Tutorial: Grant project and database access to a new user
Lakebase Autoscaling is available in the following regions: us-east-1, us-east-2, us-west-2, eu-central-1, eu-west-1, ap-south-1, ap-southeast-1, ap-southeast-2.
Lakebase Autoscaling is the latest version of Lakebase with autoscaling compute, scale-to-zero, branching, and instant restore. For feature comparison with Lakebase Provisioned, see choosing between versions.
Learn how to set up a new user with access to your Lakebase project and database. This tutorial covers both project-level permissions (for managing Lakebase resources) and database-level permissions (for accessing data through Postgres).
About the two permission systems
Lakebase Postgres uses two layers of permissions:
-
Project permissions (ACLs): Control platform-level actions, such as creating branches, managing computes, and managing project settings. These are managed through the Lakebase App.
-
Postgres role permissions: Control access to data within the database itself. These are managed through standard Postgres
GRANTcommands.
These systems have no automatic synchronization. You can grant these permissions independently or together, depending on your organization's requirements:
- Grant both layers to users who need platform access and database access.
- Grant only project permissions to users who manage infrastructure but don't need to query data.
- Grant only database access to users who need to query data but don't need to manage Lakebase resources (they can connect using tools like
psqlwith connection details).
This tutorial shows how to set up both layers of access:
- Grant project permissions so users can work with Lakebase platform resources (this tutorial uses CAN MANAGE for full access, and you can also grant CAN USE for view-and-use-only access)
- Create a Postgres role with appropriate database privileges for connecting to and querying the database
Default permissions
All workspace users inherit CAN CREATE permission by default, which allows viewing and creating projects. To grant additional access to your project's resources and databases, you must explicitly assign CAN USE or CAN MANAGE.
Prerequisites
- A Lakebase project with a database
- Workspace admin or CAN MANAGE permission on the project
- The user's Databricks identity (email address) in the same workspace where the project was created
Scenario: Add a data analyst with read-write access
Let's walk through adding a data analyst named Alex Lopez who needs:
- Ability to create and manage branches, computes, and databases (CAN MANAGE)
- Read and write access to tables in the
publicschema of your Postgres database - Ability to create new tables for analysis
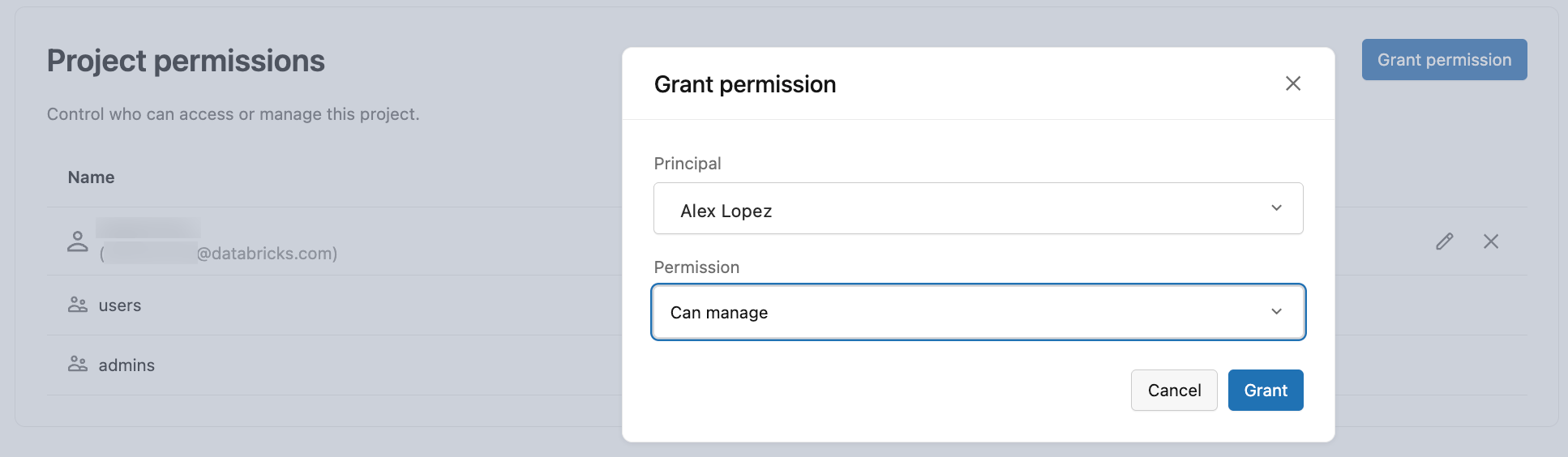
Step 1: Grant project permissions
First, grant the user CAN MANAGE permission so they can perform project management actions.
- Navigate to your project in the Lakebase App.
- Click Settings in the left sidebar.
- Scroll to the Project permissions section.
- Click Grant permission.
- Search for and select the user.
- Select CAN MANAGE permission.
- Click Grant.
What CAN MANAGE allows:
- Create and delete branches
- Manage computes and configure project settings
- Create and manage databases and Postgres roles
- Full control over project operations
CAN MANAGE grants full control over the project, including many other actions. CAN USE allows viewing and using resources (list, view, get connection URI, and certain branch operations) without full management. For a complete list of all permission levels and specific actions each allows, see Lakebase project ACLs.
