Navigate the Databricks notebook and file editor
This article describes the functions available to help you navigate the Databricks notebook and file editor, including keyboard shortcuts, code suggestions and autocomplete, variable inspection, and code folding. When you use the notebook or the file editor, Databricks Assistant is available to help you generate, explain, and debug code. See Get coding help from Databricks Assistant for details.
You can choose from a selection of editor themes. Select View > Editor theme and make a selection from the menu.
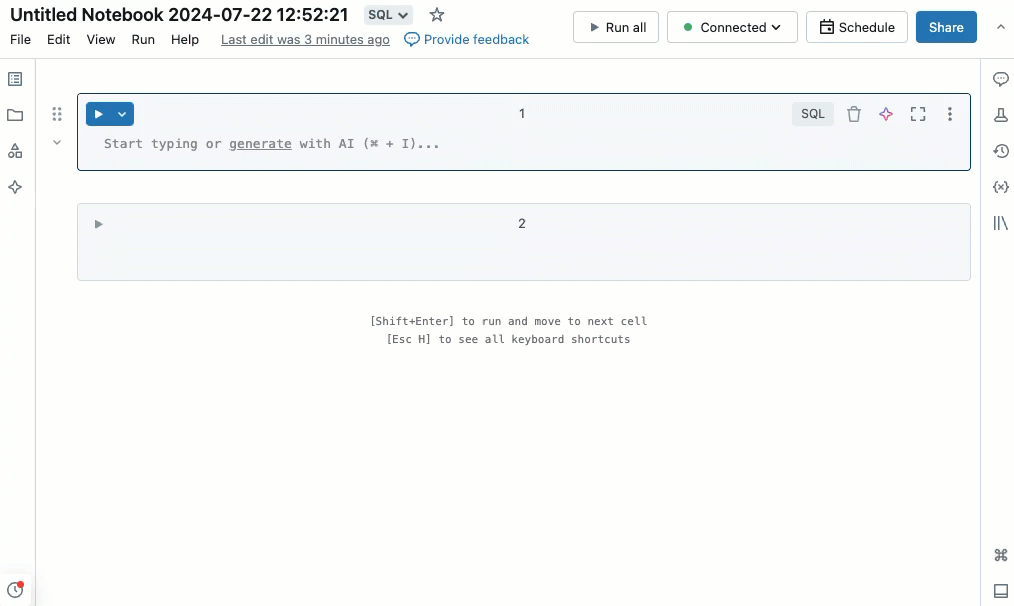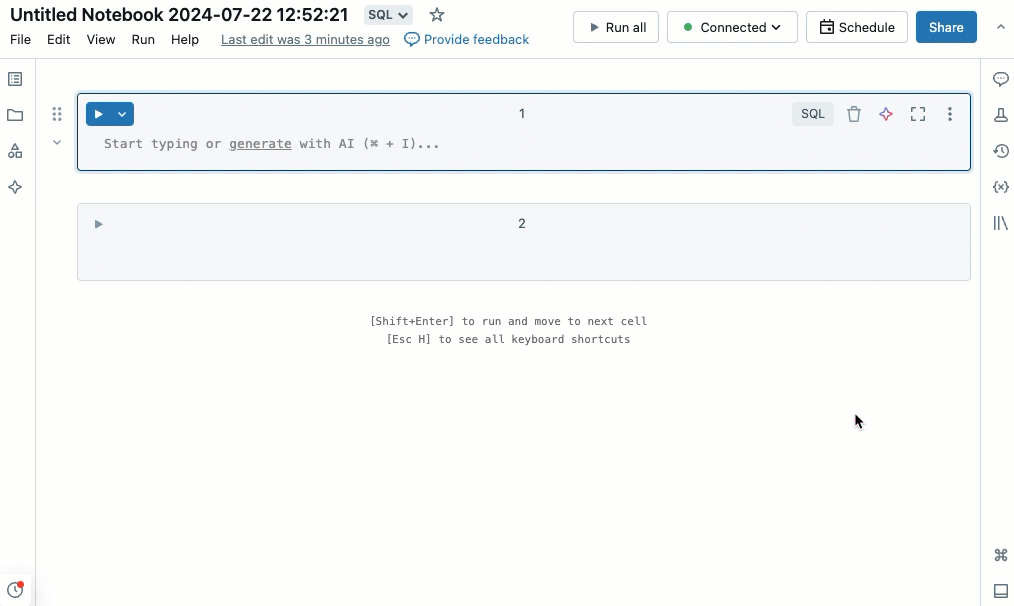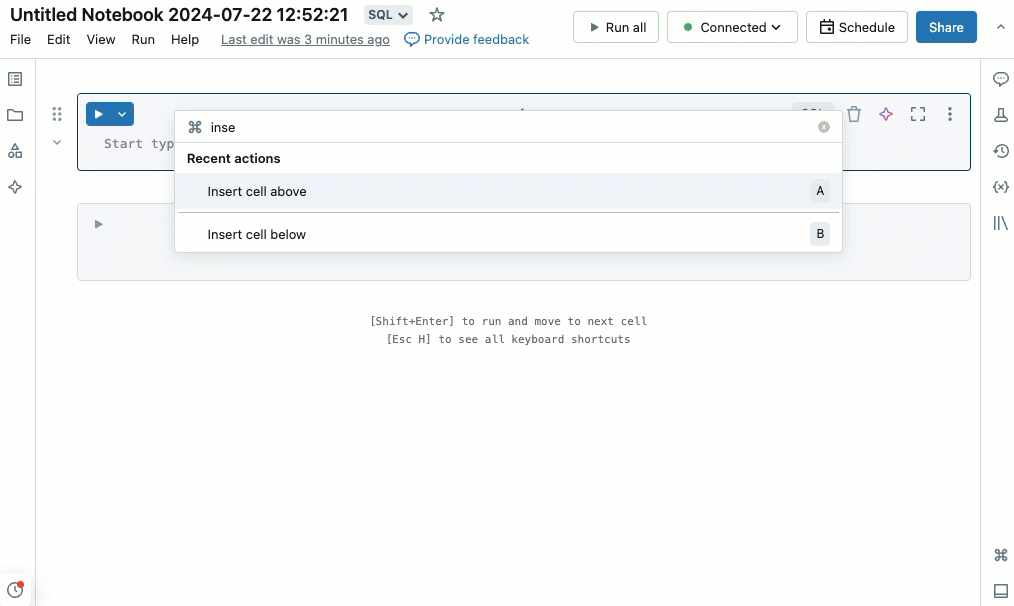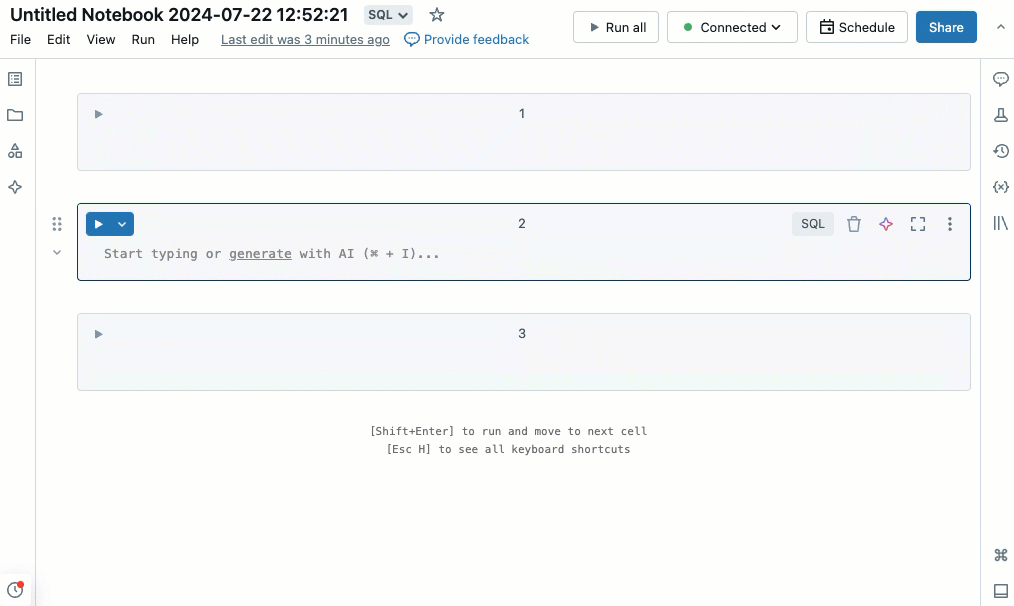
Command palette
You can quickly perform actions in the notebook using the command palette. To open a panel of notebook actions, click in the lower-right corner of the workspace or use the shortcut Cmd + Shift + P on MacOS or Ctrl + Shift + P on Windows.
