Get started with Lakebase Postgres
Lakebase Autoscaling is available in the following regions: us-east-1, us-east-2, us-west-2, eu-central-1, eu-west-1, ap-south-1, ap-southeast-1, ap-southeast-2.
Lakebase Autoscaling is the latest version of Lakebase with autoscaling compute, scale-to-zero, branching, and instant restore. For feature comparison with Lakebase Provisioned, see choosing between versions.
Get up and running with Lakebase Postgres in minutes. Create your first project, connect to your database, and explore key features including Unity Catalog integration.
Create your first project
Open the Lakebase App from the apps switcher.
Select Autoscaling to access the Lakebase Autoscaling UI.
Click New project. Give your project a name and select your Postgres version. Your project is created with a single production branch, a default databricks_postgres database, and compute resources configured for the branch.
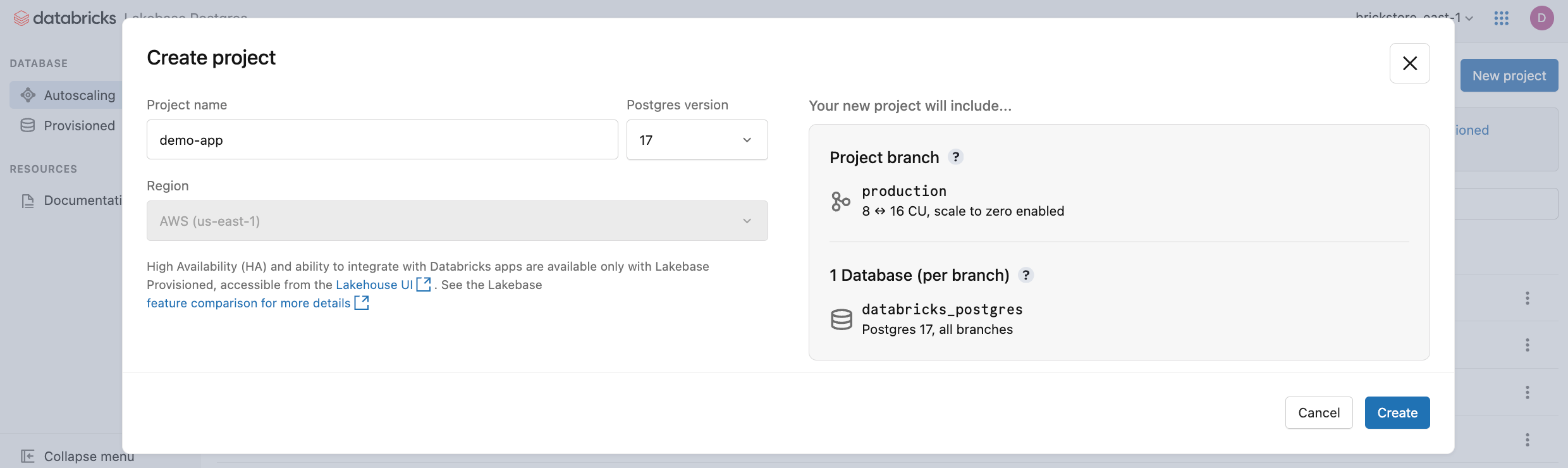
It may take a few monents for your compute to activate. The compute for the production branch is always on by default (scale-to-zero is disabled), but you can configure this setting if needed.
The region for your project is automatically set to your workspace region. For detailed configuration options, see Create a project.
Connect to your database
From your project, select the production branch and click Connect. You can connect using your Databricks identity with OAuth authentication, or create a native Postgres password role. Connection strings work with standard Postgres clients like psql, pgAdmin, or any Postgres-compatible tool.
