memória do agente deAI
A memória permite que agentes AI se lembrem de informações do início da conversa ou de conversas anteriores. Isso permite que os agentes forneçam respostas contextuais e criem experiências personalizadas ao longo do tempo. Use Databricks Lakebase, um banco de dados Postgres OLTP totalmente gerenciado, para gerenciar o estado e a história da conversa.
Requisitos
- Habilite Databricks Apps em seu workspace. Consulte Configurar seu workspace e ambiente de desenvolvimento Databricks Apps.
- Para obter informações sobre uma instância do Lakebase, consulte Criar e gerenciar uma instância de banco de dados.
Memória de curto prazo versus memória de longo prazo
A memória de curto prazo captura o contexto de uma única sessão de conversa, enquanto a memória de longo prazo extrai e armazena informações key ao longo de várias conversas. Você pode construir seu agente com um ou ambos os tipos de memória.
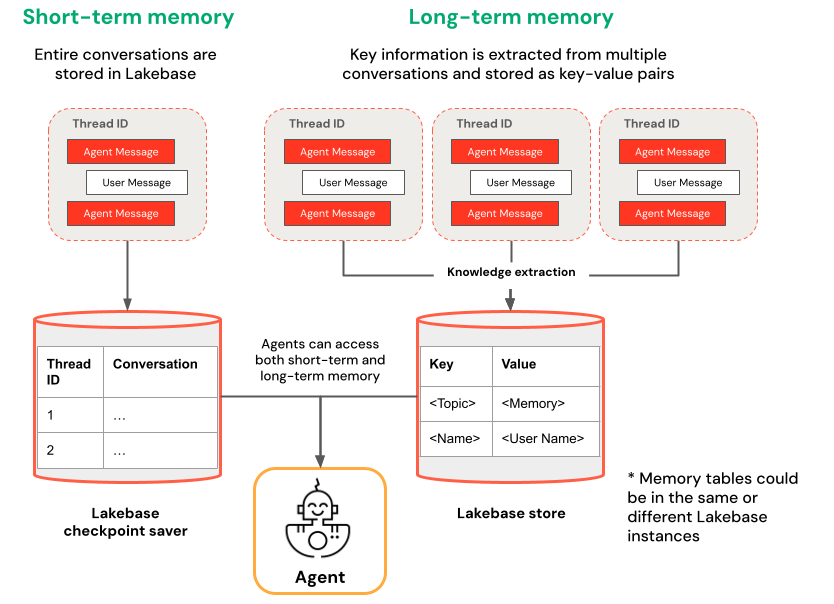
memória de curto prazo | memória de longo prazo |
|---|---|
Capture o contexto em uma única sessão de conversa usando IDs de tópicos e pontos de verificação. Mantenha o contexto para perguntas de acompanhamento durante a sessão. | Extrair e armazenar automaticamente key em várias sessões. Personalize as interações com base em preferências anteriores. Construa uma base de conhecimento sobre os usuários que melhore as respostas ao longo do tempo. |
Comece agora
Para criar um agente com memória no Databricks Apps, clone um aplicativo padrão pré-construído e siga o fluxo de trabalho de desenvolvimento descrito em Criar um agente AI e implantá-lo no Apps. O padrão a seguir demonstra como adicionar memória de curto e longo prazo a agentes usando frameworks populares.
LangGraph
Utilize o seguinte padrão baseado em LangGraph para adicionar memória ao seu agente. Esses padrões utilizam o checkpointing integrado do LangGraph com o Lakebase para gerenciamento de estado durável.
-
Memória de curto prazo : Clone o padrão agent-langgraph-short-term-memory para construir um agente LangGraph que mantenha o contexto da conversa dentro de uma sessão. O padrão utiliza IDs de threads e checkpoints do LangGraph, com suporte do Lakebase, para persistir o estado da conversa.
Bashgit clone https://github.com/databricks/app-templates.git
cd app-templates/agent-langgraph-short-term-memory -
Memória de longo prazo : Clone o padrão agent-langgraph-long-term-memory para construir um agente LangGraph que memorize informações key em várias conversas. O padrão extrai e armazena automaticamente as credenciais do usuário no Lakebase, permitindo interações personalizadas ao longo do tempo.
Bashgit clone https://github.com/databricks/app-templates.git
cd app-templates/agent-langgraph-long-term-memory
SDK de Agentes OpenAI
Utilize o seguinte padrão baseado SDKde Agentes OpenAI para adicionar memória ao seu agente. Este padrão utiliza as sessões SDK de Agentes OpenAI com o Lakebase para gerenciamento de estado persistente.
-
Memória de curto prazo : Clone o padrão agent-openai-agents-sdk-short-term-memory para criar um agente usando o SDK de Agentes OpenAI com gerenciamento automático do histórico de conversas. O padrão persiste os dados da sessão no Lakebase, permitindo conversas com estado e múltiplas interações sem a necessidade de gerenciamento manual de memória.
Bashgit clone https://github.com/databricks/app-templates.git
cd app-templates/agent-openai-agents-sdk-short-term-memory
implantar e consultar seu agente
Após configurar seu agente com memória, siga os passos descritos em Criar um agente AI e implantá-lo no Databricks Apps para executar seu agente localmente, avaliá-lo e implantá-lo no Databricks Apps.