Databricks マネージド MCP サーバーを使用する
プレビュー
この機能は パブリック プレビュー段階です。
Databricksが管理する MCP サーバーは、 AIエージェントをUnity Catalog 、 Databricksベクトル検索 インデックス、 Genie spaces 、カスタム関数に保存されているデータに接続する、すぐに使用できるサーバーです。
Unity Catalog権限は常に適用されるため、エージェントとユーザーは許可されたツールとデータにのみアクセスできます。
使用可能な管理対象サーバー
Databricks は、すぐに使用できる次の MCP サーバーを提供します。
MCP サーバ | URL パターン |
|---|---|
ベクトル検索 通用検索インデックスをクエリして、関連するドキュメントを見つけます。 インデックスでは、Databricks 管理の埋め込みを使用する必要があります。 |
|
Genieスペース 自然言語を使用して構造化データを分析するには、 Genie spacesをクエリします。 読み取り専用。 Genie MCP は Genie をツールとして呼び出すため、履歴は Genie API に渡されません。履歴を保存するには、代わりにマルチエージェント システムで Genieを使用します。 このサーバーを使用する場合は、長時間実行されるクエリの結果をポーリングする必要があります。 |
|
DBSQL 実行AI -Claude Code、Cursor、Codex などのAIコーディング ツールを使用してデータパイプラインを作成するSQLを生成しました。 読み書きします。 このサーバーを使用する場合は、長時間実行されるクエリの結果をポーリングする必要があります。 |
|
Unity Catalog の関数 Unity Catalog関数を使用して、事前定義されたSQLクエリを実行します。 |
|
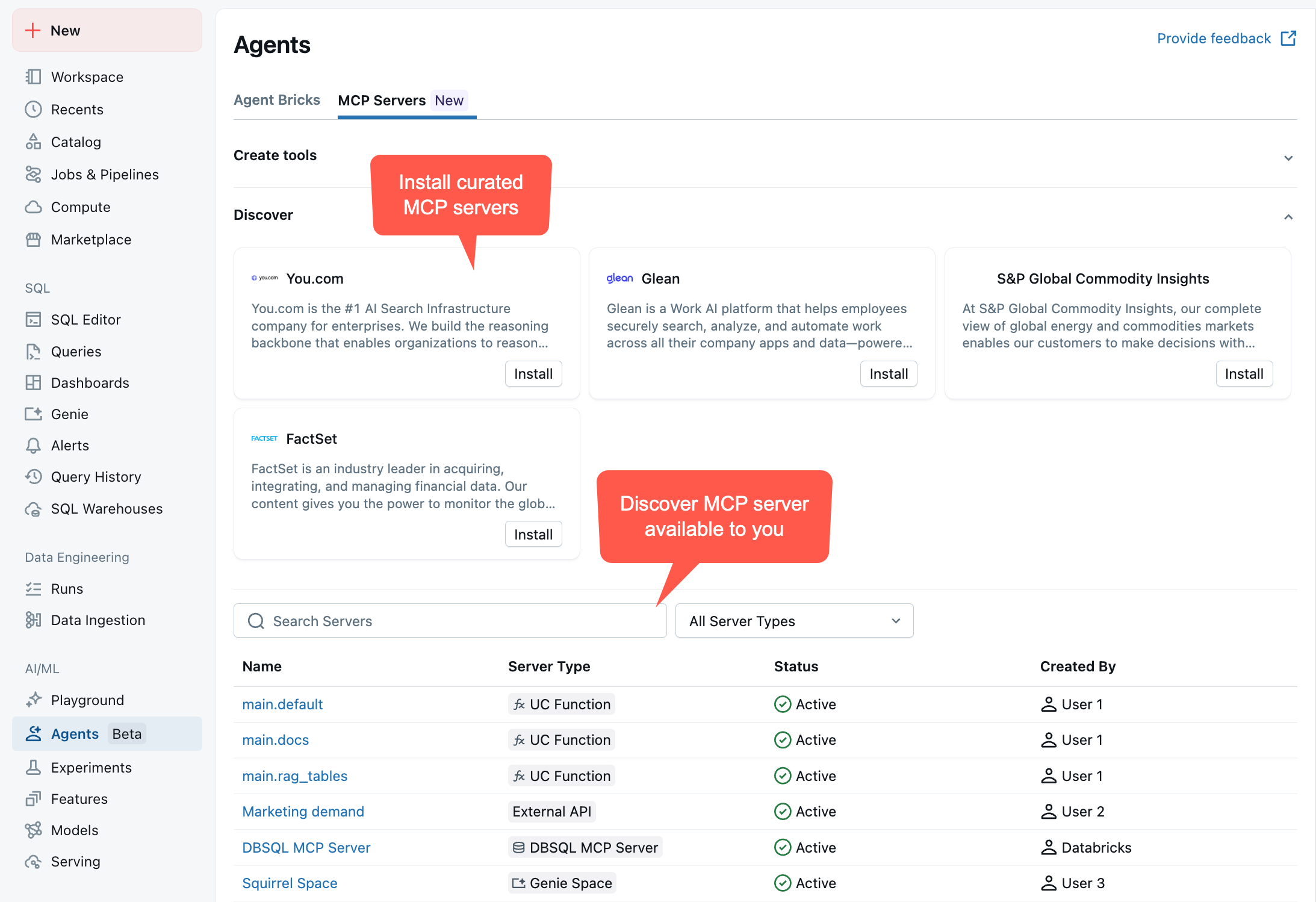
MCP サーバーとそのエンドポイント URL を表示するには、ワークスペース > エージェント > MCP サーバー に移動します。
シナリオ例
顧客サポートに役立つカスタムエージェントを検討してください。複数の管理対象 MCP サーバーに接続できます。
-
ベクトル検索 :
https://<workspace-hostname>/api/2.0/mcp/vector-search/prod/customer_support- サポートチケットとドキュメントを検索する
-
Genieスペース :
