Querying data at a point in time
Lakebase Autoscaling is available in the following regions: us-east-1, us-east-2, us-west-2, eu-central-1, eu-west-1, ap-south-1, ap-southeast-1, ap-southeast-2.
Lakebase Autoscaling is the latest version of Lakebase with autoscaling compute, scale-to-zero, branching, and instant restore. For feature comparison with Lakebase Provisioned, see choosing between versions.
Point-in-time branching allows you to query your database as it existed at any moment within your restore window. This feature creates a new branch with your data from a specific point in time, so you can analyze historical states without affecting your production data.
When to use point-in-time branches
Use a point-in-time branch when you need to:
- Analyze data as it existed at a specific point in the past
- Investigate changes made to your database over time
- Compare current data with historical states to understand data evolution
Query data at a point in time
To query your data at a point in time:
- Navigate to the Lakebase App by clicking the apps switcher in the top right corner of your workspace.
- Identify your project in the list.
- Click on the project name to get to the Project dashboard.
- In the Branches section of the left navigation, click Create branch.
- In the Create new branch dialog:
- Enter a branch name (required; for example,
historical-analysisorpast-data-query) - Select the Past data option
- Use the date and time picker to select the desired date and time you want to query
- Enter a branch name (required; for example,
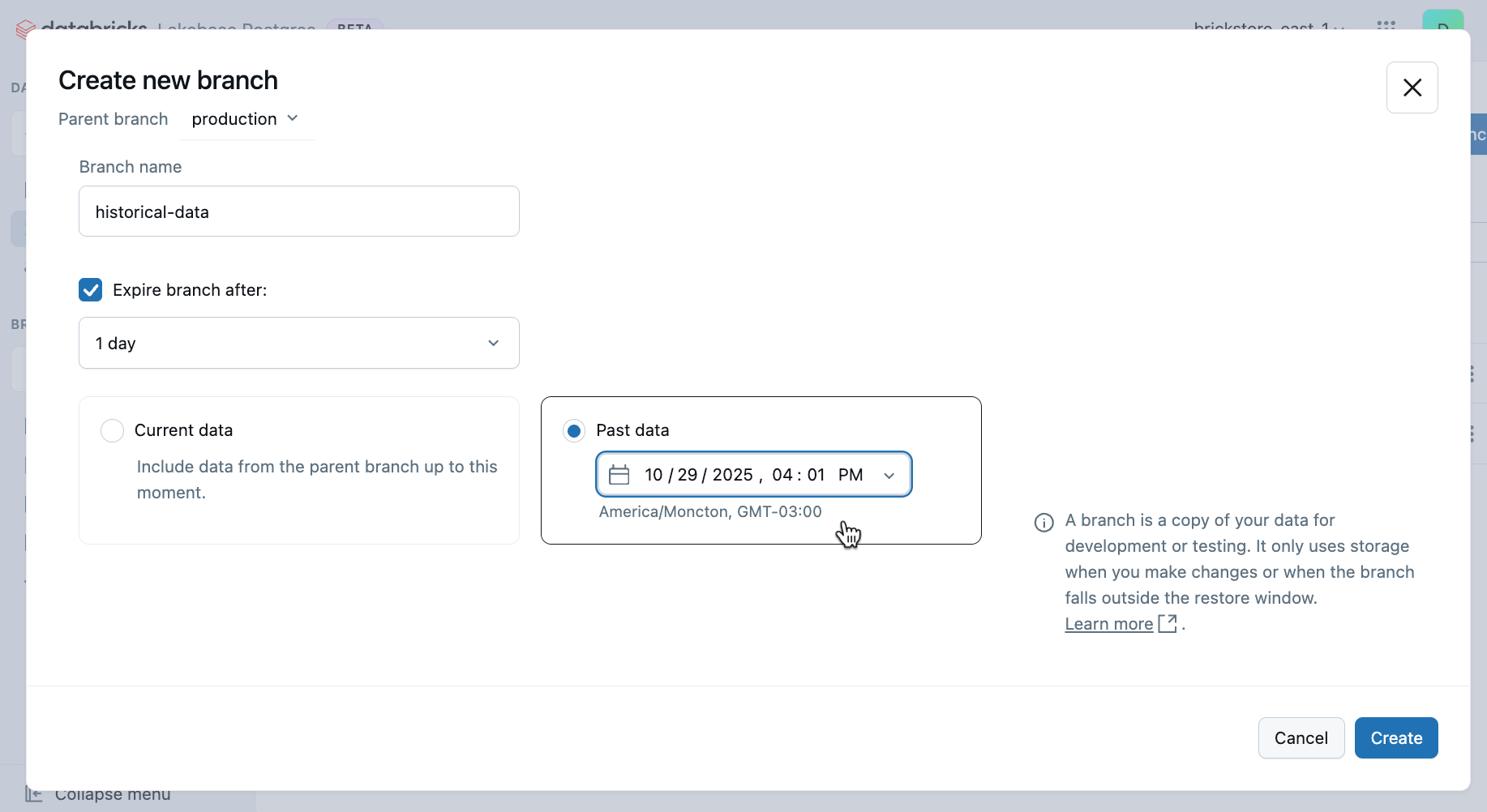
-
Click Create to create the new branch with data from the selected point in time.
noteThis creates a new branch with your data as it existed at the selected point in time, without affecting your production branch.
-
After the branch is created, you're automatically taken to the Branch Overview page for your new point-in-time branch. A Connection details modal appears with the connection string for this branch.
You have two options:
- Use external tools: Copy the connection string to connect using
psql, DBeaver, pgAdmin, or other Postgres clients - Use SQL Editor: Close the connection details modal and proceed to the next step
- Use external tools: Copy the connection string to connect using
-
To use the SQL Editor, close the connection details modal by clicking Close.
-
In the left navigation, click SQL Editor.
-
Query your database as it existed at the selected point in time.
-
Write and execute SQL queries to analyze your historical data.
For detailed information about using the SQL Editor, see Query from Lakebase SQL Editor. For information about connecting with external tools, see Postgres clients.
Clean up point-in-time branches
When you've finished your analysis and no longer need the point-in-time branch:
- Navigate to the Branches page in the left navigation.
- Find the point-in-time branch you created.
- Click the
menu next to the branch name.
- Select Delete from the dropdown menu.
- Confirm the deletion to remove the branch and free up storage space.
Important considerations
- Restore window: You can only query data from within your configured restore window. See Configure your restore window for information about adjusting this setting.
- Branch isolation: The point-in-time branch is separate from your production branch, so you can safely query and analyze without affecting current operations.
- Branch management: Delete point-in-time branches when you're finished with your analysis to avoid unnecessary storage usage.
- Full database state: The branch contains all databases and schemas as they existed at the selected point in time.