Connect to Databricks from Google Sheets
This feature is in Public Preview.
This page describes how to use the Databricks Connector for Google Sheets to connect to Databricks from Google Sheets. The Databricks Connector queries Databricks data from within Google Sheets, enabling further analysis.
Before you begin
- Create a Databricks workspace. See Create a workspace.
- Create a Databricks SQL warehouse. See Create a SQL warehouse.
- Have access to Google Sheets.
- Install the Databricks Connector for Google Sheets.
- If your Databricks workspace has IP access lists enabled, the account admin must add the Google Cloud IP list to the allow list.
- To learn more about IP access lists, see Configure IP access lists for the account console.
- For the Google Cloud IP list, see this IP list.
Connect to a Databricks Workspace
Import data from Databricks into Google Sheets using the Databricks Connector for Google Sheets by first connecting to a Databricks workspace:
-
In Google Sheets, select Extensions > Databricks Connector > Launch sidebar to open the connector.
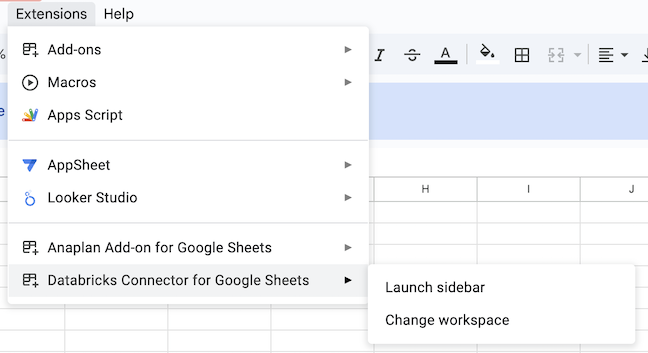
-
In the Login dialog, enter your Databricks workspace URL. To learn how to find your workspace URL, see Get identifiers for workspace objects.
- Your workspace URL is in the following format:
https://<instance-name>.cloud.databricks.com.
- Your workspace URL is in the following format:
-
Click Sign in.
-
A dialog prompts you to sign in or shows your login status.
-
After logging in, you can select which SQL warehouse to use. In the Databricks Connector sidebar, under the Data tab, choose a Databricks SQL warehouse by clicking the circle in the upper right of the connector sidebar and selecting your preferred Databricks SQL warehouse. The connector starts the chosen SQL warehouse.
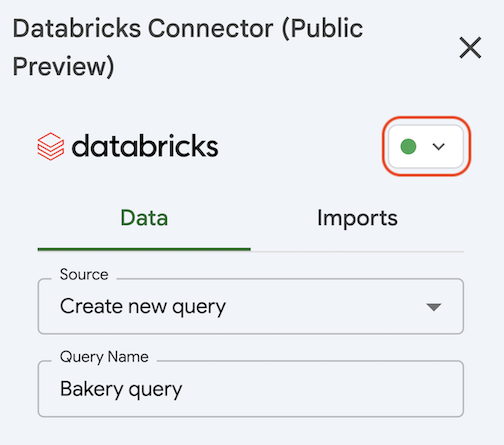
Use the Databricks Connector for Google Sheets
The Databricks Connector for Google Sheets runs queries against data that you have access to in Unity Catalog and imports the data into Google Sheets. The connector automatically saves all queries as imports. You can refresh results, reuse existing queries, and track data origins in Google Sheets.
After the data is imported, the query is tied to the sheet. Changing the sheet name breaks the mapping. For information on how to handle name changes, see Limitations.
Query execution times out after three minutes. If your query exceeds this limit, it is automatically cancelled. For large result sets, the first 1,000 rows are written immediately, with remaining data fetched progressively. If data fetching is interrupted, partial results remain in your sheet and can be cleared by re-running the query.
Choose an import method
Select one of the following methods to import data from Databricks:
- Select a table
- Write a SQL query
To import data from a table in Databricks:
- In the connector sidebar, for Import method, select Select data.
- Under Catalog, use the catalog, schema, and table drop-down menus to search for the table you want to import.
- Optionally, update the Asset Name to change the name of this import.
- Optionally, under Fields, choose which columns to include or exclude.
- You can optionally import as a pivot table.
- To add a filter, click + Filter under Filters. Select the Column to apply the filter to and the Filter type.
- Optionally, check Limit rows to set a limit for the number of rows to import.
- Under Advanced options, choose if you want to save the query results in a new sheet or in the current sheet.
- If you choose the current sheet, specify which cell to start adding the data in.
- Click Save & Import to populate the sheet.
- In the connector sidebar, for Import method, select Create new query.
- Databricks recommends entering a name for your query so it is identifiable.
- You can browse through catalogs, schemas, and tables.
