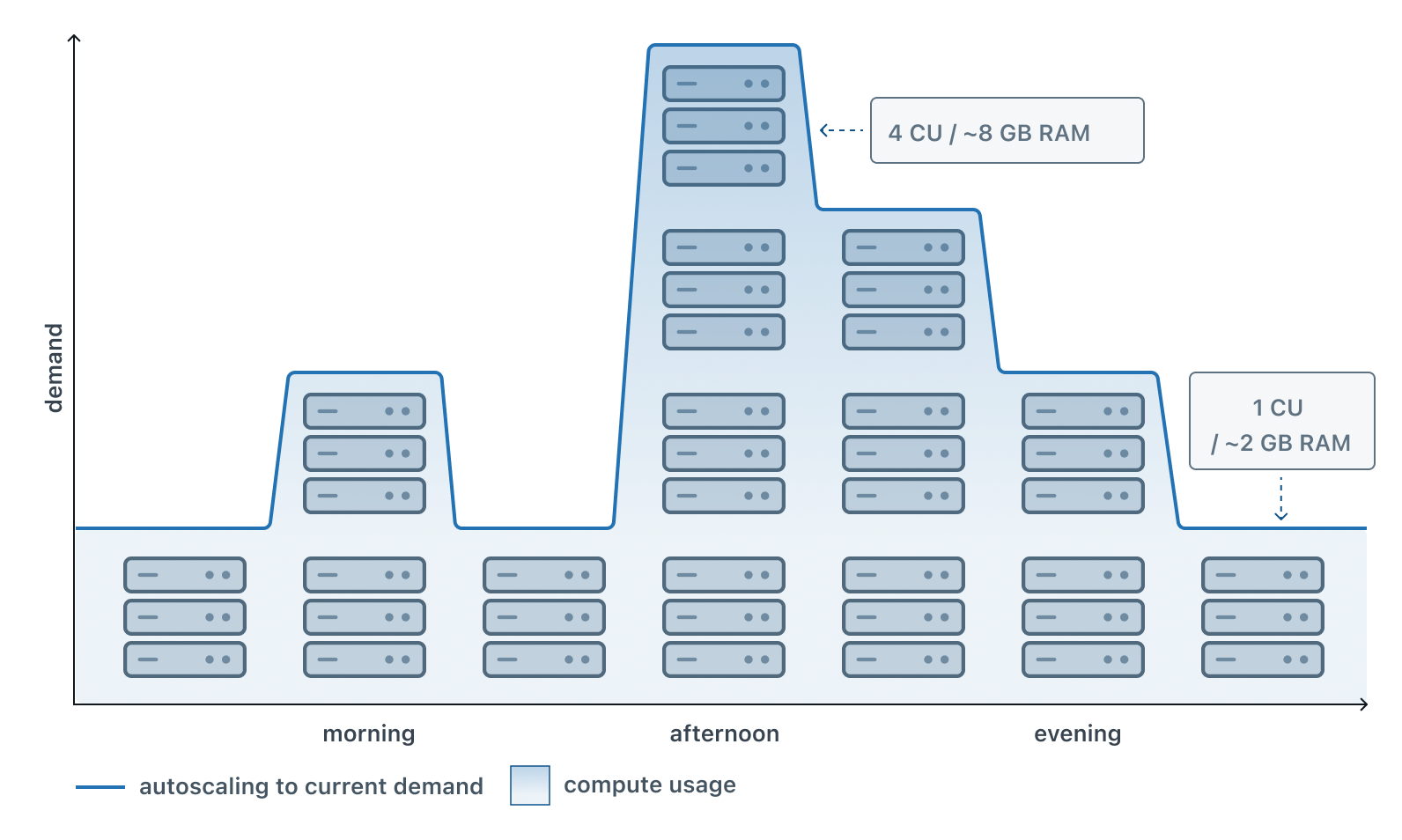
Autoscaling operates within a user-defined range. For example, you might set a compute to scale between 2 and 8 Compute Units (CU), with each CU providing 2 GB of RAM. Your compute automatically adjusts within these limits based on workload, never dropping below the minimum or exceeding the maximum regardless of demand. Autoscaling is available for computes up to 32 CU.