https://<workspace-hostname>/api/2.0/mcp/genie/{billing_space_id}- 請求データと顧客情報の照会
-
UCの関数 :
https://<workspace-hostname>/api/2.0/mcp/functions/prod/billing- アカウントの検索と更新のためのカスタム関数を実行する
これにより、エージェントは非構造化データ (サポート チケット)、構造化データ (請求テーブル)、カスタム ビジネス ロジックにアクセスできるようになります。
サンプルノートブック: Databricks MCP サーバーを使用してエージェントを構築する
次のノートブックは、Databricks が管理する MCP サーバーを使用して MCP ツールを呼び出す LangGraph および OpenAI エージェントを作成する方法を示しています。
LangGraph MCPツール呼び出しエージェント
OpenAI MCP ツール呼び出しエージェント
エージェント SDK MCP ツール呼び出しエージェント
ローカル環境からエージェントを構築する
Databricks 上の MCP サーバーへの接続は、他のリモート MCP サーバーへの接続と同様です。MCP Python SDK などの標準 SDK を使用してサーバーに接続できます。主な違いは、Databricks MCP サーバーはデフォルトでセキュリティ保護されており、クライアントが認証を指定する必要があることです。
databricks-mcp Python ライブラリは、カスタム エージェント コードでの認証を簡略化するのに役立ちます。
エージェント コードを開発する最も簡単な方法は、それをローカルで実行し、ワークスペースに対して認証することです。次のステップに従って、 Databricks MCP サーバーに接続するAIエージェントを構築します。
環境を設定する
-
OAuth を使用してワークスペースに認証します。ローカルターミナルで次のコマンドを実行します。
Bashdatabricks auth login --host https://<your-workspace-hostname> -
プロンプトが表示されたら、プロファイル名を入力し、後で使用するためにメモしておきます。安全のプロファイル名は安全です。
-
Python 3.12 以降のローカル環境があることを確認し、依存関係をインストールします。
Bashpip install -U "mcp>=1.9" "databricks-sdk[openai]" "mlflow>=3.1.0" "databricks-agents>=1.0.0" "databricks-mcp"
