Manage updates
Lakebase Autoscaling is available in the following regions: us-east-1, us-east-2, us-west-2, eu-central-1, eu-west-1, ap-south-1, ap-southeast-1, ap-southeast-2.
Lakebase Autoscaling is the latest version of Lakebase with autoscaling compute, scale-to-zero, branching, and instant restore. For feature comparison with Lakebase Provisioned, see choosing between versions.
To keep your Lakebase Postgres instances up to date with the latest patches and features, Lakebase applies updates to your project's computes. You can select an update window — a specific day and hour for updates.
Lakebase briefly restarts a compute to apply an update. The entire process takes just a few seconds, minimizing any potential disruption.
What updates are included?
Updates to Lakebase computes may include some or all of the following:
- Postgres minor version upgrades, typically released quarterly
- Security patches and updates
- Operating system updates
- Lakebase features and enhancements
- Updates to other tools and components included in Lakebase compute images
Lakebase compute updates do not include Lakebase platform maintenance.
How often are updates applied?
Updates are typically released weekly but may occur more or less frequently, as needed.
Lakebase applies updates to computes based on the following rules:
- Computes are automatically restarted every 28 days to receive updates.
- Computes that are restarted before the 28-day cycle receive available updates immediately.
- Computes in a transition state (shutting down or restarting) at the time of an update are not updated.
- If a compute is excluded from an update, Lakebase applies the missed update with the next update, assuming the compute meets the update criteria mentioned above.
Schedule updates
You can set a preferred update window by specifying the day and hour. Updates are applied within this window, letting you plan for the required compute restart.
To set your update schedule:
- Navigate to the Lakebase App by clicking the apps switcher in the top right corner of your workspace.
- Select your project.
- Click Settings > Updates.
- Choose a day of the week and an hour. Updates occur within this time window and take only a few seconds.
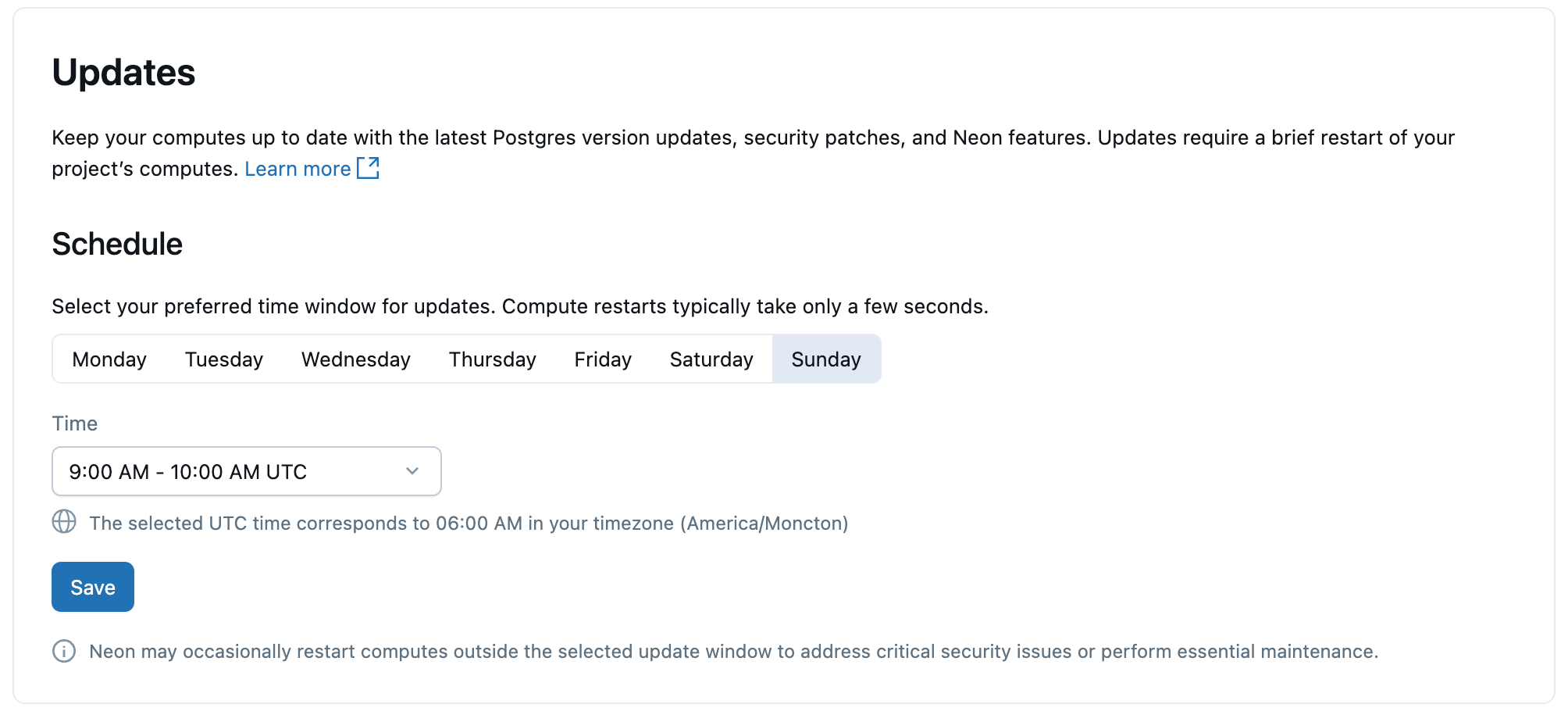
You can check your project's settings for upcoming updates. Planned updates are posted at least 7 days in advance.
Apply updates ahead of schedule
Computes receive available updates immediately upon restart. For example, if Lakebase notifies you about an upcoming update, you can apply it right away by restarting the compute. However, the notification isn't cleared in this case. When the planned update time arrives, no further action is taken since the compute is already updated.
If a compute regularly scales to zero, it receives updates when it starts up again. In such cases, you may not need to pay much attention to update notifications, as updates are applied naturally through your compute's stop/start cycles.
For compute restart instructions, see Manage computes.
Handle connection disruptions during updates
Most Postgres connection drivers include built-in retry mechanisms that automatically handle short-lived connection interruptions. This means that for most applications, a brief restart should result in minimal disruption, as the driver reconnects automatically.
However, if your application has strict availability requirements, you may want to ensure that your connection settings are configured to allow for retries. Check your driver's documentation for options like connection timeouts, retry intervals, and connection pooling strategies. Your configuration should account for the few seconds it takes to apply updates to your Lakebase compute.
If your application uses connection pooling or has custom retry logic, ensure it can handle brief connection drops during compute restarts.