Lakebase Provisioned vs Autoscaling: In Lakebase Provisioned, each Compute Unit allocated approximately 16 GB of RAM. In Lakebase Autoscaling, each CU allocates 2 GB of RAM. This change provides more granular scaling options and cost control.
How autoscaling works
Automatic resource adjustment
When you enable autoscaling and set your minimum and maximum compute sizes, Lakebase continuously monitors your workload and adjusts resources automatically. The system tracks three key metrics to make scaling decisions:
- CPU load: Monitors processor utilization to ensure your database has adequate processing power.
- Memory usage: Tracks RAM consumption to prevent memory constraints.
- Working set size: Estimates your frequently accessed data to optimize cache performance.
Based on these metrics, Lakebase scales your compute up when demand increases and scales down when activity decreases, all while staying within your configured range.
Scaling boundaries
You define the scaling range by setting minimum and maximum compute sizes. This range provides:
- Performance guarantees: The minimum ensures baseline performance even during low activity.
- Cost control: The maximum prevents unbounded resource consumption and costs.
- Automatic optimization: Within these boundaries, Lakebase handles all scaling decisions.
The difference between your maximum and minimum cannot exceed 16 CU (that is, max - min ≤ 16 CU).
No downtime or manual intervention
Autoscaling adjustments happen without requiring compute restarts or connection interruptions. Once configured, the system operates autonomously, allowing you to focus on your applications rather than infrastructure management.
Autoscaling benefits
Cost efficiency: You only pay for the compute resources you actually use. During off-peak hours, your compute scales down, reducing costs. During peak periods, it scales up to maintain performance.
Performance optimization: Your database automatically receives additional resources when workload increases, preventing performance degradation during traffic spikes or intensive operations.
Predictable costs: By setting a maximum compute size, you control the upper bound of your compute costs, preventing unexpected expenses from runaway resource consumption.
Simplified operations: Autoscaling eliminates the need to manually monitor workload patterns and adjust compute sizes, reducing operational overhead and the risk of human error.
Configuring autoscaling
Autoscaling configuration requires setting minimum and maximum compute size boundaries. Autoscaling is available for computes up to 32 CU. For workloads requiring more than 32 CU, larger fixed-size computes from 36 CU to 112 CU are available.
For detailed instructions on enabling and configuring autoscaling, see Manage computes.
Common autoscaling scenarios
AI agent and application workloads
AI agents and interactive applications built on Databricks often experience variable request patterns. Autoscaling ensures your database handles traffic spikes during active user sessions while reducing costs during quiet periods.
Development and testing environments
Development branches for testing schema changes or validating data pipelines typically see intermittent activity. Autoscaling minimizes resources during idle periods while ensuring adequate performance during active development.
Customer-facing dashboards and applications
Applications delivering analytics or operational insights to end users often have time-of-day usage patterns. Autoscaling automatically adjusts resources to match user activity throughout the day.
Autoscaling and scale to zero
Autoscaling works in combination with scale to zero. While autoscaling adjusts resources based on workload demand, scale to zero suspends a compute entirely after a period of inactivity, reducing compute costs to zero during idle periods.
When you configure both features:
- Active period: Autoscaling adjusts compute size based on workload within your defined range.
- Inactive period: After the scale-to-zero timeout, the compute suspends entirely.
- Resumed activity: The compute restarts at the minimum autoscaling size when new queries arrive.
This combination maximizes cost efficiency, particularly for development, testing, or staging environments that experience long idle periods.
Next steps
- Manage computes to learn how to enable and configure autoscaling
- Metrics dashboard to view CPU, RAM, and working set size metrics
- Scale to zero to understand how computes can suspend during inactivity
- Database branches to learn about creating isolated database environments