ローカル環境接続をテストする
サーバレス コンピュート このスニペットを実行するには、ワークスペースで有効にする必要があります。
Unity Catalogツールを一覧表示し、組み込みPythonコード インタープリター ツールを実行して、MCP サーバーへの接続を検証します。
- MCP サーバーへの接続を検証するには、次のコードを実行します。
from databricks_mcp import DatabricksMCPClient
from databricks.sdk import WorkspaceClient
# TODO: Update to the Databricks CLI profile name you specified when
# configuring authentication to the workspace.
databricks_cli_profile = "YOUR_DATABRICKS_CLI_PROFILE"
assert (
databricks_cli_profile != "YOUR_DATABRICKS_CLI_PROFILE"
), "Set databricks_cli_profile to the Databricks CLI profile name you specified when configuring authentication to the workspace"
workspace_client = WorkspaceClient(profile=databricks_cli_profile)
workspace_hostname = workspace_client.config.host
mcp_server_url = f"{workspace_hostname}/api/2.0/mcp/functions/system/ai"
# This code uses the Unity Catalog functions MCP server to expose built-in
# AI tools under `system.ai`, like the `system.ai.python_exec` code interpreter tool
def test_connect_to_server():
mcp_client = DatabricksMCPClient(server_url=mcp_server_url, workspace_client=workspace_client)
tools = mcp_client.list_tools()
print(
f"Discovered tools {[t.name for t in tools]} "
f"from MCP server {mcp_server_url}"
)
result = mcp_client.call_tool(
"system__ai__python_exec", {"code": "print('Hello, world!')"}
)
print(
f"Called system__ai__python_exec tool and got result "
f"{result.content}"
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
test_connect_to_server()
エージェントを作成する
-
上記のコードを基にして、ツールを使用する基本的なシングルターン エージェントを定義します。エージェント コードを
mcp_agent.pyという名前のファイルとしてローカルに保存します。Pythonimport json
import uuid
import asyncio
from typing import Any, Callable, List
from pydantic import BaseModel
import mlflow
from mlflow.pyfunc import ResponsesAgent
from mlflow.types.responses import ResponsesAgentRequest, ResponsesAgentResponse
from databricks_mcp import DatabricksMCPClient
from databricks.sdk import WorkspaceClient
from databricks_openai import DatabricksOpenAI
# 1) CONFIGURE YOUR ENDPOINTS/PROFILE
LLM_ENDPOINT_NAME = "databricks-claude-sonnet-4-5"
SYSTEM_PROMPT = "You are a helpful assistant."
DATABRICKS_CLI_PROFILE = "YOUR_DATABRICKS_CLI_PROFILE"
assert (
DATABRICKS_CLI_PROFILE != "YOUR_DATABRICKS_CLI_PROFILE"
), "Set DATABRICKS_CLI_PROFILE to the Databricks CLI profile name you specified when configuring authentication to the workspace"
workspace_client = WorkspaceClient(profile=DATABRICKS_CLI_PROFILE)
host = workspace_client.config.host
# Add more MCP server URLs here if desired, for example:
# f"{host}/api/2.0/mcp/vector-search/prod/billing"
# to include vector search indexes under the prod.billing schema, or
# f"{host}/api/2.0/mcp/genie/<genie_space_id>"
# to include a Genie space
MANAGED_MCP_SERVER_URLS = [
f"{host}/api/2.0/mcp/functions/system/ai",
]
# Add Custom MCP Servers hosted on Databricks Apps
CUSTOM_MCP_SERVER_URLS = []
# 2) HELPER: convert between ResponsesAgent “message dict” and ChatCompletions format
def _to_chat_messages(msg: dict[str, Any]) -> List[dict]:
"""
Take a single ResponsesAgent‐style dict and turn it into one or more
ChatCompletions‐compatible dict entries.
