Configure Databricks Serverless Private Git
Databricks Serverless Private Git is in Public Preview. Compute and networking costs apply when serverless compute resources connect to external resources. See Understand Databricks serverless networking costs for billing details.
Databricks Serverless Private Git lets you connect a Databricks workspace to a private Git server using serverless compute and PrivateLink. A Git server is private if internet users can't access it.
The following diagram illustrates the overall system architecture:

Why use Serverless Private Git?
Compared to Git server proxy, Serverless Private Git offers the following advantages:
- Serverless Private Git acquires serverless compute only when it receives a Git request, and it can be inactive when not in use. In contrast, the Git proxy requires the proxy cluster to be active when the user submits a Git request.
- Serverless Private Git uses PrivateLink to securely connect to the private Git instance.
Set up Serverless Private Git
- Follow the steps to set up a VPC endpoint service for your private Git server. This VPC endpoint allows you to create an AWS PrivateLink connection from Serverless to backends in your network behind a Network Load Balancer (NLB).
- An administrator must create an AWS interface VPC endpoint in the Databricks NCC for each Git server.
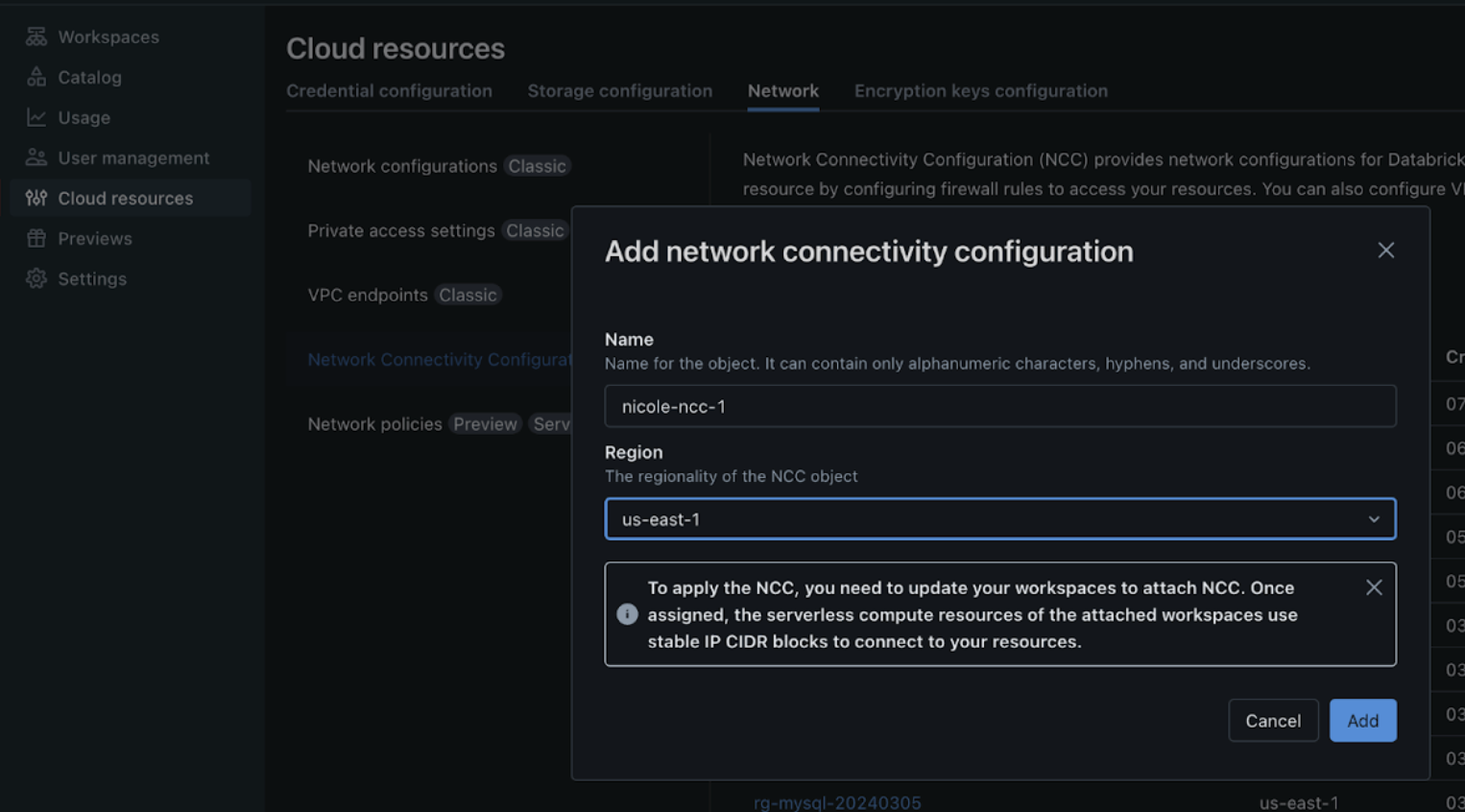
- Create a network connectivity configuration (NCC) to configure egress to a network load balancer.
