AWS インバウンド PrivateLink の DNS を構成する
Databricks ワークスペースの受信 PrivateLink を使用する場合は、ユーザー要求をプライベート ネットワーク経由でルーティングするように DNS を構成します。このページでは、DNS 構成パターンと段階的なセットアップ手順について説明します。AWS PrivateLink の DNS は複数の方法で設定できますが、このページでは、ほとんどのデプロイメントで機能する推奨アプローチがデフォルトで設定されています。
VPC エンドポイントで DNS 名の有効化 オプションを有効にすると、バックエンドの PrivateLink エンドポイントは AWS DNS 解決を自動的に使用します。このページでは、受信 PrivateLink DNS 構成に焦点を当てています。
アーキテクチャの概要
次の図は、AWS PrivateLink の 2 つの DNS 解決パターンを示しています。選択するパターンは、エンドポイントの管理と分離に関する組織の要件によって異なります。
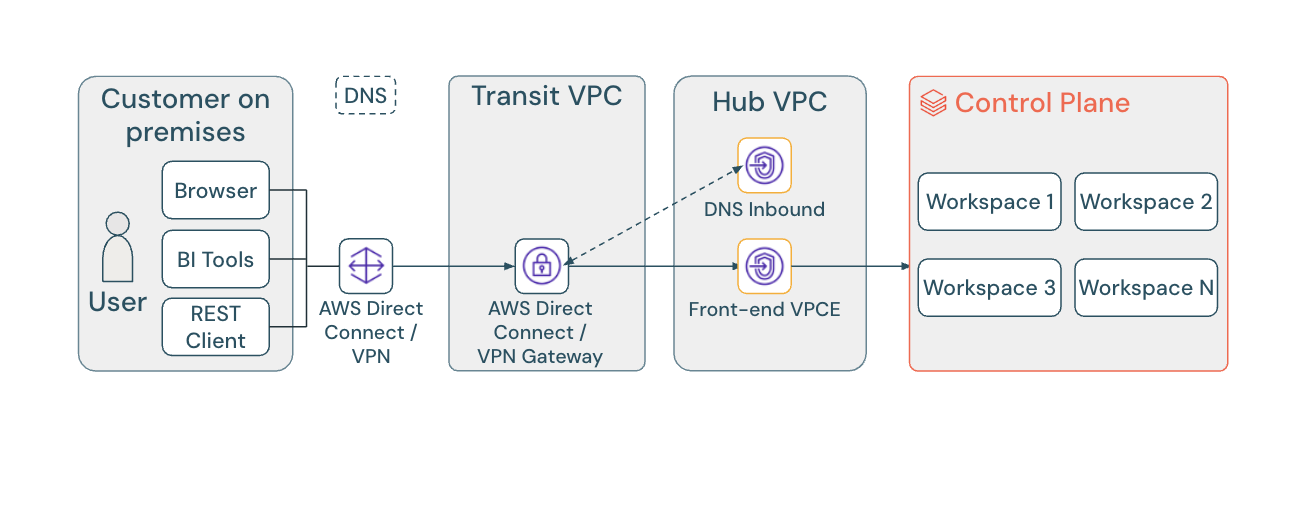
単一エンドポイント アプローチでは、リージョン内のすべてのワークスペースが 1 つの共有 VPC エンドポイントを介してルーティングされるため、DNS の構成と管理が簡素化されます。このページでは、すべての構成手順に対してこの推奨アプローチがデフォルトになっています。
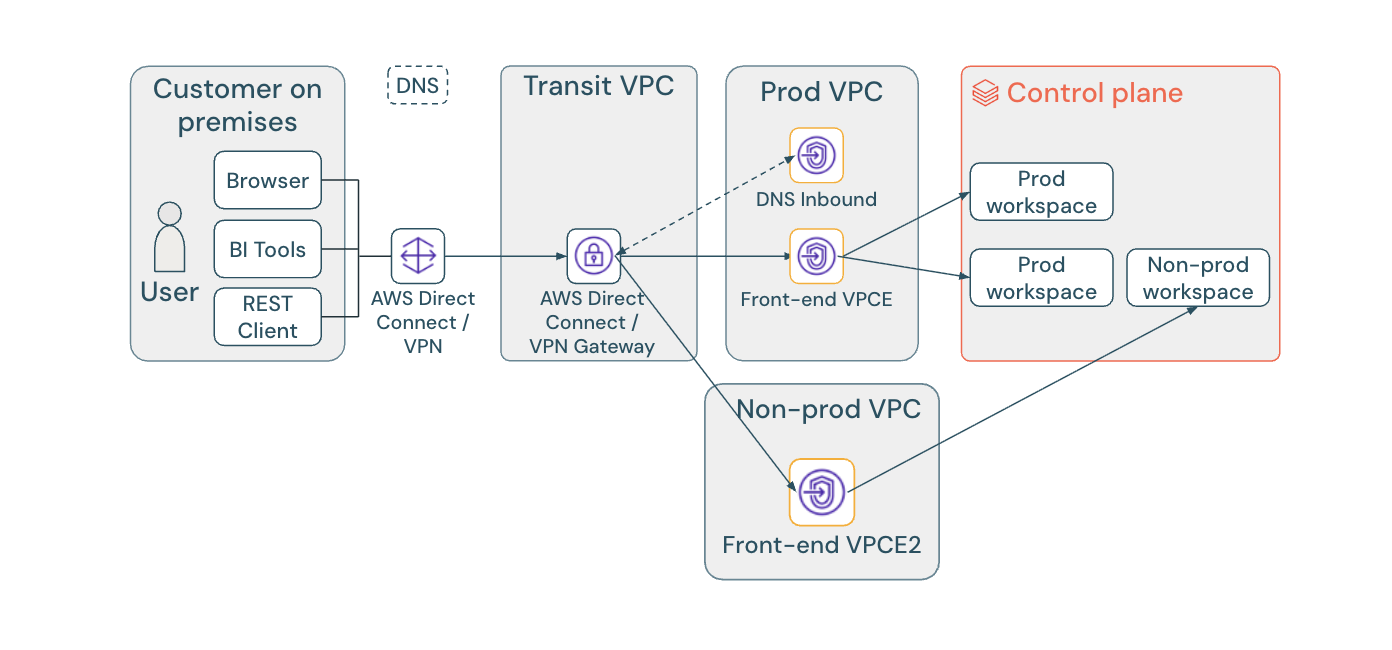
マルチエンドポイント アプローチでは、各ワークスペースに専用の VPC エンドポイントが提供され、複雑さが増す代わりにワークスペース レベルのネットワーク分離が可能になります。
PrivateLinkによるDNS解決
PrivateLink がない場合、ワークスペース URL は、パブリック AWS Elastic Load Balancer を指すsydney.cloud.databricks.comなどのリージョンホスト名を介してパブリック IP アドレスに解決されます。例えば:
$ nslookup myworkspace.cloud.databricks.com
myworkspace.cloud.databricks.com canonical name = sydney.cloud.databricks.com
sydney.cloud.databricks.com canonical name = public-ingress-xxxxx.elb.ap-southeast-2.amazonaws.com
Name: public-ingress-xxxxx.elb.ap-southeast-2.amazonaws.com
Address: 3.26.4.13
プライベート アクセス設定オブジェクトをワークスペースにアタッチすると、Databricks は DNS 解決チェーンを更新してprivatelinkサブドメインを含めます。
$ nslookup myworkspace.cloud.databricks.com
myworkspace.cloud.databricks.com canonical name = sydney.privatelink.cloud.databricks.com
Name: sydney.privatelink.cloud.databricks.com
Address: 10.176.10.182
ワークスペース URL はsydney.privatelink.cloud.databricks.comに解決され、VPC エンドポイントのプライベート IP アドレスを指すように構成されます。これにより、他の Databricks サービスに影響を与えずに、 privatelink.cloud.databricks.comドメインのみをオーバーライドできます。
プライベート アクセス設定オブジェクトをワークスペースにアタッチした後は、削除することはできません。別のプライベート アクセス設定オブジェクトにのみ置き換えることができます。この構成は永続的です。
DNS解決
必要な特定の DNS レコードは設定方法によって異なりますが、すべての設定でワークスペース URL が受信 VPC エンドポイントのプライベート IP アドレスに解決されます。
- Single endpoint approach (recommended)
- Multi-endpoint approach
