Query from SQL Editor in Lakehouse
Lakebase Autoscaling is available in the following regions: us-east-1, us-east-2, us-west-2, eu-central-1, eu-west-1, ap-south-1, ap-southeast-1, ap-southeast-2.
Lakebase Autoscaling is the latest version of Lakebase with autoscaling compute, scale-to-zero, branching, and instant restore. For feature comparison with Lakebase Provisioned, see choosing between versions.
This page describes how to query databases in your Lakebase project from the SQL editor in Lakehouse using two different connection methods.
The SQL editor in Lakehouse is a collaborative SQL workspace where you can author queries, browse data catalogs, create visualizations, and share results with colleagues. It provides advanced features for analytics, collaboration, and automation.
For Postgres-native features like EXPLAIN/ANALYZE and meta-commands (\dt, \d, \l), use the Lakebase SQL Editor. See Query from Lakebase SQL Editor.
For complete information about SQL editor capabilities, see Write queries and explore data in the SQL editor.
Connection methods
You can connect to your Lakebase database from the SQL editor using two methods:
- Direct compute connection: Connect directly to your Lakebase compute for immediate query access to a specific project and branch.
- Unity Catalog registration: Register your database in Unity Catalog to enable federated queries, unified governance, and cross-source analytics.
Choose your connection method
Feature | Direct compute connection | Unity Catalog registration |
|---|---|---|
Data access | Full read-write access to your Lakebase database | Read-only access through Unity Catalog |
Best for | Working primarily with Lakebase data without combining it with other data sources | Combining Lakebase data with other Unity Catalog tables in federated queries |
Setup complexity | Immediate access to query a specific database without registration | Requires catalog registration and Unity Catalog privileges |
Governance | No Unity Catalog governance features | Unified governance controls (permissions, lineage, audit logs) |
Access control | Postgres role-based permissions only | Centralized discovery and access control across multiple data sources |
Use cases | Direct database operations and modifications | Dashboards and applications that integrate transactional and analytical data |
Method 1: Connect directly to Lakebase compute
Use this method to connect directly to your Lakebase compute for immediate query access.
Before you begin
If you're not the project owner, verify you have:
- Postgres role: A corresponding Postgres role to access the database. See Manage Postgres roles.
- Database permissions: The necessary permissions to access the database, schema, or table. See Manage permissions.
If you lack the necessary role or permissions, contact the project owner to request access.
The Lakebase compute must be in an active state to attach to it. If the compute is idle, you can't attach. Computes typically become inactive when scale to zero is enabled and there's no database activity.
To activate an idle compute, run a query in the Lakebase SQL Editor or disable scale to zero to ensure your compute remains active. See Scale to zero.
To connect directly to your Lakebase compute:
- Use the apps switcher to navigate to Lakehouse.
- Open the SQL editor by clicking
SQL Editor in the sidebar.
- From the Connect drop-down menu, select More...
- On the the Attach to an existing compute resource dialog, select Lakebase Postgres, choose the Autoscaling option, and then select your Project and Branch.
