Manage read replicas
Lakebase Autoscaling is available in the following regions: us-east-1, us-east-2, us-west-2, eu-central-1, eu-west-1, ap-south-1, ap-southeast-1, ap-southeast-2.
Lakebase Autoscaling is the latest version of Lakebase with autoscaling compute, scale-to-zero, branching, and instant restore. For feature comparison with Lakebase Provisioned, see choosing between versions.
This guide walks you through creating and managing read replicas for your projects. Read replicas segregate read-only work from your production database operations, with applications ranging from horizontal scaling to analytics workloads. For detailed information about read replica architecture and use cases, see Read replicas.
Understanding read replicas
Read replicas enable you to create one or more read-only computes for any branch in your project. You can configure the compute size allocated to each replica, and both autoscaling and scale-to-zero features are supported, providing you with control over read replica compute usage.
The steps for creating, configuring, and connecting to a read replica are the same regardless of your use case.
Region support
Lakebase supports creating read replicas in the same region as your project. Cross-region read replicas are not supported.
Compute setting synchronization
For Lakebase read replicas, certain Postgres settings should not have lower values than your primary read-write compute. For this reason, the following settings on read replica computes are synchronized with the settings on the primary read-write compute when the read replica compute is started:
max_connectionsmax_prepared_transactionsmax_locks_per_transactionmax_wal_sendersmax_worker_processes
No user action is required. The settings are synchronized automatically when you create a read replica. However, if you change the compute size configuration on the primary read-write compute, you need to restart your read replica computes to ensure that settings remain synchronized. See Troubleshoot replication delay for more information.
Create and manage read replicas
Prerequisites
- A Lakebase project. See Create a project.
Create a read replica
To create a read replica:
- UI
- Python SDK
- Java SDK
- CLI
- curl
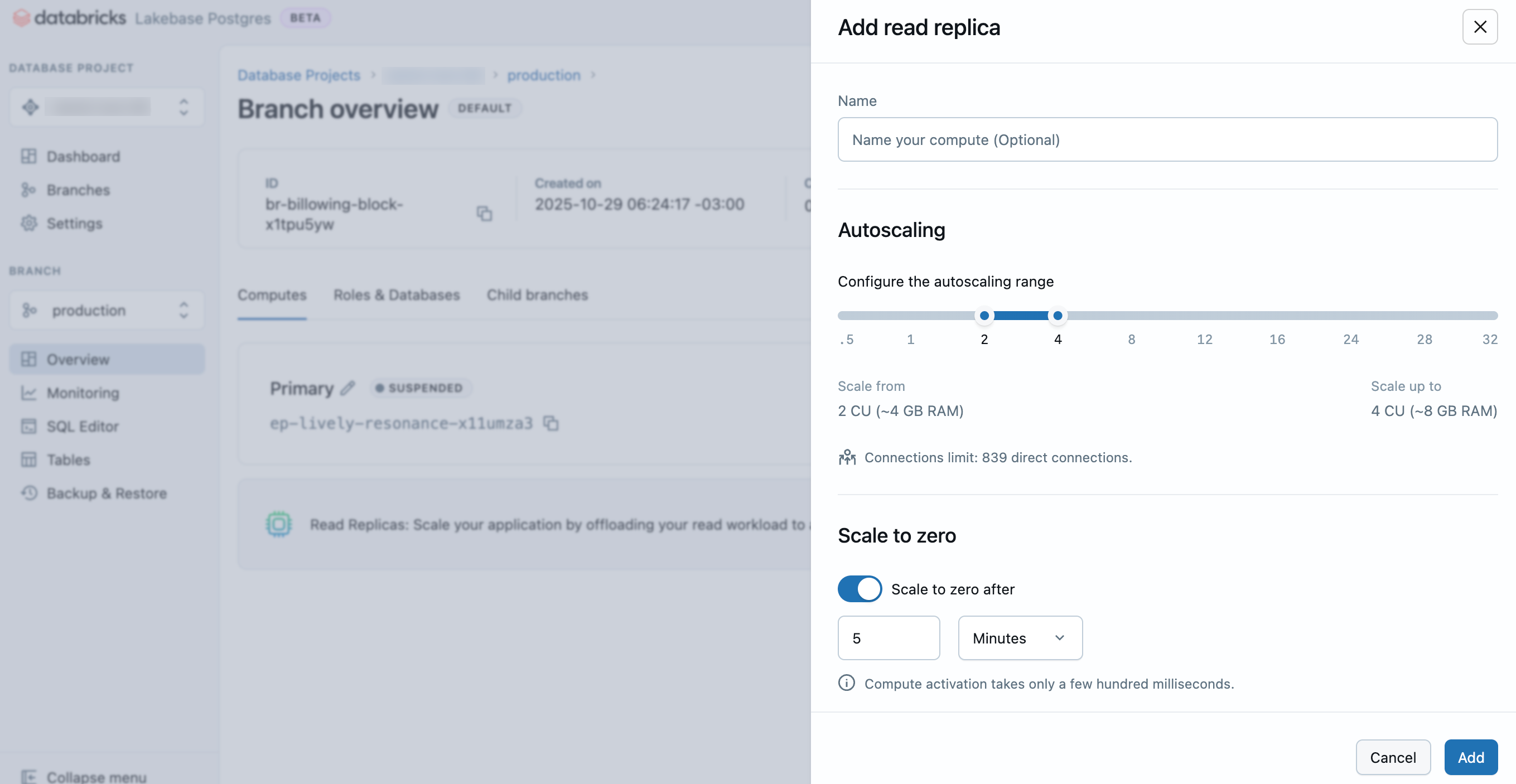
- In the Lakebase App, navigate to your project, branch, and the Computes tab.