ほとんどのデプロイメントでは、リージョンエンドポイントを VPC エンドポイントのプライベート IP に解決するように DNS を構成します。リージョン内のすべてのワークスペースは同じ VPC エンドポイントを共有します。
オンプレミスのDNS構成
企業の DNS で条件付き転送を構成して、Databricks ドメインクエリを AWS に転送します。
ドメイン | 転送先 |
|---|---|
クラウド.databricks.com | AWS DNSエンドポイント(Route 53インバウンドリゾルバー) |
*.aws.databricksapps.com | AWS DNSエンドポイント(Route 53インバウンドリゾルバー) |
プライベートホストゾーンの構成
privatelink.cloud.databricks.comドメインのプライベート ホストゾーンを作成します。
構成 | Value |
|---|---|
プライベートホストゾーン | プライベートリンククラウドデータブリックス |
レコード名 |
|
レコードタイプ | A(別名) |
記録的な価値 | VPCエンドポイントID |
region値は AWS リージョン名ではなく、Databricks リージョン名 (例: sydney 、 virginia 、 oregonです。ワークスペースの正しいリージョン名を見つけるには、「Databricks コントロール プレーンへの受信 IP」 の 「Web アプリケーションを含むコントロール プレーン サービス」 行を参照してください。
インバウンド PrivateLink を使用する同じリージョン内のすべてのワークスペースは、同じ VPC エンドポイントを共有し、同じリージョン エンドポイントに解決できます。これは、管理を簡素化するために推奨されるアプローチです。
個々のワークスペースに個別のVPCエンドポイントが必要な場合は、ALIAS レコードを使用してワークスペース固有のプライベート ホスト ゾーンを作成します。 このアプローチでは、複雑さが増す代わりに、ワークスペース間のネットワーク分離が実現されます。
オンプレミスのDNS構成
企業の DNS で条件付き転送を構成して、Databricks ドメインクエリを AWS に転送します。
ドメイン | 転送先 |
|---|---|
クラウド.databricks.com | AWS DNSエンドポイント(Route 53インバウンドリゾルバー) |
*.aws.databricksapps.com | AWS DNSエンドポイント(Route 53インバウンドリゾルバー) |
本番運用VPC DNS 構成
本番運用VPCにワークスペース固有のプライベート ホスト ゾーンを作成します。
構成 | Value |
|---|---|
プライベートホストゾーン |
|
レコードタイプ | A(別名) |
記録的な価値 | VPCエンドポイントID |
<workspace>ワークスペースのデプロイメント名 (例: myworkspace.cloud.databricks.com ) に置き換えます。
非本番運用VPC DNS 構成
非本番運用VPCにワークスペース固有のプライベート ホスト ゾーンを作成します。
構成 | Value |
|---|---|
プライベートホストゾーン |
|
レコードタイプ | A(別名) |
記録的な価値 | VPCエンドポイントID |
<workspace2>ワークスペースのデプロイメント名 (例: myworkspace-dev.cloud.databricks.com ) に置き換えます。
ワークスペースごとのエンドポイントを使用するには、ワークスペースごとに DNS エントリを作成する必要があり、管理の複雑さが増します。特定のセキュリティまたはネットワーク要件のために、ワークスペースごとに分離された VPC エンドポイントが必要な場合にのみ、このアプローチを使用します。
別の AWS アカウント内の VPC の場合:
- エイリアス レコードを作成するときは、VPC エンドポイントの完全な DNS を入力します。たとえば、
vpce-xxx-xxx.vpce-svc-xxx.us-east-1.vpce.amazonaws.com。エンドポイントは、利用可能なエンドポイントのリストに表示されません。 - 作成 をクリックします。
AWS は、クロスアカウント DNS に対してこれらの名前をグローバルに自動的に解決します。クロスアカウント DNS には AWS RAM は必要ありません。
設定オプション
- Conditional forwarding to Route 53 for single endpoint (recommended)