Step 2: Create a Postgres role for the user
Now create an OAuth role that allows Alex to authenticate using their Databricks identity with OAuth tokens. As the project owner, you have the necessary permissions to create roles.
-
Open the Lakebase SQL Editor and connect to your project.
-
Create the
databricks_authextension (if not already enabled):SQLCREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS databricks_auth; -
Use the
databricks_create_rolefunction to create the OAuth Postgres role for Alex:SQLSELECT databricks_create_role('alex.lopez@databricks.com', 'USER');
This creates an OAuth role that:
- Has the same name as their Databricks identity (
alex.lopez@databricks.com) - Can authenticate using OAuth tokens
- Has LOGIN privileges
- Has no database permissions yet (we'll grant these next)
About OAuth roles:
- OAuth roles authenticate using time-limited tokens (expire after 1 hour)
- Users get tokens from the Lakebase App connection dialog
- Best for interactive sessions and workspace-integrated workflows
- For more information, see About authentication
Step 3: Grant Postgres database permissions
Now grant Alex the database permissions they need. We'll give them read-write access to the public schema.
-- Grant CONNECT permission on the database
GRANT CONNECT ON DATABASE databricks_postgres TO "alex.lopez@databricks.com";
-- Grant USAGE permission on the public schema (required to access objects in it)
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA public TO "alex.lopez@databricks.com";
-- Grant CREATE permission on the public schema (allows creating new tables)
GRANT CREATE ON SCHEMA public TO "alex.lopez@databricks.com";
-- Grant read-write access to all existing tables in public schema
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA public TO "alex.lopez@databricks.com";
-- Grant permissions on future tables (so Alex can access new tables automatically)
ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES IN SCHEMA public
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE ON TABLES TO "alex.lopez@databricks.com";
-- Grant permission to use sequences (needed for SERIAL columns)
GRANT USAGE, SELECT ON ALL SEQUENCES IN SCHEMA public TO "alex.lopez@databricks.com";
-- Grant permissions on future sequences
ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES IN SCHEMA public
GRANT USAGE, SELECT ON SEQUENCES TO "alex.lopez@databricks.com";
What these permissions allow:
CONNECT: Connect to the databaseUSAGEon schema: Access objects within the schemaCREATEon schema: Create new tables, views, functionsSELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETEon tables: Read and write data- Sequence permissions: Use auto-incrementing columns
Step 4: Test the connection
Have Alex verify they can connect and access the database.
Using the Lakebase SQL Editor:
-
Alex opens the Lakebase App and navigates to your project.
-
Alex opens the Lakebase SQL Editor.
-
In the SQL Editor, Alex should be able to run the following queries to verify permissions:
SQL-- Check role memberships
SELECT rolname FROM pg_roles WHERE rolname = 'alex.lopez@databricks.com';
-- Verify can read data
SELECT * FROM your_table LIMIT 5;
-- Verify can write data
INSERT INTO your_table (column1, column2) VALUES ('test', 'value');
-- Verify can create tables
CREATE TABLE alex_analysis (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
notes TEXT,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT NOW()
);
Alternatively, using psql:
Alex can also connect from external tools like psql:
- From the project dashboard, click Connect.
- Select the branch, compute, and database.
- From the Roles dropdown, select
alex.lopez@databricks.com. - Copy the
psqlconnection snippet. - Click Copy OAuth Token to get an authentication token.
- Connect using the copied
psqlcommand and enter the OAuth token when prompted for password. - Run the same verification queries shown above.
Alternative: Read-only database access
For users who only need to query data without modifying it, grant the same project permissions but use more restrictive database permissions:
Project permissions
Grant CAN USE for view-and-use-only project access (e.g. connection URI, list branches). Grant CAN MANAGE to allow creating databases, roles, and other project operations.
Database permissions
-- Create OAuth role
SELECT databricks_create_role('analyst@databricks.com', 'USER');
-- Grant CONNECT permission
GRANT CONNECT ON DATABASE databricks_postgres TO "analyst@databricks.com";
-- Grant USAGE on the public schema
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA public TO "analyst@databricks.com";
-- Grant SELECT-only access to all existing tables
GRANT SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA public TO "analyst@databricks.com";
-- Grant SELECT-only access to future tables
ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES IN SCHEMA public
GRANT SELECT ON TABLES TO "analyst@databricks.com";
-- Grant USAGE on sequences (needed to view sequence values)
GRANT USAGE ON ALL SEQUENCES IN SCHEMA public TO "analyst@databricks.com";
This grants:
- Read access to all tables
- View database structure
- Cannot modify data (no INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE)
- Cannot create tables or other objects
Working with groups and service principals
You can follow the same process to grant access to Databricks groups and service principals. Grant project permissions through the Lakebase App UI, create OAuth roles using databricks_create_role(), and grant database permissions. For more information, see Groups and Service principals.
Using native Postgres password roles
As an alternative to OAuth roles, you can create native Postgres password roles for applications that can't refresh tokens hourly, long-running processes, or external tools that don't support OAuth. For instructions on creating and managing password roles, see Manage Postgres roles.