"""
msg_type = msg.get("type")
if msg_type == "function_call":
return [
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": None,
"tool_calls": [
{
"id": msg["call_id"],
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": msg["name"],
"arguments": msg["arguments"],
},
}
],
}
]
elif msg_type == "message" and isinstance(msg["content"], list):
return [
{
"role": "assistant" if msg["role"] == "assistant" else msg["role"],
"content": content["text"],
}
for content in msg["content"]
]
elif msg_type == "function_call_output":
return [
{
"role": "tool",
"content": msg["output"],
"tool_call_id": msg["tool_call_id"],
}
]
else:
# fallback for plain {"role": ..., "content": "..."} or similar
return [
{
k: v
for k, v in msg.items()
if k in ("role", "content", "name", "tool_calls", "tool_call_id")
}
]
# 3) “MCP SESSION” + TOOL‐INVOCATION LOGIC
def _make_exec_fn(
server_url: str, tool_name: str, ws: WorkspaceClient
) -> Callable[..., str]:
def exec_fn(**kwargs):
mcp_client = DatabricksMCPClient(server_url=server_url, workspace_client=ws)
response = mcp_client.call_tool(tool_name, kwargs)
return "".join([c.text for c in response.content])
return exec_fn
class ToolInfo(BaseModel):
name: str
spec: dict
exec_fn: Callable
def _fetch_tool_infos(ws: WorkspaceClient, server_url: str) -> List[ToolInfo]:
print(f"Listing tools from MCP server {server_url}")
infos: List[ToolInfo] = []
mcp_client = DatabricksMCPClient(server_url=server_url, workspace_client=ws)
mcp_tools = mcp_client.list_tools()
for t in mcp_tools:
schema = t.inputSchema.copy()
if "properties" not in schema:
schema["properties"] = {}
spec = {
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": t.name,
"description": t.description,
"parameters": schema,
},
}
infos.append(
ToolInfo(
name=t.name, spec=spec, exec_fn=_make_exec_fn(server_url, t.name, ws)
)
)
return infos
# 4) "SINGLE‐TURN" AGENT CLASS
class SingleTurnMCPAgent(ResponsesAgent):
def _call_llm(self, history: List[dict], ws: WorkspaceClient, tool_infos):
"""
Send current history → LLM, returning the raw response dict.
"""
client = DatabricksOpenAI()
flat_msgs = []
for msg in history:
flat_msgs.extend(_to_chat_messages(msg))
return client.chat.completions.create(
model=LLM_ENDPOINT_NAME,
messages=flat_msgs,
tools=[ti.spec for ti in tool_infos],
)
def predict(self, request: ResponsesAgentRequest) -> ResponsesAgentResponse:
ws = WorkspaceClient(profile=DATABRICKS_CLI_PROFILE)
# 1) build initial history: system + user
history: List[dict] = [{"role": "system", "content": SYSTEM_PROMPT}]
for inp in request.input:
history.append(inp.model_dump())
# 2) call LLM once
tool_infos = [
tool_info
for mcp_server_url in (MANAGED_MCP_SERVER_URLS + CUSTOM_MCP_SERVER_URLS)
for tool_info in _fetch_tool_infos(ws, mcp_server_url)
]
tools_dict = {tool_info.name: tool_info for tool_info in tool_infos}
llm_resp = self._call_llm(history, ws, tool_infos)
raw_choice = llm_resp.choices[0].message.to_dict()
raw_choice["id"] = uuid.uuid4().hex
history.append(raw_choice)
tool_calls = raw_choice.get("tool_calls") or []
if tool_calls:
# (we only support a single tool in this “single‐turn” example)
fc = tool_calls[0]
name = fc["function"]["name"]
args = json.loads(fc["function"]["arguments"])
try:
tool_info = tools_dict[name]
result = tool_info.exec_fn(**args)
except Exception as e:
result = f"Error invoking {name}: {e}"
# 4) append the “tool” output
history.append(
{
"type": "function_call_output",
"role": "tool",
"id": uuid.uuid4().hex,
"tool_call_id": fc["id"],
"output": result,
}
)
# 5) call LLM a second time and treat that reply as final
followup = (
self._call_llm(history, ws, tool_infos=[]).choices[0].message.to_dict()
)
followup["id"] = uuid.uuid4().hex
assistant_text = followup.get("content", "")
return ResponsesAgentResponse(
output=[
{
"id": uuid.uuid4().hex,
"type": "message",
"role": "assistant",