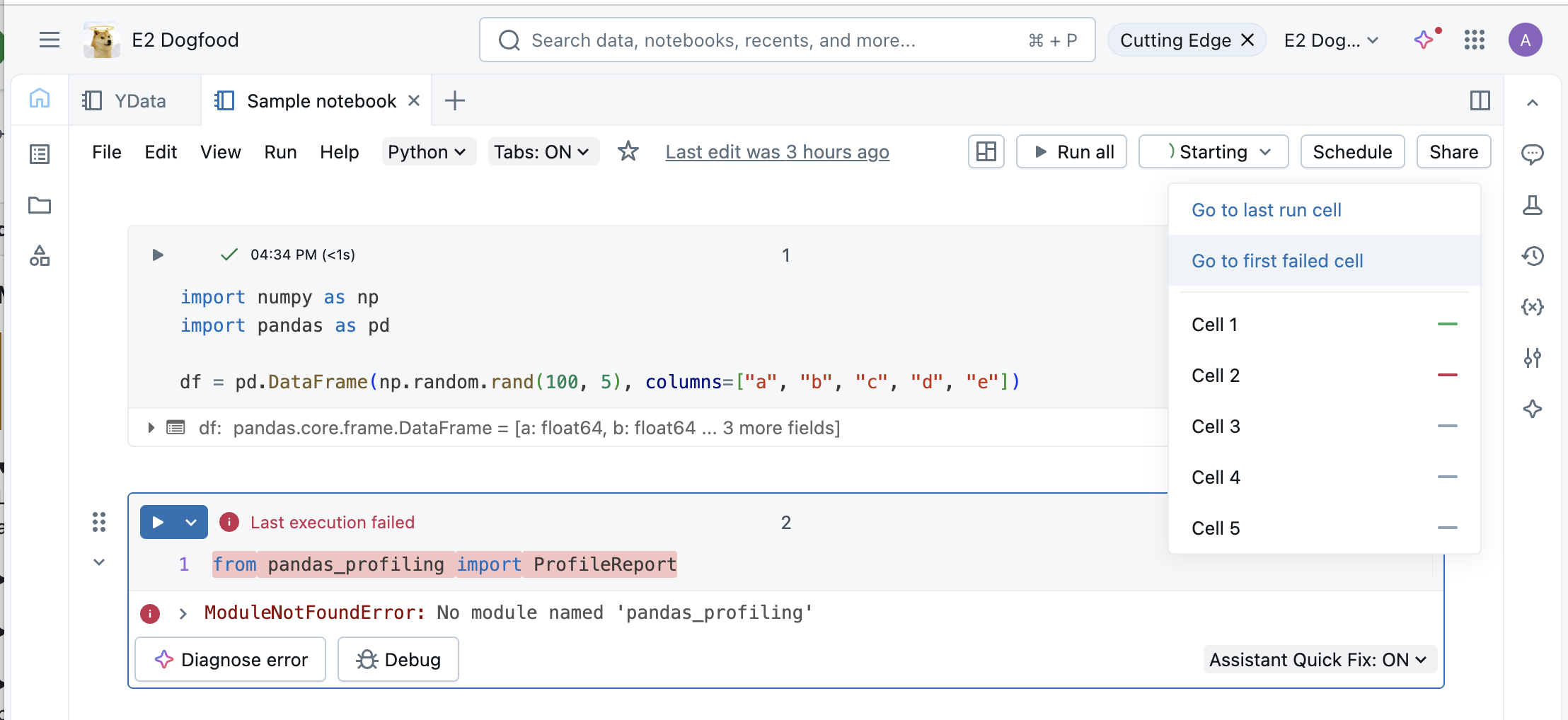
Cell execution minimap
To get a visual overview of your notebook’s execution status, use the cell execution minimap. The minimap appears in the right margin and shows a status bar for each executable cell.
Status bars indicate the following execution states:
- Light grey: Cell is static.
- Dark grey: Cell is either skipped or queued for execution.
- Light grey with moving bar: Cell is currently running.
- Green: Cell ran successfully without errors.
- Red: Cell failed with an error.
To interact with the minimap:
- Hover over the minimap to see a list of executable cells, their titles, and their execution states.
- Click an entry to jump directly to that cell in the notebook.
- Click Go to last run cell or Go to first failed cell to navigate to the most recently run or first failed cell.
The minimap helps you track execution progress at a glance and quickly navigate while debugging or developing.
Find and replace text
To find and replace text within a notebook, use the keyboard shortcut, Cmd + F (Mac) or Ctrl + F(Windows), or click Edit > Find... to open the Find dialog box. Enter the text you want to find. The current match is highlighted in orange and all other matches are highlighted in yellow. To access the native browser search, press Cmd + F (Mac) or Ctrl + F(Windows) again.
Click the to open the Replace option. Enter the text you want to use instead. To replace the current match, click Replace. To replace all matches in the notebook, click Replace All.
To move between matches, click (previous match) or
(next match). You can also press
Shift + Enter and Enter to go to the previous and next matches, respectively.
To close the find and replace tool, click or press esc.
Variable inspection
To display information about a variable defined in a SQL or Python notebook, hover your cursor over the variable name. Python variable inspection requires Databricks Runtime 12.2 LTS or above.
See Variable explorer.
Go to definition
When a Python notebook is attached to a compute resource, you can quickly go to the definition of a variable, function, system module, or the code behind a %run statement.
To do this, hold down the Cmd key on macOS or the Ctrl key on Windows and hover over the variable, function name, or system module. If a definition is found, the name turns into a hyperlink. Click on the link to jump to its definition, which may open in a new tab. You can also right-click, and then click Go to definition or Peek definition.