- You can configure only one NCC per workspace for private Git. If the workspace connects to multiple private Git servers, they must all use the same NCC.
- For NCC limitations, such as regional limits and workspace attachment limits, see Configure a firewall for serverless compute access.
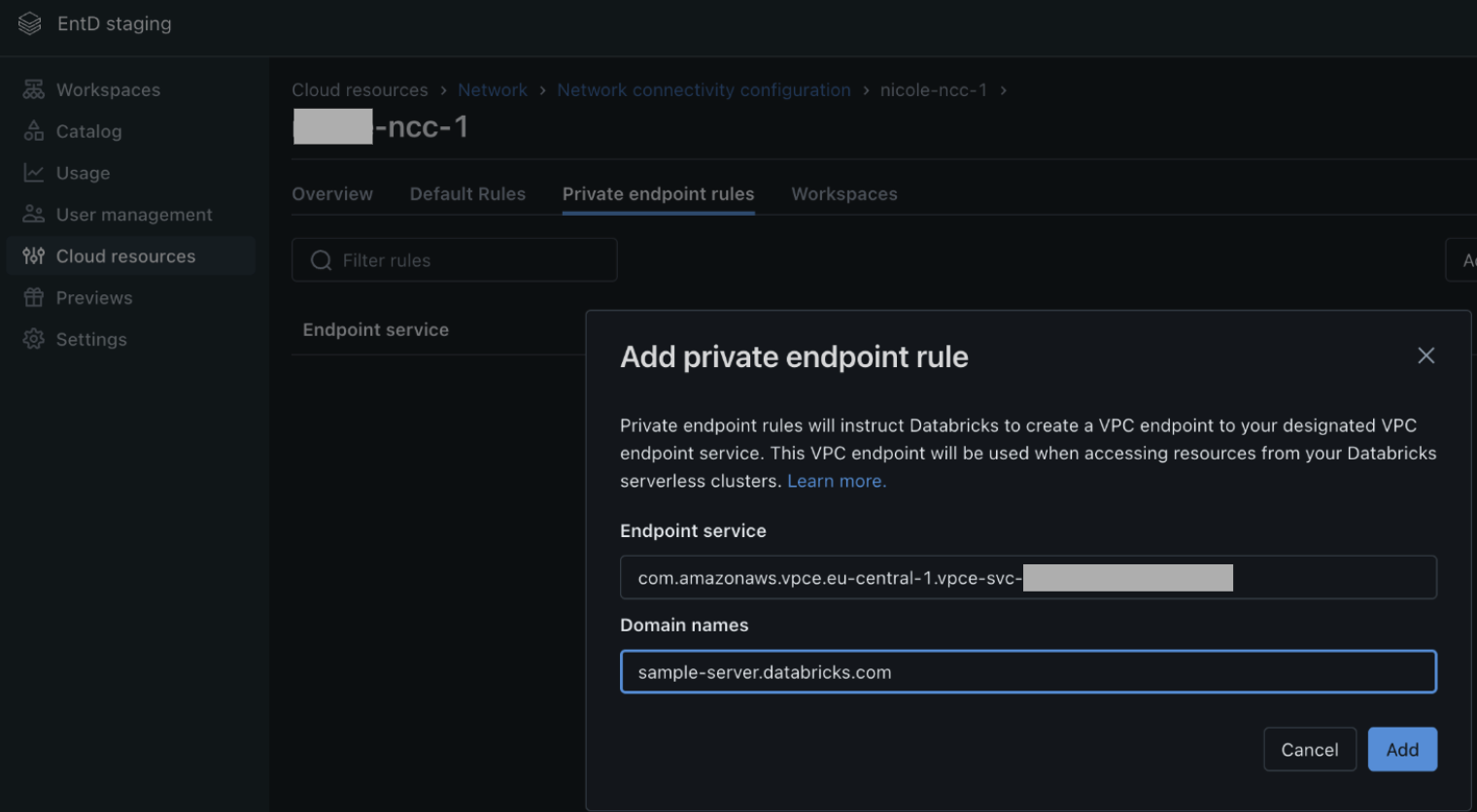
- Add a private endpoint rule.