- Conditional forwarding to Route 53 for multi-endpoint
- Manual DNS zone and records
Databricks ドメインのクエリを Amazon Route 53 に転送するように企業の DNS を設定します。AWS は、手動でのレコード管理なしで、ワークスペース URL をプライベート IP に自動的に解決します。このアプローチでは、リージョン内のすべてのワークスペースに対して単一の VPC エンドポイントを使用します。
条件付き転送の利点
- 自動解決 : VPC エンドポイントで DNS 名の有効化 オプションが有効になっている場合、Route 53 はワークスペース URL をプライベート IP に自動的に解決します。
- 手動更新なし : VPC エンドポイント IP が変更されると、Route 53 は DNS レコードを自動的に更新します。
- 管理を簡素化 : 単一の構成でリージョン内のすべてのワークスペースを処理します。
前提条件
始める前に、次のことを確認してください。
- DNS 名を有効 にするが有効になっているインバウンド PrivateLink VPC エンドポイント
- Direct Connect または VPN を使用した企業ネットワークと AWS 間のネットワーク接続
- Route 53 リソースを作成し、企業の DNS を変更するための権限
ステップ 1: プライベートホストゾーンを作成する
Databricks ワークスペース DNS レコード用に Route 53 にプライベート ホストゾーンを作成します。
- AWS マネジメントコンソールのRoute 53 ホストゾーンページに移動します。
- 「ホストゾーンの作成」を クリックします。
- ドメイン名 には
privatelink.cloud.databricks.comと入力します。 - タイプ には、 プライベートホストゾーン を選択します。
- 関連付ける VPC セクションで、インバウンド VPC エンドポイントが配置されている VPC を選択します。これは通常、トランジット VPC です。
- 「ホストゾーンの作成」を クリックします。
ステップ 2: DNS A レコードを作成する
リージョンエンドポイントを VPC エンドポイントのプライベート IP アドレスにマッピングする A レコードを作成します。
-
Route 53 コンソールで、作成した
privatelink.cloud.databricks.comホストゾーンを選択します。 -
[レコードの作成] をクリックします。
-
レコード名 に、Databricks リージョン名を入力します (例:
sydney、virginia、oregon)。 -
レコード タイプ には、 A - トラフィックを IPv4 アドレスにルーティングするを 選択します。
-
[値] には、受信 VPC エンドポイントのプライベート IP アドレスを入力します。
プライベート IP を見つけるには:
- VPC エンドポイントページに移動します。
- 受信 VPC エンドポイントを選択します。
- [サブネット] タブで、 IPv4 アドレスをメモします。
-
[レコードの作成] をクリックします。
ステップ 3: Route 53 インバウンドリゾルバーエンドポイントを作成する
企業の DNS がクエリを Route 53 に転送できるように、インバウンド リゾルバ エンドポイントを作成します。
-
Route 53 Resolverページに移動します。
-
左側のナビゲーションで、 [受信エンドポイント] をクリックします。
-
[受信エンドポイントの作成]を クリックします。
-
エンドポイントの名前(
databricks-privatelink-resolverなど)を指定します。 -
VPC を選択します。
-
[セキュリティ グループ] では、オンプレミス ネットワークからのポート 53 での受信 TCP および UDP トラフィックを許可するセキュリティ グループを選択または作成します。
-
IP アドレス セクションでは、次の操作を行います。
- 高可用性を実現するには、異なるアベイラビリティーゾーンにある少なくとも 2 つのサブネットを選択します。
- 各サブネットに対して、AWS に IP アドレスを自動的に割り当てるか、サブネット範囲内の特定の IP アドレスを選択します。
-
[受信エンドポイントの作成]を クリックします。
-