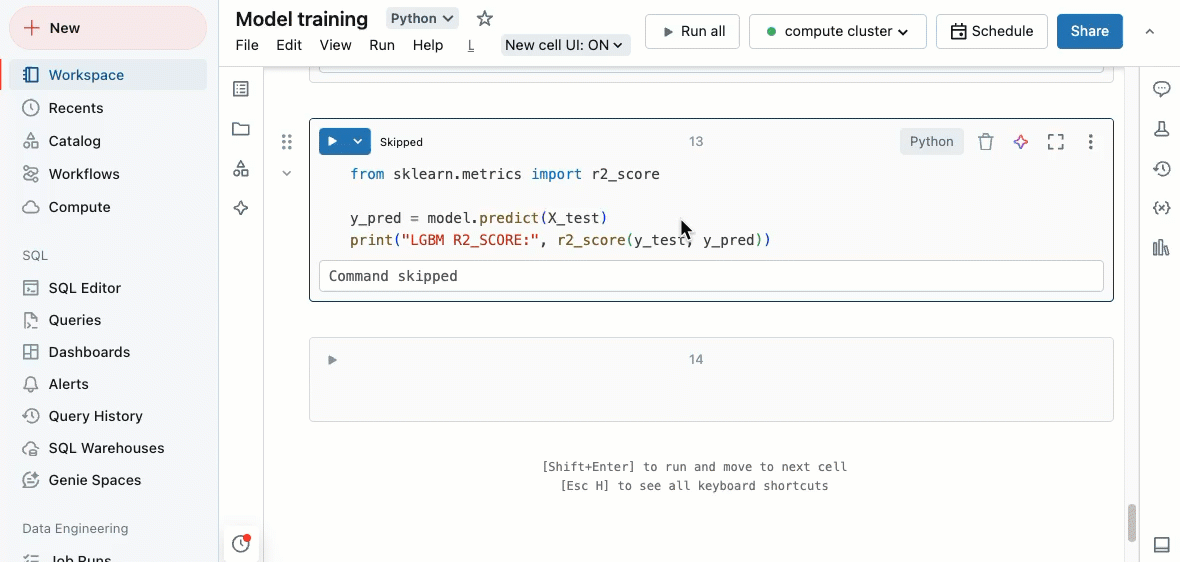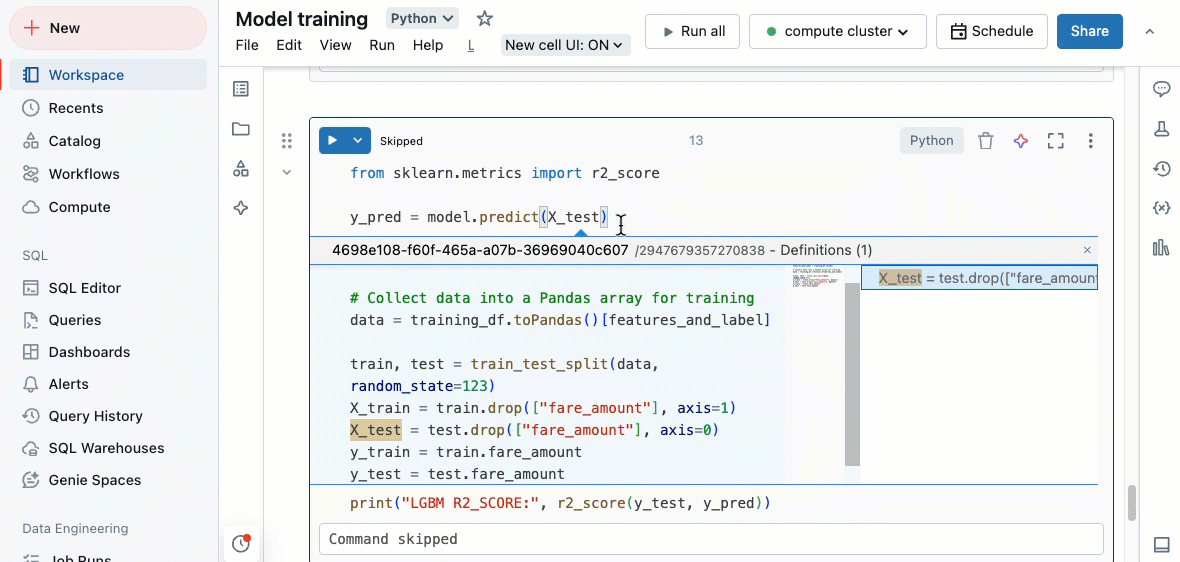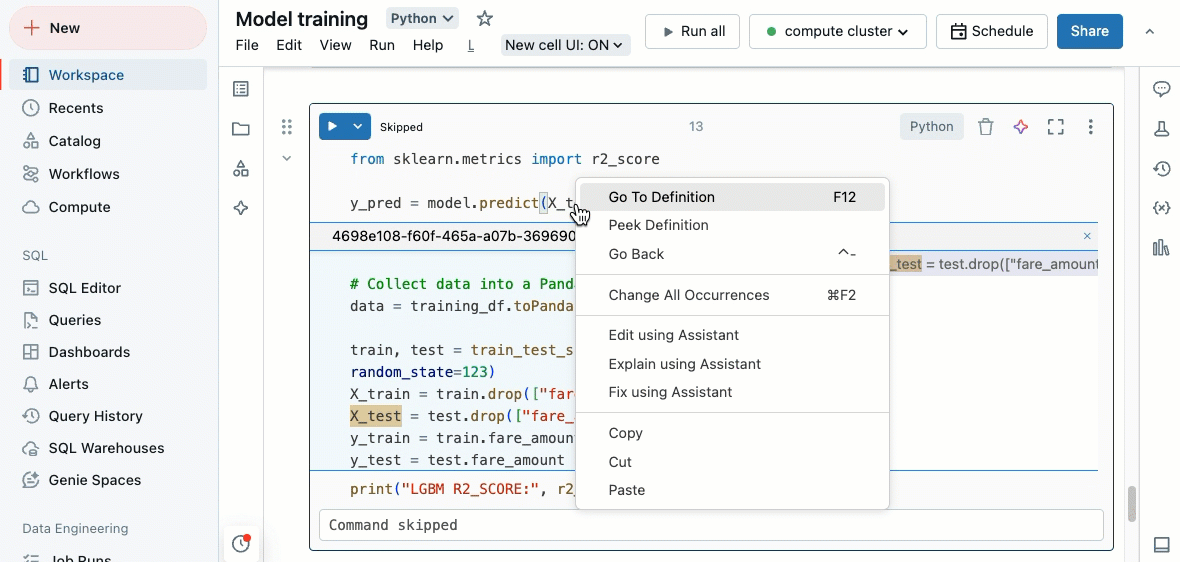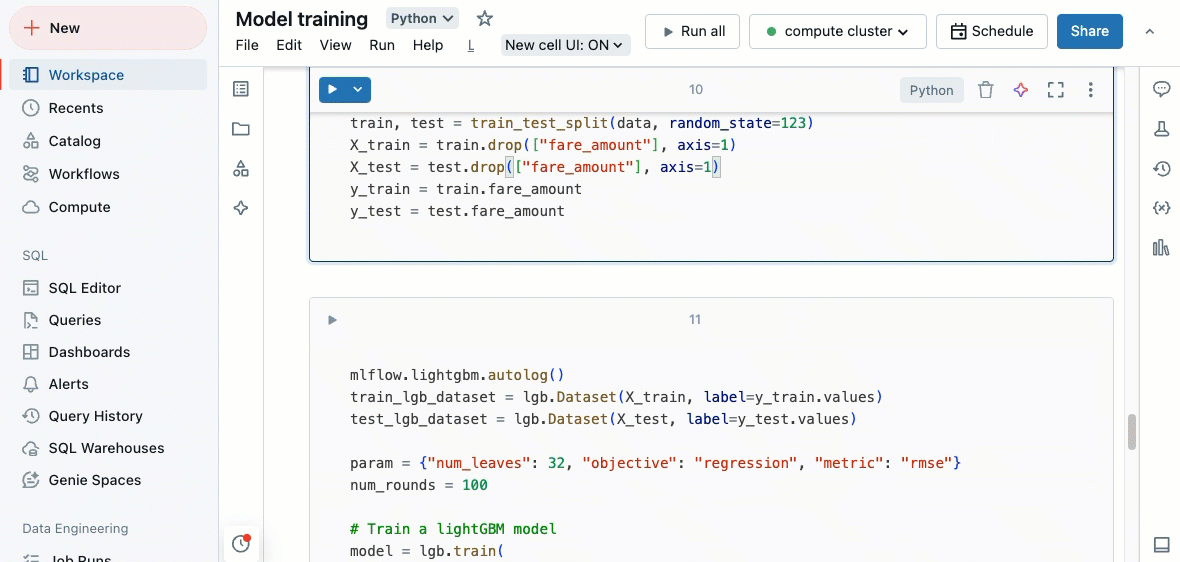
The “go to definition” feature is available in Databricks Runtime 12.2 LTS and above and serverless environment 1 and above.
Code folding
Code folding lets you temporarily hide sections of code. This can be helpful when working with long code blocks because it lets you focus on specific sections of code you are working on.
To hide code, place your cursor at the far left of a cell. Downward-pointing arrows appear at logical points where you can hide a section of code. Click the arrow to hide a code section. Click the arrow again (now pointing to the right) to show the code.

For more details, including keyboard shortcuts, see the VS Code documentation.