- Wait at least ten minutes after setting up the NCC private endpoint rules, then enable the Serverless Private Git preview in your workspace settings.
- Perform a Git operation in the workspace. A UI indicator confirms that Serverless Private Git is active. The indicator might take a few seconds to appear while serverless compute starts.
After you configure it, Serverless Private Git takes precedence over other forms of private Git connectivity you already provisioned, such as classic Git proxy and Enterprise private Git. If you have a Git proxy cluster running, pause it after setting up Serverless Private Git.
Additional configurations
Customize Git operations using a configuration file.
- Create a configuration file at
/Workspace/.git_settings/config.jsonfollowing the specification below. - Grant all Git users View permissions to the configuration file and any CA certificate files it references.
- Validate connectivity to the Git remote by performing a Git operation, such as cloning a Git folder.
- The system can take up to one minute to apply configuration file changes.
Top-level config file structure
{
"default": { ... }, // Optional global settings
"remotes": [ ... ] // Optional list of per-remote settings
}
default section (optional)
Global defaults apply to all Git operations unless a specific remote overrides them.
Field | Type | Required | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| boolean | No | true | Whether to verify SSL certificates. |
| string | No | "" (empty) | Workspace path to a custom CA certificate. |
| string | No | "" (empty) | HTTP proxy to route Git traffic through. |
| integer | No | Unspecified | Custom HTTP port of the Git server. |
remotes section (optional)
A list of objects defining settings for individual remote Git servers. These settings override the default block on a per-remote basis.
Field | Type | Required | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
urlPrefix | string | Yes | — | Prefix to match Git remote URLs. |
sslVerify | boolean | No | true | Whether to verify SSL certificates. |
caCertPath | string | No | "" (empty) | Workspace path to a custom CA certificate path for this remote. |
httpProxy | string | No | "" (empty) | HTTP proxy to route Git traffic through. |
customHttpPort | integer | No | Unspecified | Custom HTTP port of the Git server. |
Example configuration with no remote-specific configuration
{
"default": {
"sslVerify": false
}
}
Full configuration example
{
"default": {
"sslVerify": true,
"caCertPath": "/Workspace/my_ca_cert.pem",
"httpProxy": "https://git-proxy-server.company.com",
"customHttpPort": "8080"
},
"remotes": [
{
"urlPrefix": "https://my-private-git.company.com/",
"caCertPath": "/Workspace/my_ca_cert_2.pem"
},
{
"urlPrefix": "https://another-git-server.com/project.git",
"sslVerify": false
}
]
}
Notes
- The
defaultsection must be at least partially present. - The
remotessection is optional. If included, each entry must include aurlPrefixfield. - Unspecified fields use their default values.
- Unknown fields are ignored.