- In Query text, enter your SQL query.
- You can optionally add query parameters.
- Under Advanced options, choose if you want to save the query results in a new sheet or in the current sheet.
- If you choose the current sheet, specify which cell to start adding the data in.
- Click Save & Import to run the query and populate the sheet.
If you are using "Select data" to import Unity Catalog metric views, they can only be imported as pivot tables because Unity Catalog metrics represent pivoted data.
Add query parameters (optional)
To add query parameters to your SQL query:
-
Ensure your query has at least one query parameter, in the format of
:parameter_name. For more on query parameters, see Work with query parameters. -
Click + Add Parameter.
-
Enter the parameter in the first box. Make sure the parameter name matches what you entered in the query editor.
-
Enter the sheet name and cell location of your parameter value in the second box, including the exclamation point after the sheet name.
-
To add more query parameters, click + Add Parameter again.
For example, the following query includes the query parameter
:trip_distance, which is defined in sheetsheet_1, cell H1.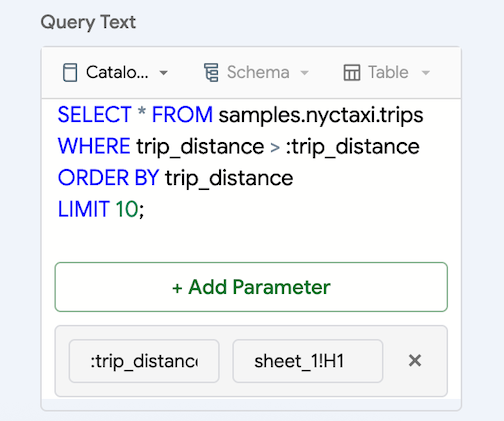
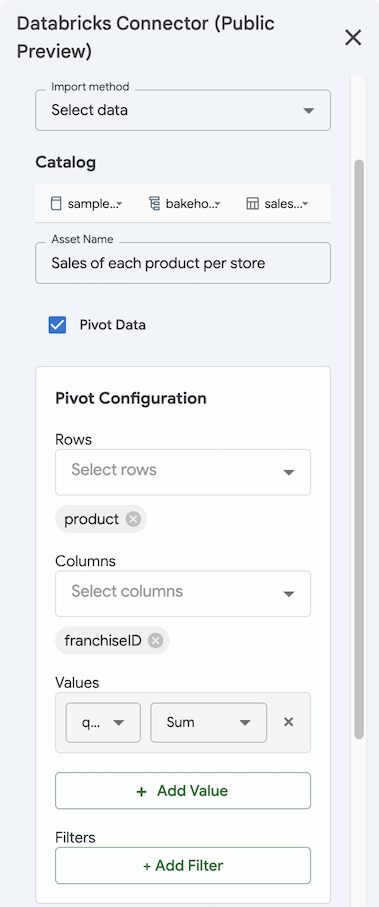
Import as a pivot table (optional)
To import your data as a pivot table:
- When importing data, select Pivot table.
- Under Pivot Configuration, select the Rows and Columns for the dimensions of your pivot table.
- Specify values to aggregate by. Click + Add Value and select the column and aggregation method.
- Optionally, add filters by clicking + Add Filter and select the Column and Filter type.
- Click Save & Import to import the results as a pivot table. Import pivot tables are automatically imported to a new sheet.
Manage imported data
To manage the data you import from Databricks:
- Select the Imports tab in the connector sidebar.
- To refresh an import, click the refresh icon next to the query name.
- To see which sheet an import is connected to, click
> Go to Sheet next to the query name.
- To edit an import, click
> Edit next to the query name.
- To delete an import, click
> Delete next to the query name. This deletes the query, not the data imported into Google Sheets. You must manually delete imported data.
Change Databricks workspace
To change the Databricks workspace you are connected to:
- Select Extensions > Databricks Connector > Change workspace.
- Enter the new workspace URL and authenticate to the workspace.
Sharing implications
The add-on does not impact your ability to share your Google Sheet. However, the way you share the file impacts the actions that your recipients can take using the add-on.
- Recipients with the Viewer or Commenter role can't access the add-on.
- Recipients with the Editor role and equivalent data asset access can use the add-on with their Google account. They can use the connector just like the owner.
- Recipients with the Editor role and the same access to the underlying resources can refresh the imports if they are logged in to the same Databricks workspace.
Limitations
-
Renaming or deleting a sheet that is attached to an existing import prevents you from refreshing the import. To fix this, do one of the following:
- Recreate the sheet with the exact same name.
- Create a new import by choosing Select a Query as the source, reusing the import, and clicking Save as New.
-
If two queries map to the same or overlapping ranges, the add-on displays the results of the most recently executed query. This overwrites previously imported data.