Multicursor support
You can create multiple cursors to make simultaneous edits easier, as shown in the video:
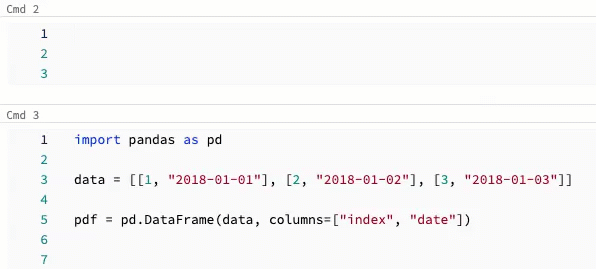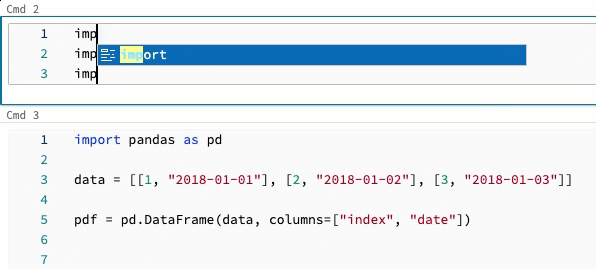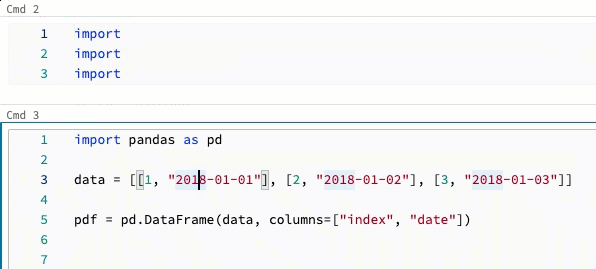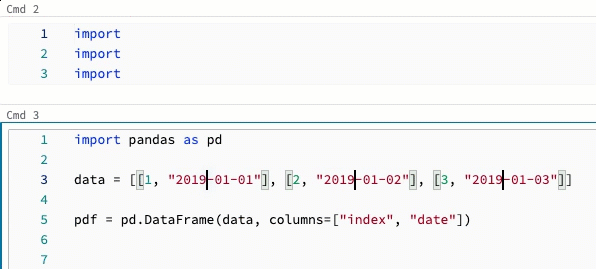
To create multiple cursors in a cell:
- On macOS, hold down the
Optionkey and click in each location to add a cursor. - On Windows, hold down the
Altkey and click in each location to add a cursor. - You also have the option to change the shortcut. See Change shortcut for multicursor and column selection.
On macOS, you can create multiple vertically aligned cursors by using the keyboard shortcut Option+Command+ up or down arrow key.
Column (box) selection
To select multiple items in a column, click at the upper left of the area you want to capture. Then:
- On macOS, press
Shift+Optionand drag to the lower right to capture one or more columns. - On Windows, press
Shift+Altand drag to the lower right to capture one or more columns. - You also have the option to change the shortcut. See Change shortcut for multicursor and column selection.
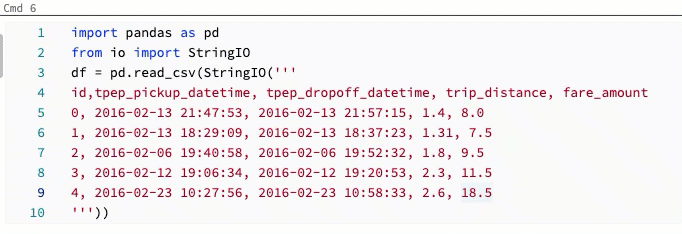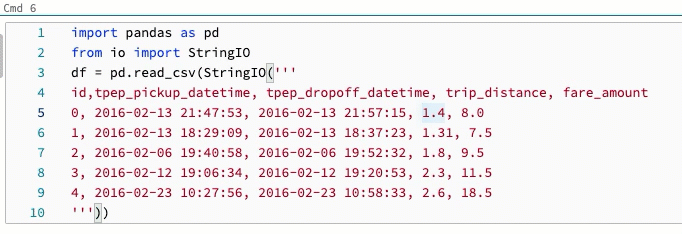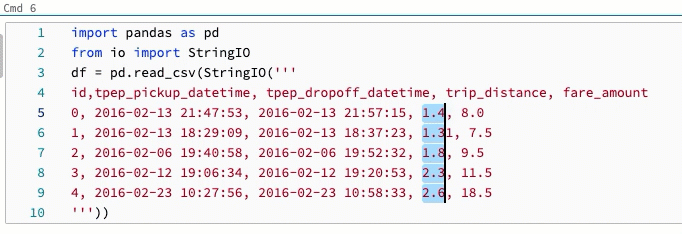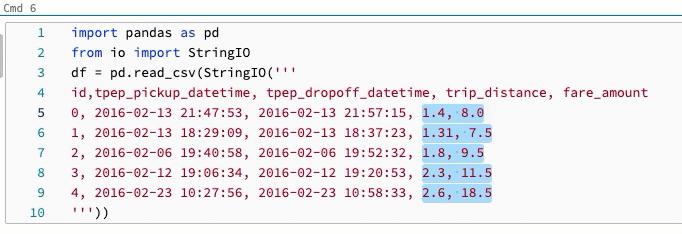
Change shortcut for multicursor and column selection
An alternate shortcut is available for multicursor and column (box) selection. With the alternate selection, the shortcuts change as follows:
- To create multiple cursors in a cell:
- On macOS, hold down the
Cmdkey and click in each location to add a cursor. - On Windows, hold down the
Ctrlkey and click in each location to add a cursor.
- On macOS, hold down the
- To select multiple items in a column, click at the upper left of the area you want to capture. Then:
- On macOS, press
Optionand drag to the lower right to capture one or more columns. - On Windows, press
Altand drag to the lower right to capture one or more columns.
- On macOS, press
To enable the alternate shortcuts, do the following:
- Click your username at the upper-right of the workspace, then click Settings in the dropdown list.
- In the Settings sidebar, select Developer.
- In the Code editor section, change the Key modifier for multi-cursor click setting to Cmd for macOS or Ctrl for Windows.