Other security recommendations
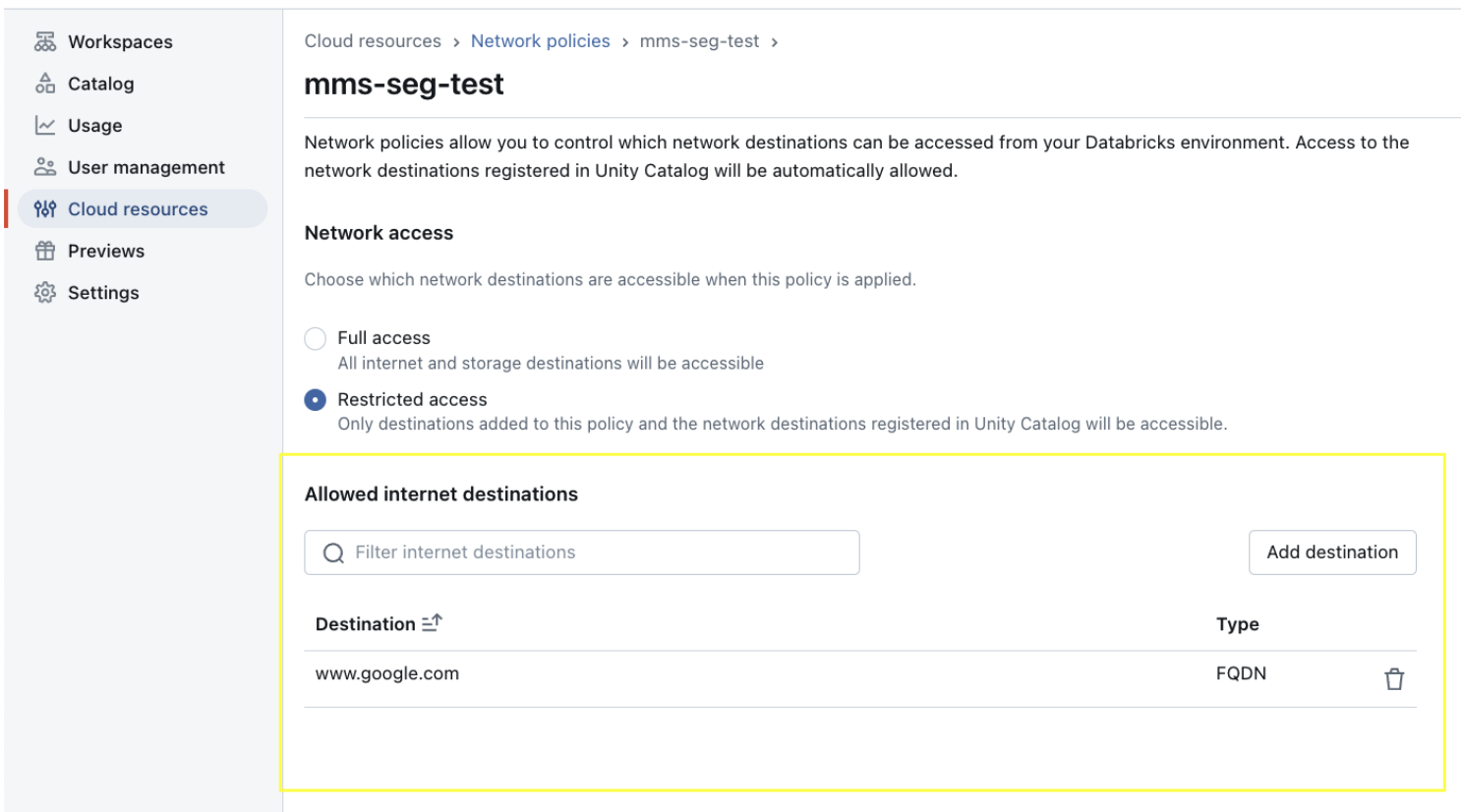
If the secure egress gateway is enabled, verify that the network policy in the account console applied to the specific workspace includes the Git Server's fully qualified domain name (FQDN) in the allowed internet destination.
Limitations
- Serverless proxy logs aren't available.
- Serverless Private Git is available only in serverless regions. For a list of supported regions, see Databricks clouds and regions.
- You can't create a VPC endpoint service to serve workspaces in multiple regions. Currently, the AWS NCC is a regional object and doesn’t support multi-region VPC endpoints. To connect another workspace from a different region to the Git server, set up another NLB and VPC endpoint service in the new region.