- Click Add Read Replica.
- Enter a name for your read replica, configure the compute settings (autoscaling range and scale-to-zero behavior), and click Add.
from databricks.sdk import WorkspaceClient
from databricks.sdk.service.postgres import Endpoint, EndpointSpec, EndpointType
w = WorkspaceClient()
# Create read replica endpoint (READ_ONLY)
endpoint_spec = EndpointSpec(
endpoint_type=EndpointType.ENDPOINT_TYPE_READ_ONLY,
autoscaling_limit_max_cu=2.0
)
endpoint = Endpoint(spec=endpoint_spec)
result = w.postgres.create_endpoint(
parent="projects/my-project/branches/production",
endpoint=endpoint,
endpoint_id="my-read-replica"
).wait()
print(f"Endpoint created: {result.name}")
print(f"Host: {result.status.hosts.host}")
import com.databricks.sdk.WorkspaceClient;
import com.databricks.sdk.service.postgres.*;
WorkspaceClient w = new WorkspaceClient();
// Create read replica endpoint (READ_ONLY)
EndpointSpec endpointSpec = new EndpointSpec()
.setEndpointType(EndpointType.ENDPOINT_TYPE_READ_ONLY)
.setAutoscalingLimitMaxCu(2.0);
Endpoint endpoint = new Endpoint()
.setSpec(endpointSpec);
Endpoint result = w.postgres().createEndpoint(
new CreateEndpointRequest()
.setParent("projects/my-project/branches/production")
.setEndpoint(endpoint)
.setEndpointId("my-read-replica")
).waitForCompletion();
System.out.println("Endpoint created: " + result.getName());
System.out.println("Host: " + result.getStatus().getHosts().getHost());
# Create a read replica for a branch
databricks postgres create-endpoint projects/my-project/branches/production my-read-replica \
--json '{
"spec": {
"endpoint_type": "ENDPOINT_TYPE_READ_ONLY",
"autoscaling_limit_min_cu": 0.5,
"autoscaling_limit_max_cu": 4.0
}
}'
curl -X POST "$WORKSPACE/api/2.0/postgres/projects/my-project/branches/production/endpoints?endpoint_id=my-read-replica" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATABRICKS_TOKEN}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"spec": {
"endpoint_type": "ENDPOINT_TYPE_READ_ONLY",
"autoscaling_limit_min_cu": 0.5,
"autoscaling_limit_max_cu": 4.0
}
}' | jq
The compute size configuration determines the processing power of your database. Learn more: Manage computes
Your read replica is provisioned in a few seconds and appears on the Computes tab for the branch.
View read replicas
To view read replicas for a branch, navigate to your project in the Lakebase App, select a branch from the Branches page, and view the Computes tab where all read replica computes are listed.
Connect to a read replica
Connecting to a read replica follows the same process as connecting to your primary read-write compute, except you select a read replica compute when obtaining your connection information.
To get connection information for a read replica:
- In the Lakebase App, click Connect on your project dashboard.
- Select the branch, database, role, and the read replica compute from the Compute dropdown, then copy the provided connection string.
You can connect using either an OAuth Postgres role, just as you would with your primary read-write compute.
Write operations are not permitted on read replica connections. Attempting to execute write operations will result in an error.
For complete information about authentication methods and connection options, see Connect to your project.
Edit a read replica
You can edit a read replica to change the compute size or scale-to-zero configuration.
To edit a read replica:
- UI
- Python SDK
- Java SDK
- CLI
- curl
- Navigate to your branch's Computes tab in the Lakebase App.