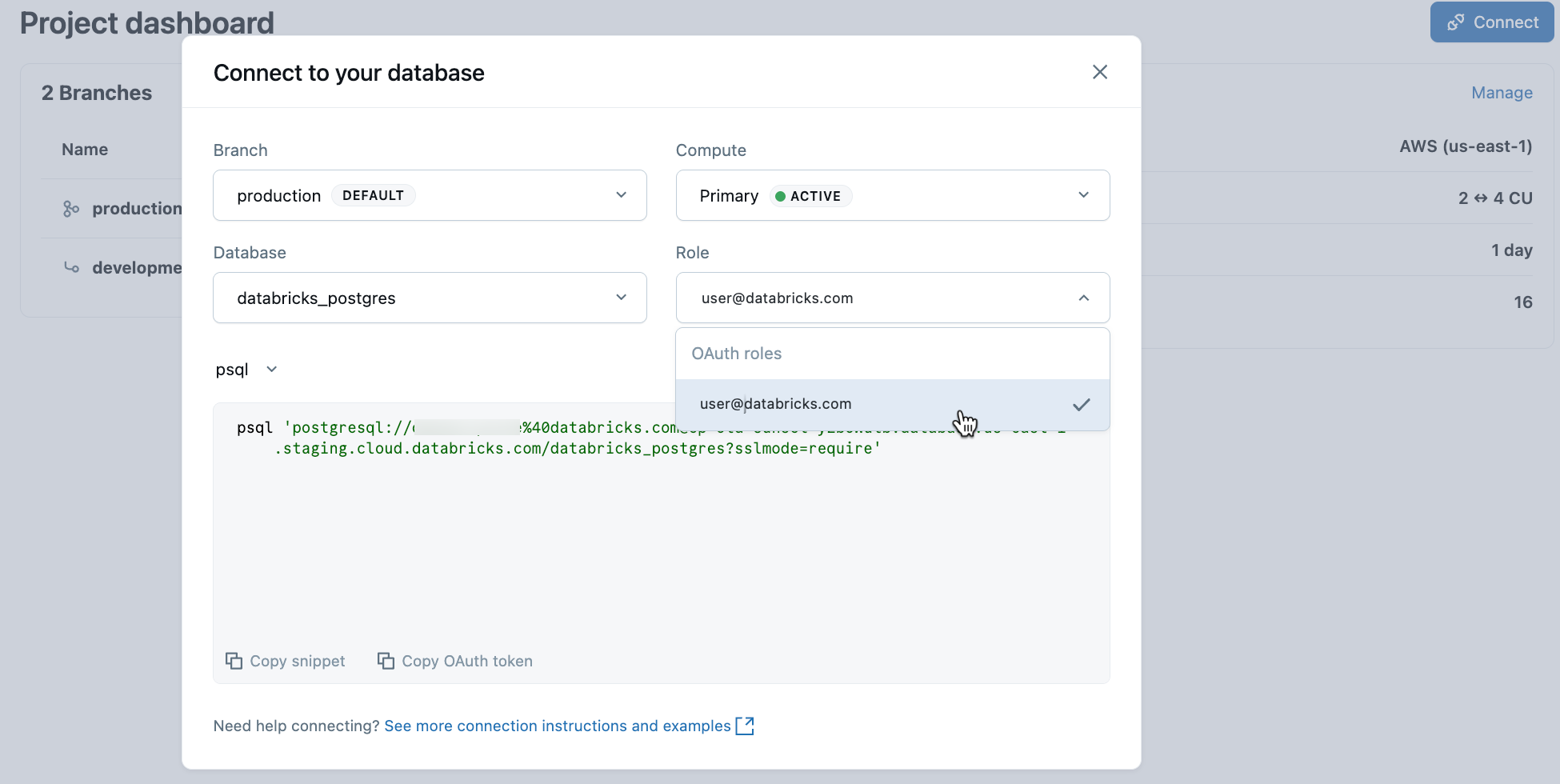
When you create a project, a Postgres role for your Databricks identity (for example, user@databricks.com) is automatically created. This role owns the default databricks_postgres database and is a member of databricks_superuser, giving it broad privileges to manage database objects.
To connect using your Databricks identity with OAuth, copy the psql connection snippet from the connection dialog.
psql 'postgresql://your-email@databricks.com@ep-abc-123.databricks.com/databricks_postgres?sslmode=require'
After entering the psql connection commoand in your terminal, you are prompted to provide an OAuth token. Get your token by clicking the Copy OAuth token option in the connection dialog.