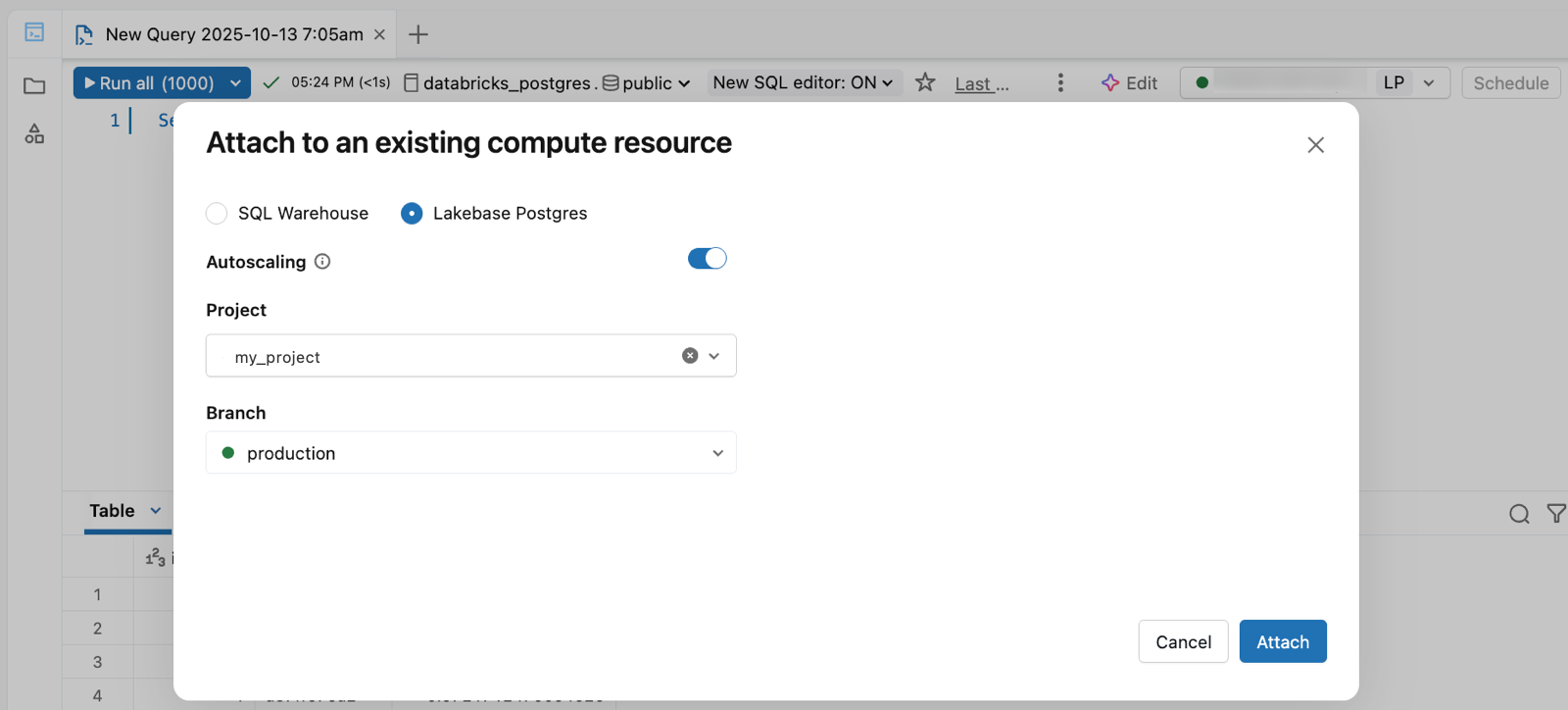
- Click Attach to connect.
Example queries with direct connection
After connecting, you can run standard Postgres SQL queries against your Lakebase database.
Create a table, insert data, and query it:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS playing_with_lakebase(id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, name TEXT NOT NULL, value REAL);
INSERT INTO playing_with_lakebase(name, value)
SELECT LEFT(md5(i::TEXT), 10), random() FROM generate_series(1, 10) s(i);
SELECT * FROM playing_with_lakebase;
Query a specific table:
SELECT * FROM public.playing_with_lakebase;
Limitations with direct connection:
- Federated queries not supported: You can only query the connected Lakebase project and branch. You can't combine Lakebase data with other Unity Catalog tables in a single query.
- Postgres meta-commands not supported: The Postgres meta-commands (like
\dt,\d,\l) that work in the Lakebase SQL Editor don't work in the SQL editor (Lakehouse).
Method 2: Register database in Unity Catalog
Use this method to register your Lakebase database in Unity Catalog, enabling federated queries and unified governance across your data sources.
Before you begin
Verify you have:
- Postgres role: A corresponding Postgres role to access the database. See Manage Postgres roles.
- Database permissions: The necessary permissions to access the database, schema, or table. See Manage permissions.
- Unity Catalog privileges:
CREATE CATALOGprivileges on the Unity Catalog metastore to register the database - SQL warehouse: A serverless SQL warehouse to query the registered catalog
If you lack the necessary role or permissions, contact the project owner to request access.
Register your database
To register a Lakebase database in Unity Catalog:
- Use the apps switcher to navigate to Lakehouse.
- In Catalog Explorer, click the plus icon and Create a catalog.
- Enter a catalog name (for example,
lakebase_catalog). - Select Lakebase Postgres as the catalog type, then choose the Autoscaling option.
- Select your project, branch, and Postgres database.
- Click Create.
The catalog appears in Catalog Explorer, where you can browse schemas, tables, and views.
Query through Unity Catalog
After registration, query your Lakebase database using SQL warehouses or any tool that connects to Unity Catalog.
Query a registered database:
-- Query a registered :re[LKB] database
SELECT * FROM chatbot_catalog.public.conversations
WHERE created_at >= current_date - INTERVAL 7 DAYS;
Combine Lakebase and lakehouse data:
-- Join :re[LKB] and Unity Catalog data
SELECT
c.conversation_id,
c.user_id,
c.agent_response,
u.user_name,
u.subscription_tier
FROM chatbot_catalog.public.conversations c
JOIN main.user_analytics.users u
ON c.user_id = u.user_id;
For information about Unity Catalog permissions and granting access to other users, see Permissions and access control.
Limitations with Unity Catalog registration:
- Read-only access: Catalogs registered from Lakebase databases are read-only through Unity Catalog. To modify data, use the Lakebase SQL Editor or connect directly to your database.
- Single database per catalog: Each Unity Catalog catalog represents one Lakebase database. To expose multiple databases, register each one separately.
- Metadata sync: Unity Catalog caches metadata to reduce Postgres requests. New objects may not appear immediately. Click
to trigger a full refresh.
For complete information about registering databases in Unity Catalog, see Register a Lakebase database in Unity Catalog.