次のステップで使用するために、受信リゾルバー エンドポイントの IP アドレスをメモします。
ステップ 4: 企業 DNS で条件付き転送を構成する
企業の DNS サーバーを構成して、Databricks ドメインのクエリを Route 53 受信リゾルバー エンドポイントに転送します。
正確なステップは、BIND、 Windows DNS、Infoblox などの DNS ソフトウェアによって異なります。 特定の構成ステップについては、DNS サーバーのドキュメントを参照してください。
次のドメインに対して条件付き転送を構成します。
*.cloud.databricks.com- ワークスペース URL 解決に必要*.aws.databricksapps.com- Databricksアプリを使用する場合は必須
これらのドメインを Route 53 インバウンド リゾルバ エンドポイントの IP アドレスに転送します。
検証
構成が完了したら、企業ネットワークから DNS 解決をテストします。
$ nslookup myworkspace.cloud.databricks.com
myworkspace.cloud.databricks.com canonical name = sydney.privatelink.cloud.databricks.com
Name: sydney.privatelink.cloud.databricks.com
Address: 10.176.10.182
ワークスペース URL は、VPC エンドポイントのプライベート IP アドレスに解決される必要があります。パブリック IP アドレスが表示される場合は、条件付き転送ルールと Route 53 の構成を確認してください。
Databricks ドメインのクエリを AWS Route 53 に転送するように企業 DNS を設定します。このアプローチでは、個々のワークスペースに個別のVPCエンドポイントを使用し、ワークスペース レベルのネットワーク分離を実現します。
条件付き転送の利点
- 自動解決 : VPC エンドポイントで DNS 名の有効化 オプションが有効になっている場合、Route 53 はワークスペース URL をプライベート IP に自動的に解決します。
- 手動更新なし : VPC エンドポイント IP が変更されると、Route 53 は DNS レコードを自動的に更新します。
- ワークスペースの分離 : 各ワークスペースは、ネットワーク分離のために専用のVPCエンドポイントを使用します。
前提条件
始める前に、次のことを確認してください。
- 各ワークスペースで DNS 名の有効 化が有効になっているインバウンド PrivateLink VPC エンドポイント
- Direct Connect または VPN を使用した企業ネットワークと AWS 間のネットワーク接続
- Route 53 リソースを作成し、企業の DNS を変更するための権限
ステップ 1: プライベートホストゾーンを作成する
各ワークスペースに対して、Route 53 にワークスペース固有のプライベートホストゾーンを作成します。
- AWS マネジメントコンソールのRoute 53 ホストゾーンページに移動します。
- 「ホストゾーンの作成」を クリックします。
- ドメイン名 に、ワークスペースのデプロイメント名を入力します (例:
myworkspace.cloud.databricks.comまたはmyworkspace-dev.cloud.databricks.com)。 - タイプ には、 プライベートホストゾーン を選択します。
- 関連付ける VPC セクションで、インバウンド VPC エンドポイントが配置されている VPC を選択します。
- 「ホストゾーンの作成」を クリックします。
- 個別の VPC エンドポイントを必要とするワークスペースごとにこのプロセスを繰り返します。
ステップ 2: DNS A レコードを作成する
ワークスペース URL を VPC エンドポイントにマッピングする A エイリアス レコードを作成します。
-
Route 53 コンソールで、作成したワークスペース固有のホストゾーン (例:
myworkspace.cloud.databricks.com) を選択します。 -
[レコードの作成] をクリックします。
-
レコード名 は空白のままにします (レコードはゾーンの頂点に適用されます)。
-
レコード タイプ には、 A - トラフィックを IPv4 アドレスにルーティングするを 選択します。
-