For connection details and authentication options, see Quickstart.
Create your first table
The Lakebase SQL Editor comes preloaded with sample SQL to help you get started. From your project, select the production branch, open the SQL Editor, and run the provided statements to create a playing_with_lakebase table and insert sample data. You can also use the Tables Editor for visual data management or connect with external Postgres clients.
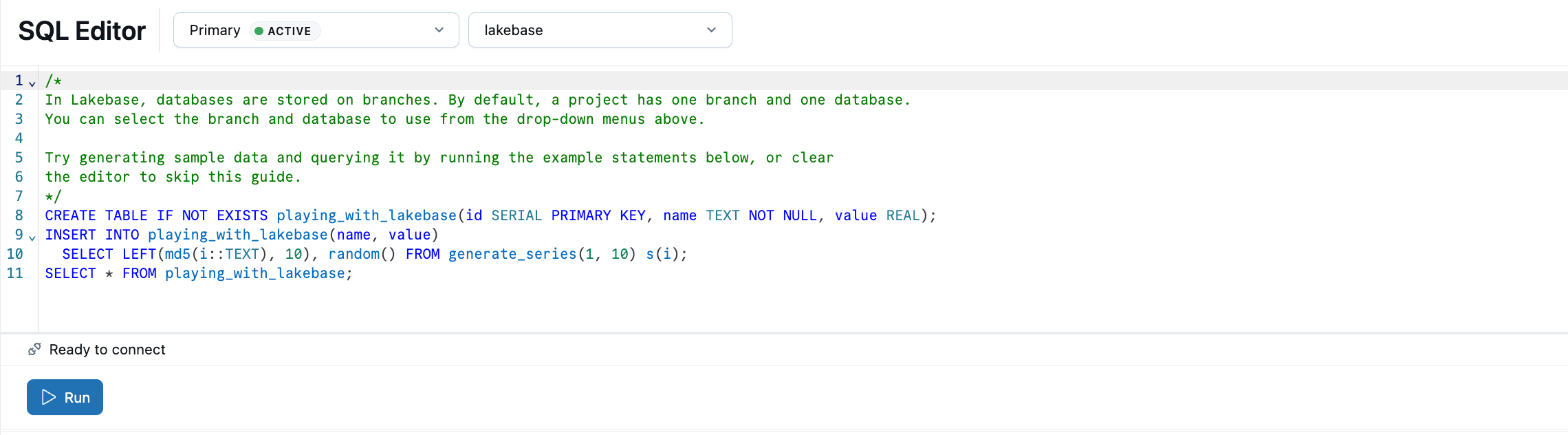
Learn more about querying options: SQL Editor | Tables Editor | Postgres clients
Register in Unity Catalog
Now that you've created a table on your production branch, let's register the database in Unity Catalog so you can query that data from Databricks SQL Editor.
- Use the apps switcher to navigate to Lakehouse.
- In Catalog Explorer, click the plus icon and Create a catalog.
- Enter a catalog name (for example,
lakebase_catalog). - Select Lakebase Postgres as the catalog type and enable the Autoscaling option.
- Select your project, the
productionbranch, and thedatabricks_postgresdatabase. - Click Create.
