Point-in-time restore
Lakebase Autoscaling is available in the following regions: us-east-1, us-east-2, us-west-2, eu-central-1, eu-west-1, ap-south-1, ap-southeast-1, ap-southeast-2.
Lakebase Autoscaling is the latest version of Lakebase with autoscaling compute, scale-to-zero, branching, and instant restore. For feature comparison with Lakebase Provisioned, see choosing between versions.
You can restore from any point in time within your project's restore window. This restore option lets you quickly recover from an accidental data loss or modification such as an unintended deletion or schema change.
When to use point-in-time restore
Point-in-time restore is best for unexpected events like data loss, unintended deletions, or accidental schema changes. Use this method when you need to quickly restore to a specific moment in time to recover from recent issues.
Perform a restore operation
To perform a restore operation:
-
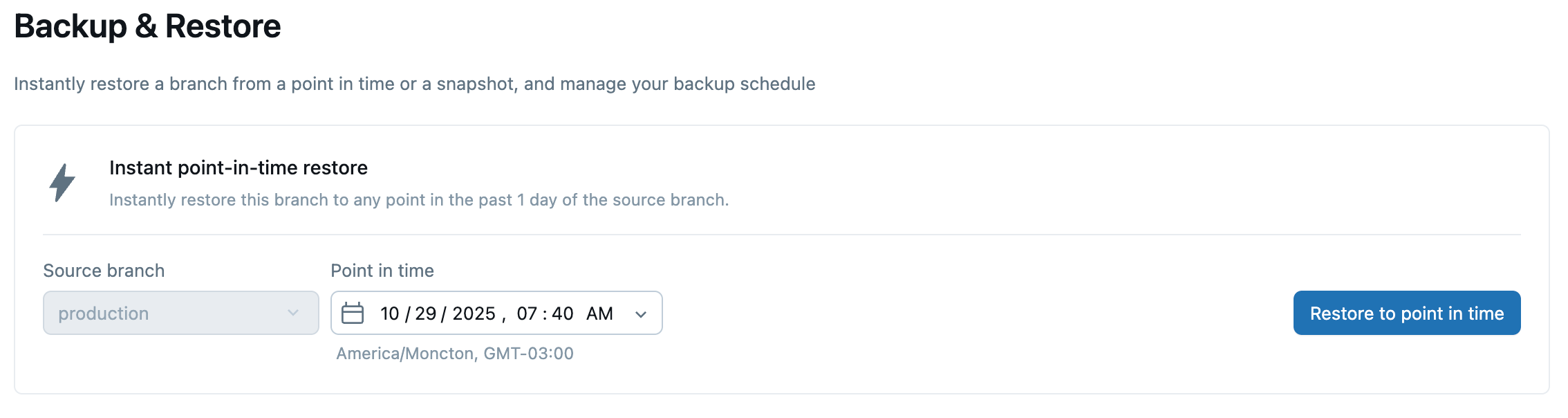
In the Lakebase App, navigate to your project and select Backup & Restore from the sidebar.
-
Under Instant point-in-time restore, select your source branch and choose a restore point using the date & time picker. Optionally, click Preview data to verify the branch state before proceeding.
-
Click Restore to point in time, review the confirmation details, then click Restore.
What happens after a restore?
When you perform a point-in-time restore, Lakebase creates a new root branch with your data as it existed at the selected moment. Here's what happens:
- A new root branch is created containing your data from the specified point in time.
- Your original branch remains unchanged and continues to operate normally.
- Existing connections continue working with your original branch without interruption.
The restored branch is created as a root branch, which means you can configure snapshot schedules and other root-branch features on it. Projects have a maximum of 3 root branches, so you may need to delete unused root branches before performing additional restores.
If you want to use the restored data, update your application connection configuration to point to the new branch.
This approach lets you safely recover data without disrupting active operations on your original branch.
Configure your restore window
Lakebase retains a history of changes for root branches in your project. This history enables point-in-time restore for recovering lost data, querying data at a point in time for investigating data issues, and branching from past states for development workflows.
You can configure the restore window from 0 days up to 30 days, which defines how far back you can restore. Note that:
- Extending the restore window increases your storage
- The restore window setting affects all branches in your project
To configure the restore window for a project:
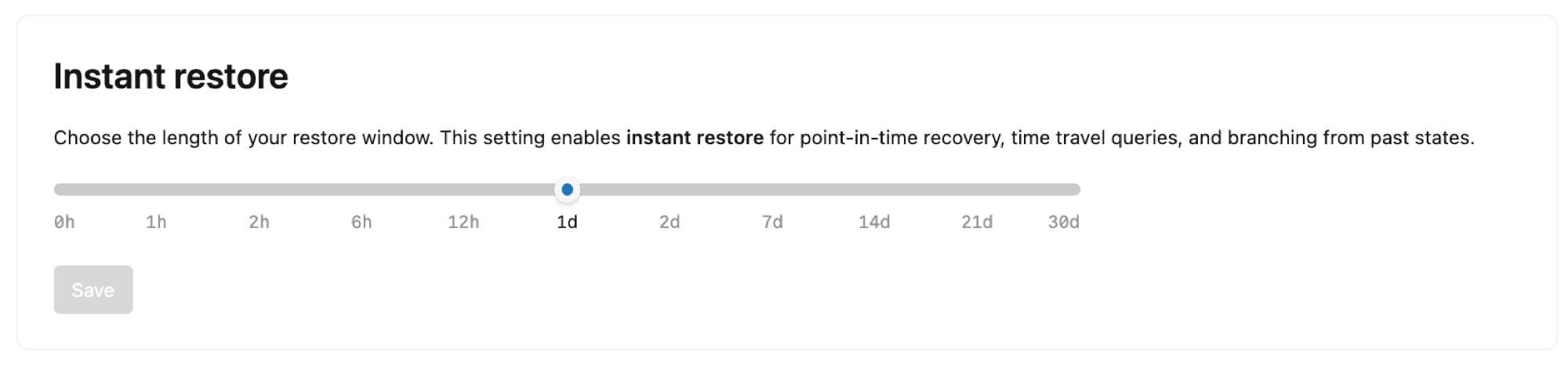
- Navigate to your project in the Lakebase App and select Settings on the Project dashboard.
- Select Instant restore and use the slider to set the restore window length from 0 days up to 30 days.
Restore details
This section outlines key details about point-in-time restore.
- Creates a new branch, not in-place modification
- All databases on a branch are restored
- Connections remain unchanged
Creates a new branch, not in-place modification
Point-in-time restore creates a new branch containing your data from the specified point in time. This is not an in-place modification of your existing branch. The new branch contains a complete copy of all data and schema as they existed at the restore point. Your original branch remains unchanged and continues operating normally with all its current data.
Restores apply to all Postgres databases
Each branch is an instance of Postgres. A Postgres instance can have more than one database. Keep this in mind when performing point-in-time restores. For example, if you want to recover lost data in a given database and you create a new branch from a point in time before the data loss occurred, the new branch includes all Postgres databases from that point in time, not just the one you're troubleshooting.
Connections remain unchanged
Point-in-time restore does not affect existing connections to your original branch. Since the restore creates a new branch rather than modifying your existing branch, all applications and connections continue to work with your original branch without any interruption. To use the restored data, you must manually update your application connection configuration to point to the new branch.