When you enable alternate shortcuts, the keyboard shortcut for creating multiple vertically aligned cursors does not change.
Browse data
Use the schema browser to explore Unity Catalog objects available for the notebook. Click at the left side of the notebook to open the schema browser.
The For you button displays only those objects that you've used in the current session or previously marked as a Favorite.
As you type text into the Filter box, the display changes to show only those objects that contain the text you type. Only objects that are currently open or have been opened in the current session appear. The Filter box does not do a complete search of the catalogs, schemas, tables, and volumes available for the notebook.
To open the kebab menu, hover the cursor over the object's name as shown:
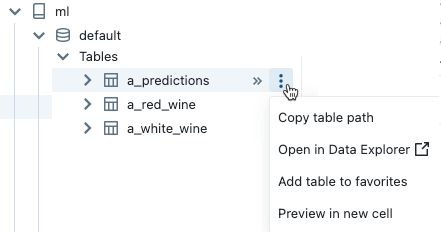
If the object is a table, you can do the following:
- Automatically create and run a cell to display a preview of the data in the table. Select Preview in a new cell from the kebab menu for the table.
- View a catalog, schema, or table in Catalog Explorer. Select Open in Catalog Explorer from the kebab menu. A new tab opens showing the selected object.
- Get the path to a catalog, schema, or table. Select Copy … path from the kebab menu for the object.
- Add a table to Favorites. Select Add to favorites from the kebab menu for the table.
If the object is a catalog, schema, or volume, you can copy the object's path or open it in Catalog Explorer.
To insert a table or column name directly into a cell:
- Click your cursor in the cell at the location you want to enter the name.
- Move your cursor over the table name or column name in the schema browser.
- Click the double arrow
that appears at the right of the object's name.
Use web terminal and Databricks CLI
To open the web terminal in a notebook, click the terminal icon at the bottom of the right sidebar.
In Databricks Runtime 15.0 and above, you can use the Databricks CLI from the web terminal in a notebook. See Run shell commands in Databricks web terminal for requirements and usage information.
You cannot use the CLI from a notebook cell. In a notebook, commands like %sh databricks ... do not work with Databricks Runtime 15.0 or above.
Personalized autocomplete
Autocomplete automatically completes code segments as you type them. Completable objects include types, classes, and objects, as well as SQL database, table names, structs, maps, arrays, and query snippets. When referencing common table expressions (CTEs) that use SELECT *, autocomplete provides column recommendations based on the underlying table structure. Databricks uses your Unity Catalog metadata and usage to personalize suggestions.
- For Python cells, the notebook must be attached to a compute resource for autocomplete to work, and you must run all cells that define completable objects.
- For SQL cells, autocomplete suggests keywords and basic syntax even if the notebook is not attached to any compute resource.
- If the workspace is enabled for Unity Catalog, autocomplete also suggests catalog, schema, table, and column names for tables in Unity Catalog.
- If the workspace is not enabled for Unity Catalog, the notebook must be attached to an all-purpose compute resource or a SQL warehouse to suggest table or column names.
Autocomplete suggestions automatically appear when you type in a cell. Use the up and down arrow keys or your mouse to select a suggestion, and press Tab or Enter to insert the selection into the cell.
Server autocomplete in R notebooks is blocked during command execution.
Autocomplete is enabled by default but can be disabled in your user settings:
- To turn off autocomplete suggestions, toggle Autocomplete as you type. When autocomplete is off, you can display autocomplete suggestions by pressing Ctrl + Space.
- To prevent Enter from inserting autocomplete suggestions, toggle Enter key accepts autocomplete suggestions.
Bracket matching
When you click near a parenthesis, square bracket, or curly brace, the editor highlights that character and its matching bracket.
Python error highlighting

Workspaces with Partner-powered AI features enabled can also select Fix with Assistant for AI-assisted suggestions.
Databricks notebooks support the following error highlighting:
- Python syntax error highlighting: Any syntax errors in Python code cells are highlighted in red. If possible, the Assistant will suggest a quick fix for you. This is supported for compute running Databricks Runtime 12.1 and above or serverless compute. You can configure syntax error highlighting with
pyproject.tomlfiles. See Configure Python syntax highlighting. - Python format error highlighting: Python code formatting errors and warnings are underlined in yellow or red, depending on severity. This can help identify formatting issues such as unexpected indentation, long line length, and more. Hover over the syntax warnings to see more information. This is supported for compute running Databricks Runtime 12.1 and above or serverless compute.
- Python type error highlighting: Type checking can improve code quality, readability, and maintainability in Python and PySpark projects. Type checkers can flag errors related to non-existent attributes, missing arguments, and mismatched arguments in function calls before code execution. Hover over the highlighted warnings to see more information. This is supported for compute running Databricks Runtime 16.0 and above or serverless environment 2.
Enable Python error highlighting
To enable or disable error highlighting, do the following:
- Click your username at the upper-right of the workspace, then click Settings in the dropdown list.
- In the Settings sidebar, select Developer.