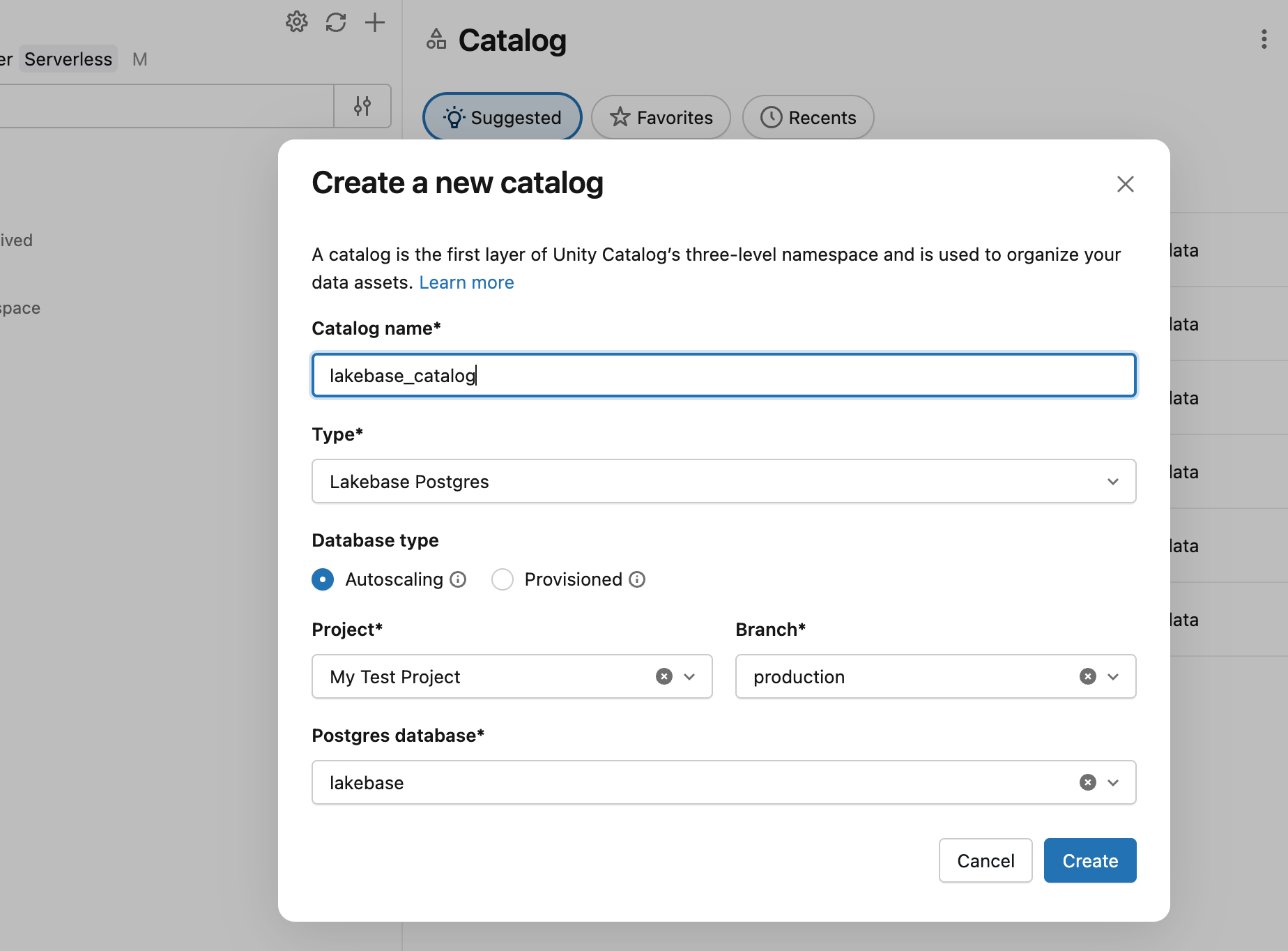
You can now query the playing_with_lakebase table you just created from Databricks SQL Editor using an SQL warehouse:
SELECT * FROM lakebase_catalog.public.playing_with_lakebase;
This enables federated queries that join your Lakebase transactional data with lakehouse analytics. For details, see Register in Unity Catalog.
Sync data with Reverse ETL
You've just seen how to make Lakebase data queryable in Unity Catalog. Lakebase also works in the reverse direction: bringing curated analytical data FROM Unity Catalog INTO your Lakebase database. This is useful when you have enriched data, ML features, or aggregated metrics computed in your lakehouse that need to be served by applications with low-latency transactional queries.
First, create a table in Unity Catalog that represents analytical data. Open a SQL warehouse or notebook and run:
CREATE TABLE main.default.user_segments AS
SELECT * FROM VALUES
(1001, 'premium', 2500.00, 'high'),
(1002, 'standard', 450.00, 'medium'),
(1003, 'premium', 3200.00, 'high'),
(1004, 'basic', 120.00, 'low')
AS segments(user_id, tier, lifetime_value, engagement);
Now sync this table to your Lakebase database:
- In the Lakehouse Catalog Explorer, navigate to main > default > user_segments.