エイリアス トグルを有効にして、 VPC エンドポイントへのエイリアス を選択します。次に、リストからワークスペースの VPC エンドポイント ID を選択します。
別の AWS アカウントの VPC エンドポイントの場合:
- VPC エンドポイントの完全な DNS 名を入力します (例:
vpce-xxx-xxx.vpce-svc-xxx.us-east-1.vpce.amazonaws.com)。エンドポイントは、利用可能なエンドポイントのリストに表示されません。 - AWS は、クロスアカウント DNS に対してこれらの名前をグローバルに自動的に解決します。クロスアカウント DNS にはAWSリソース Access Manager は必要ありません。
- VPC エンドポイントの完全な DNS 名を入力します (例:
-
[レコードの作成] をクリックします。
-
各ワークスペースに対してこのプロセスを繰り返します。
ワークスペースごとのエンドポイントを使用するには、ワークスペースごとに DNS エントリを作成する必要があり、管理の複雑さが増します。特定のセキュリティまたはネットワーク要件のために、ワークスペースごとに分離された VPC エンドポイントが必要な場合にのみ、このアプローチを使用します。
ステップ 3: Route 53 インバウンドリゾルバーエンドポイントを作成する
企業の DNS がクエリを Route 53 に転送できるように、インバウンド リゾルバ エンドポイントを作成します。
-
Route 53 Resolverページに移動します。
-
左側のナビゲーションで、 [受信エンドポイント] をクリックします。
-
[受信エンドポイントの作成]を クリックします。
-
エンドポイントの名前(
databricks-privatelink-resolverなど)を指定します。 -
VPC を選択します。
-
[セキュリティ グループ] では、オンプレミス ネットワークからのポート 53 での受信 TCP および UDP トラフィックを許可するセキュリティ グループを選択または作成します。
-
IP アドレス セクションでは、次の操作を行います。
- 高可用性を実現するには、異なるアベイラビリティーゾーンにある少なくとも 2 つのサブネットを選択します。
- 各サブネットに対して、AWS に IP アドレスを自動的に割り当てるか、サブネット範囲内の特定の IP アドレスを選択します。
-
[受信エンドポイントの作成]を クリックします。
-
次のステップで使用するために、受信リゾルバー エンドポイントの IP アドレスをメモします。
ステップ 4: 企業 DNS で条件付き転送を構成する
企業の DNS サーバーを構成して、Databricks ドメインのクエリを Route 53 受信リゾルバー エンドポイントに転送します。
正確なステップは、BIND、 Windows DNS、Infoblox などの DNS ソフトウェアによって異なります。 特定の構成ステップについては、DNS サーバーのドキュメントを参照してください。
次のドメインに対して条件付き転送を構成します。
*.cloud.databricks.com- ワークスペース URL 解決に必要*.aws.databricksapps.com- Databricksアプリを使用する場合は必須
これらのドメインを Route 53 インバウンド リゾルバ エンドポイントの IP アドレスに転送します。
検証
構成が完了したら、企業ネットワークから DNS 解決をテストします。
$ nslookup myworkspace.cloud.databricks.com
myworkspace.cloud.databricks.com canonical name = sydney.privatelink.cloud.databricks.com
Name: sydney.privatelink.cloud.databricks.com
Address: 10.176.10.182
ワークスペース URL は、VPC エンドポイントのプライベート IP アドレスに解決される必要があります。パブリック IP アドレスが表示される場合は、条件付き転送ルールと Route 53 の構成を確認してください。
ご使用の環境で Route 53 への条件付き転送が利用できない場合は、企業の DNS サーバーに DNS ゾーンとレコードを手動で作成できます。このアプローチでは、VPC エンドポイントの IP アドレスが変更された場合に手動で更新する必要があります。
手動DNSゾーンの利点
次の場合には手動 DNS 構成を使用します。