- Toggle the setting for Python syntax error highlighting (under Code editor), Python format error highlighting (under Experimental features), and/or Python type error highlighting (under Experimental features).
Configure Python syntax highlighting
When a notebook is connected to compute running Databricks Runtime 16.4 or above or serverless environment version 3 or above, you can customize the behavior of syntax highlighting by creating a pyproject.toml file. For a given notebook, the closest pyproject.toml file in its direct ancestor path in the Workspace File System will be used. If one cannot be found in the ancestor path, then a pyproject.toml file in the current user's home folder will be used.
For example, if you have a notebook with the path a/b/c/d/notebook.py and there are pyproject.toml files at a/b/pyproject.toml and a/b/c/pyproject.toml then the second one will be used since it is closer. A pyproject.toml file at /a/b/c/e/pyproject.toml would not be considered because it is not in the direct ancestor path.
Databricks uses standard syntax for pyproject.toml files. For example, you can refer to the Ruff documentation to see how to configure the Ruff linter with a pyproject.toml file.
Currently, Databricks only supports configuring ruff, pylint, pyright and flake8 for linting through pyproject.toml.
To enable a linter, the pyproject.toml file needs to have a [tool.<name-of-linter>] block.
To explicitly disable a linter, add the following block:
[tool.<name-of-linter>]
disabled=true
You can also disable Databricks-written syntax highlighting rules with a block such as:
[tool.databricks]
disabled_rules = ['DB01', 'DB03']
Because Flake8 expects a configuration in a different format, you have to pass in the configuration for Flake8 as a string:
[tool.flake8]
config = """ \
[flake8] \
extend_ignore = E303 \
"""
Customize SQL formatting
You can customize settings for SQL formatting in new SQL editor and the notebook editor. Click View > Developer Settings. Scroll down to SQL Format and specify your settings.

Use keyboard shortcuts
To display keyboard shortcuts, select Help > Keyboard shortcuts. The keyboard shortcuts available depend on whether the cursor is in a code cell (edit mode) or not (command mode).
The tables below show available keyboard shortcuts.
Edit mode shortcuts
Function | MacOS shortcut | Windows shortcut |
|---|---|---|
Switch to Command Mode |
|
|
Run command and insert new cell below |
|
|
Insert a cell above |
|
|
Insert a cell below |
|
|
Move to previous/next cell |
|
|
Split a cell at cursor |
|
|
Delete current line |
|
|
Delete current cell |
|
|
Move up or to previous cell |
|
|
Move down or to next cell |
|
|
Autocomplete |
|
|
Automatic Assistant Autocomplete |
|
|
Inline Assistant |
|
|
Parameter hints |
|
|
Docstring |
|
|
Multiple cursors |
|
|
Column (box) select |
|
|
Indent/Unindent selection |
|
|
Undo typing |
|
|
Redo typing |
|
|
Toggle line comment |
|
|
Add line comment |
|
|
Remove line comment |
|
|
Multi-cursor edit |
|
|
Increase font size |
|
|
Decrease font size |
|
|
Command mode shortcuts
Function | Mac OS shortcut | Windows shortcut |
|---|---|---|
Switch to Edit Mode |
|
|
Cancel execution for selected cells |
|
|
Cancel execution (skip prompt) |
|
|
Delete current cell |
|
|
Delete current cell (skip prompt) |
|
|
Go to first cell |
|
|
Go to last cell |
|
|
Undo cut/delete cells |
|
|
Copy current cell |
|
|
Cut current cell |
|
|
Paste cell |
|
|
Insert a cell above |
|
|
Insert a cell below |
|
|
Toggle cell output |
|
|
Toggle cell title |
|
|
Scroll down |
|
|
Scroll up |
|
|
Toggle keyboard shortcuts menu |
|
|
Merge with cell below |
|
|
Move to previous cell |
|
|
Move to next cell |
|
|
Add adjacent cell to selection |
|
|
Select all cells |
|
|
Select multiple cells |
|
|
Toggle line numbers |
|
|
Expand/Collapse cell headings |
|
|
Shared shortcuts
Function | MacOS shortcut | Windows shortcut |
|---|---|---|
Toggle command palette |
|
|
Find |
|
|
Replace |
|
|
Format code |
|
|
Run command and move to next cell |
|
|
Run selected command(s) |
|
|
Debug cell |
|
|
Debugger: Continue |
|
|
Debugger: Next Line |
|
|
Debugger: Step Into |
|
|
Debugger: Step Out |
|
|
Run all commands |
|
|
Run all above commands (exclusive) |
|
|
Run all below commands (inclusive) |
|
|
Clear state and outputs |
|
|
Run selected text or active statement |
|
|
Run active SQL statement |
|
|
Move a cell up |
|
|
Move a cell down |
|
|
Toggle comments panel / add comment |
|
|
Toggle workspace panel |
|
|
Toggle catalog panel |
|
|
Toggle assistant panel |
|
|
Toggle focus mode |
|
|
Close current tab |
|
|
Create new tab |
|
|
Switch to left tab |
|
|
Switch to right tab |
|
|
Close all tabs |
|
|