- Click Create > Synced table.
- Configure the sync:
- Table name: Enter
user_segments_synced. - Database type: Select Lakebase Serverless (Autoscaling).
- Sync mode: Choose Snapshot for a one-time data sync.
- Select your project, the production branch, and the
databricks_postgresdatabase.
- Table name: Enter
- Click Create.
After the sync completes, the table appears in your Lakebase database. The sync process creates a default schema in Postgres to match the Unity Catalog schema, so main.default.user_segments_synced becomes default.user_segments_synced. Navigate back to Lakebase using the apps switcher and query it in the Lakebase SQL Editor:
SELECT * FROM "default"."user_segments_synced" WHERE "engagement" = 'high';
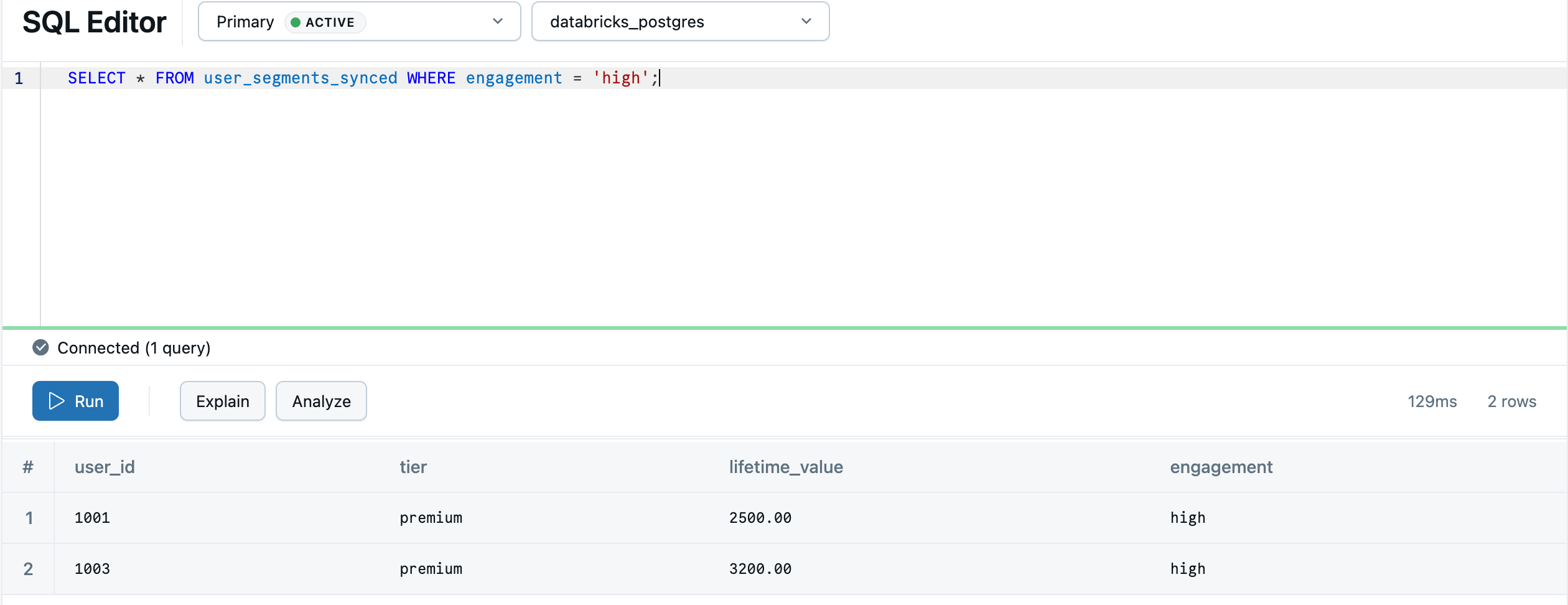
Your lakehouse analytics are now available for real-time serving in your transactional database. For continuous syncing, advanced configurations, and data type mappings, see Reverse ETL.
Next steps
- Tutorials
- Connect
- Key features
- Explore more