- Find the read replica, click Edit, update the compute settings, and click Save.
from databricks.sdk import WorkspaceClient
from databricks.sdk.service.postgres import Endpoint, EndpointSpec, FieldMask
w = WorkspaceClient()
# Update read replica size
endpoint_name = "projects/my-project/branches/production/endpoints/my-read-replica"
endpoint_spec = EndpointSpec(
autoscaling_limit_min_cu=1.0,
autoscaling_limit_max_cu=8.0
)
endpoint = Endpoint(name=endpoint_name, spec=endpoint_spec)
update_mask = FieldMask(field_mask=[
"spec.autoscaling_limit_min_cu",
"spec.autoscaling_limit_max_cu"
])
result = w.postgres.update_endpoint(
name=endpoint_name,
endpoint=endpoint,
update_mask=update_mask
).wait()
print(f"Updated read replica size: {result.spec.autoscaling_limit_min_cu}-{result.spec.autoscaling_limit_max_cu} CU")
import com.databricks.sdk.WorkspaceClient;
import com.databricks.sdk.service.postgres.*;
import com.google.protobuf.FieldMask;
WorkspaceClient w = new WorkspaceClient();
// Update read replica size
String endpointName = "projects/my-project/branches/production/endpoints/my-read-replica";
EndpointSpec endpointSpec = new EndpointSpec()
.setAutoscalingLimitMinCu(1.0)
.setAutoscalingLimitMaxCu(8.0);
FieldMask updateMask = FieldMask.newBuilder()
.addPaths("spec.autoscaling_limit_min_cu")
.addPaths("spec.autoscaling_limit_max_cu")
.build();
w.postgres().updateEndpoint(
new UpdateEndpointRequest()
.setName(endpointName)
.setEndpoint(new Endpoint().setSpec(endpointSpec))
.setUpdateMask(updateMask)
);
System.out.println("Update initiated");
# Update a read replica's autoscaling settings
databricks postgres update-endpoint projects/my-project/branches/production/endpoints/my-read-replica "spec.autoscaling_limit_min_cu,spec.autoscaling_limit_max_cu" \
--json '{
"spec": {
"autoscaling_limit_min_cu": 1.0,
"autoscaling_limit_max_cu": 8.0
}
}'
# Update a read replica's autoscaling settings
curl -X PATCH "$WORKSPACE/api/2.0/postgres/projects/my-project/branches/production/endpoints/my-read-replica?update_mask=spec.autoscaling_limit_min_cu,spec.autoscaling_limit_max_cu" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATABRICKS_TOKEN}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"name": "projects/my-project/branches/production/endpoints/my-read-replica",
"spec": {
"autoscaling_limit_min_cu": 1.0,
"autoscaling_limit_max_cu": 8.0
}
}' | jq
Learn more: Manage computes
Delete a read replica
Deleting a read replica is a permanent action. However, you can quickly create a new read replica if you need one.
To delete a read replica:
- UI
- Python SDK
- Java SDK
- CLI
- curl
- Navigate to your branch's Computes tab in the Lakebase App.
- Find the read replica, click Edit, Delete, and confirm the deletion.
from databricks.sdk import WorkspaceClient
w = WorkspaceClient()
# Delete endpoint
w.postgres.delete_endpoint(
name="projects/my-project/branches/production/endpoints/my-read-replica"
).wait()
print("Endpoint deleted")
The delete operation is asynchronous. The .wait() method blocks until the deletion is complete.
import com.databricks.sdk.WorkspaceClient;
WorkspaceClient w = new WorkspaceClient();
// Delete endpoint
w.postgres().deleteEndpoint(
"projects/my-project/branches/production/endpoints/my-read-replica"
);
System.out.println("Delete initiated");
# Delete a read replica
databricks postgres delete-endpoint projects/my-project/branches/production/endpoints/my-read-replica
curl -X DELETE "$WORKSPACE/api/2.0/postgres/projects/my-project/branches/production/endpoints/my-read-replica" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATABRICKS_TOKEN}" | jq
Response:
{
"name": "projects/my-project/branches/production/endpoints/my-read-replica/operations/...",
"done": true,
"response": {
"@type": "type.googleapis.com/google.protobuf.Empty"
}
}
Troubleshoot replication delay
If your read replicas are falling behind, follow these steps to diagnose and resolve the issue:
Verify configuration alignment
If replication lag is detected, ensure that the configurations for the primary and read replica computes are aligned. Specifically, confirm that the following parameters match between your primary compute and read replica compute:
max_connectionsmax_prepared_transactionsmax_locks_per_transactionmax_wal_sendersmax_worker_processes
You can run the following query on both your primary read-write compute and read replica compute using the Lakebase SQL editor or a SQL client like psql:
SELECT name, setting
FROM pg_settings
WHERE name IN (
'max_connections',
'max_prepared_transactions',
'max_locks_per_transaction',
'max_wal_senders',
'max_worker_processes'
);
Compare the results from both computes to identify any misaligned settings.
Restart read replica computes
If the configurations are not aligned, restart your read replica computes to automatically update their settings. Navigate to your branch's Computes tab, find the read replica, and click Edit, then Restart.
When increasing the size of your primary read-write compute, always restart associated read replicas to ensure their configurations remain aligned.