- AWS Route 53への条件付き転送を設定できない
- 企業のDNSポリシーでは、すべてのDNSレコードを社内で管理する必要がある
- DNSレコード管理を完全に制御する必要がある
手動 DNS 構成では、VPC エンドポイントの IP アドレスが変更されるたびに A レコードを更新します。レコードが古くなると、接続の問題が発生する可能性があります。
ステップ 1: DNS ゾーンを作成する
企業の DNS サーバーに、 privatelink.cloud.databricks.comのゾーンを作成します。
ステップ 2: A レコードを追加する
リージョンエンドポイントを VPC エンドポイントのプライベート IP にマッピングする A レコードを作成します。
レコード名 | レコードタイプ | Value |
|---|---|---|
| A | インバウンド VPC エンドポイントのプライベート IP |
たとえば、ワークスペースがシドニーリージョンにあり、VPC エンドポイントの IP アドレスが10.176.10.182である場合は、 10.176.10.182を指すsydney.privatelink.cloud.databricks.comの A レコードを作成します。
検証
企業ネットワークから DNS 解決をテストします。
$ dig +short myworkspace.cloud.databricks.com
sydney.privatelink.cloud.databricks.com
10.176.10.182
ワークスペース URL は、VPC エンドポイントのプライベート IP アドレスに解決される必要があります。
特別な展開シナリオ
- Mixed deployments
- Hybrid access (private and public endpoints)
- Databricks Apps domains
同じアカウント内で、一部のワークスペースではインバウンド PrivateLink を使用し、他のワークスペースではパブリック エンドポイントを使用できます。DNS 解決により、このシナリオは自動的に処理されます。
プライベート アクセス設定オブジェクトのないワークスペースは、 <region>.cloud.databricks.comを使用してパブリック IP アドレスに解決されます。プライベート アクセス設定オブジェクトを持つワークスペースは<region>.privatelink.cloud.databricks.comに解決され、プライベート IP を使用します。
混合展開では追加の DNS 構成は必要ありません。
PrivateLink を使用するプライベート エンドポイントとインターネットを使用するパブリック エンドポイントの両方からアクセスできるようにワークスペースを構成できます。
ハイブリッド アクセスを有効にするには:
- プライベート アクセス設定オブジェクトを作成するときは、 パブリック アクセスの有効化を True に設定します。
- ワークスペースは、PrivateLink とパブリック インターネットの両方からアクセスできるようになりました。
- プライベート DNS が構成されている企業ネットワーク上のユーザーは、プライベート エンドポイントを自動的に使用します。
- 企業ネットワーク外のユーザーはパブリック エンドポイントを使用します。
ワークスペースにアクセスできるパブリック IP アドレスを制限するには、 IP アクセス リストを構成します。これにより、信頼できるサードパーティの SaaS アプリケーションなどの特定のソース IP アドレスを許可リストに登録できるようになります。
Databricks アプリはドメイン*.aws.databricksapps.comを使用します。これらのドメインは、 dbc-<workspace-deployment-id>.cloud.databricks.comに解決される CNAME レコードを使用し、これは地域のエンドポイントに解決されます。
例えば:
$ nslookup natural-language-to-qdrant-1016658646341465.aws.databricksapps.com
natural-language-to-qdrant-1016658646341465.aws.databricksapps.com
canonical name = dbc-35bfa1f1-1292.cloud.databricks.com
dbc-35bfa1f1-1292.cloud.databricks.com