"content": [{"type": "output_text", "text": assistant_text}],
}
],
custom_outputs=request.custom_inputs,
)
# 6) if no tool_calls at all, return the assistant’s original reply
assistant_text = raw_choice.get("content", "")
return ResponsesAgentResponse(
output=[
{
"id": uuid.uuid4().hex,
"type": "message",
"role": "assistant",
"content": [{"type": "output_text", "text": assistant_text}],
}
],
custom_outputs=request.custom_inputs,
)
mlflow.models.set_model(SingleTurnMCPAgent())
if __name__ == "__main__":
req = ResponsesAgentRequest(
input=[{"role": "user", "content": "What's the 100th Fibonacci number?"}]
)
resp = SingleTurnMCPAgent().predict(req)
for item in resp.output:
print(item)
エージェントをデプロイする
管理対象 MCP サーバーに接続するエージェントをデプロイする準備ができたら、 「生成AIアプリケーション用のエージェントのデプロイ (モデルサービング)」を参照してください。
ログ記録時にエージェントが必要とするすべてのリソースを指定します。Databricksの認証」リソースを参照してください。
たとえば、エージェントが以下にリストされている MCP サーバー URL を使用している場合、 prod.customer_supportスキーマとprod.billingスキーマですべての検索インデックスを指定する必要があります。 prod.billingですべてのUnity Catalog関数を指定する必要があります。
https://<your-workspace-hostname>/api/2.0/mcp/vector-search/prod/customer_supporthttps://<your-workspace-hostname>/api/2.0/mcp/vector-search/prod/billinghttps://<your-workspace-hostname>/api/2.0/mcp/functions/prod/billing
エージェントが Databricks 上の MCP サーバーに接続してツールを検出および実行する場合は、これらの MCP サーバーに必要なリソースをエージェントとともにログに記録します。Databricks では、このプロセスを簡素化するためにdatabricks-mcp PyPI パッケージをインストールすることをお勧めします。
特に、管理対象 MCP サーバーを使用する場合は、 databricks_mcp.DatabricksMCPClient().get_databricks_resources(<server_url>)使用して、管理対象 MCP サーバーに必要なリソースを取得できます。エージェントがDatabricks アプリでホストされているカスタム MCP サーバーをクエリする場合は、モデルをログに記録するときにサーバーをリソースとして明示的に含めることで承認を構成できます。
たとえば、上記で定義したエージェントをデプロイするには、エージェント コード定義をmcp_agent.pyに保存したと仮定して、次のコードを実行します。
import os
from databricks.sdk import WorkspaceClient
from databricks import agents
import mlflow
from mlflow.models.resources import DatabricksFunction, DatabricksServingEndpoint, DatabricksVectorSearchIndex
from mcp_agent import LLM_ENDPOINT_NAME
from databricks_mcp import DatabricksMCPClient
# TODO: Update this to your Databricks CLI profile name
databricks_cli_profile = "YOUR_DATABRICKS_CLI_PROFILE"
assert (
databricks_cli_profile != "YOUR_DATABRICKS_CLI_PROFILE"
), "Set databricks_cli_profile to the Databricks CLI profile name you specified when configuring authentication to the workspace"
workspace_client = WorkspaceClient(profile=databricks_cli_profile)
# Configure MLflow and the Databricks SDK to use your Databricks CLI profile
current_user = workspace_client.current_user.me().user_name
mlflow.set_tracking_uri(f"databricks://{databricks_cli_profile}")
mlflow.set_registry_uri(f"databricks-uc://{databricks_cli_profile}")
mlflow.set_experiment(f"/Users/{current_user}/databricks_docs_example_mcp_agent")
os.environ["DATABRICKS_CONFIG_PROFILE"] = databricks_cli_profile
MANAGED_MCP_SERVER_URLS = [
f"{host}/api/2.0/mcp/functions/system/ai",
]
# Log the agent defined in mcp_agent.py
here = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
agent_script = os.path.join(here, "mcp_agent.py")
resources = [
DatabricksServingEndpoint(endpoint_name=LLM_ENDPOINT_NAME),
DatabricksFunction("system.ai.python_exec"),
# --- Uncomment and edit the following lines to include custom mcp servers hosted on Databricks Apps ---
# DatabricksApp(app_name="app-name")
]
for mcp_server_url in MANAGED_MCP_SERVER_URLS:
mcp_client = DatabricksMCPClient(server_url=mcp_server_url, workspace_client=workspace_client)
resources.extend(mcp_client.get_databricks_resources())
with mlflow.start_run():
logged_model_info = mlflow.pyfunc.log_model(
artifact_path="mcp_agent",
python_model=agent_script,
resources=resources,
)
# TODO Specify your UC model name here
UC_MODEL_NAME = "main.default.databricks_docs_mcp_agent"
registered_model = mlflow.register_model(logged_model_info.model_uri, UC_MODEL_NAME)
agents.deploy(
model_name=UC_MODEL_NAME,
model_version=registered_model.version,
)