canonical name = oregon.cloud.databricks.com
*.cloud.databricks.comに条件付き転送を使用すると、アプリのドメインは自動的に正しく解決されます。手動 DNS 構成を使用する場合は、 *.aws.databricksapps.com転送するか、対応するレコードを作成する必要があります。
Databricksアプリのネットワークの詳細については、 「Ingress コントロール」を参照してください。
検証
DNS を構成した後、ワークスペース URL がプライベート IP アドレスに正しく解決されることを確認します。
- Use nslookup
- Use dig
- Test workspace access
企業ネットワーク上のマシンから、ワークスペースの DNS 解決をテストします。
$ nslookup myworkspace.cloud.databricks.com
期待される出力:
myworkspace.cloud.databricks.com canonical name = sydney.privatelink.cloud.databricks.com
Name: sydney.privatelink.cloud.databricks.com
Address: 10.176.10.182
ワークスペース URL は、 privatelinkサブドメインを介してプライベート IP アドレス (通常は10.x.x.x 、 172.16.x.x 、または192.168.x.x範囲) に解決される必要があります。
より詳細な DNS 情報を得るには、 dig使用することもできます。
$ dig +short myworkspace.cloud.databricks.com
sydney.privatelink.cloud.databricks.com
10.176.10.182
DNS 解決を確認した後、ワークスペースにアクセスできることをテストします。
- 企業ネットワーク上のマシンまたは VPN 経由で接続されたマシンから、Web ブラウザを開きます。
- ワークスペースの URL に移動します。
- ログインしてワークスペースにアクセスできることを確認します。
ワークスペースにアクセスできない場合:
- VPC エンドポイントで DNS 名の有効化 オプションが有効になっていることを確認します。
- プライベートホストゾーンが正しい VPC に関連付けられていることを確認します。
- 条件付き転送ルールが企業の DNS で正しく設定されていることを確認します。
- Direct Connect または VPN を使用して、企業ネットワークと AWS VPC の間にネットワーク接続が存在することを確認します。
- VPC エンドポイントのセキュリティ グループ ルールで、ポート 443 での受信 TCP トラフィックが許可されていることを確認します。
よくある問題
DNS 解決でパブリック IP が返される : 条件付き転送ルールが正しく機能していないか、クエリが Route 53 に到達していません。DNS サーバー構成と Route 53 インバウンド リゾルバ エンドポイントを確認します。
ワークスペース URL が解決されません : プライベート ホストゾーンに正しい A レコードがないか、ホストゾーンが適切な VPC に関連付けられていない可能性があります。Route 53 の設定を確認します。
DNS 解決後にワークスペースにアクセスできません : ネットワーク接続とセキュリティ グループ ルールを確認してください。企業ネットワークがポート 443 で VPC エンドポイントのプライベート IP にアクセスできることを確認します。
次は何?
- 受信 (フロントエンド) PrivateLink を有効にする : PrivateLink をまだ設定していない場合は、 「受信 PrivateLink の構成」を参照してください。
- クラシック コンピュート プレーン (バックエンド) PrivateLink を有効にする : コンピュート プレーンからコントロール プレーンへの PrivateLink を構成することで、プライベート接続のセットアップを完了します。 「Databricks への従来のプライベート接続を構成する」を参照してください。
- IP アクセス リスト : ワークスペースにアクセスできるパブリック IP アドレスを制御することで、セキュリティをさらに強化します。「ワークスペースの IP アクセス リストを構成する」を参照してください。