Create and manage attribute-based access control (ABAC) policies
This feature is in Public Preview.
This page describes how to configure row filter and column mask policies in Unity Catalog. For more information on attribute-based access control (ABAC) and policies, see Unity Catalog attribute-based access control (ABAC). To apply tags to objects, see Governed tags and Apply tags to Unity Catalog securable objects.
Compute requirements
To use ABAC policies, you must use one of the following compute configurations:
- Serverless compute
- Standard compute on Databricks Runtime 16.4 or above
- Dedicated compute on Databricks Runtime 16.4 or above with fine-grained access control filtering enabled
Standard and dedicated compute running older runtimes cannot access tables secured by ABAC. As a temporary workaround, you can configure ABAC to apply only to a specific group. Add the users you want to restrict to that group. Users who are not in the group can still access the tables.
Policy quotas
The following lists the number of ABAC policies you can create on different securable objects:
- Catalog: 10 policies per catalog
- Schema: 10 policies per schema
- Table: 5 policies per table
- Principals per policy: 20 principals per policy (applies to both
TOandEXCEPTclauses).
Create a policy on an object
To create a row filter or column mask policy, you must have:
- An existing user-defined function (UDF) in Unity Catalog that you have the
EXECUTEprivilege on that implements the row filter or column mask logic you want to enforce.
For best practices, limitations, and example UDFs, see UDFs for ABAC policies best practices. MANAGEon the object or ownership of the object.
Compute requirements
- You must use compute on Databricks Runtime 16.4 or above or serverless compute.
Compute running older runtimes cannot access tables secured by ABAC. As a temporary workaround, you can configure ABAC to apply only to a specific group. Add the users you want to restrict to that group. Users who are not in the group can still access the tables.
- Catalog Explorer
- SQL
-
In your Databricks workspace, click
Catalog.
-
Select the object that determines the policy scope, such as a catalog, schema, or table.
-
Click the Policies tab.
-
Click New policy.
-
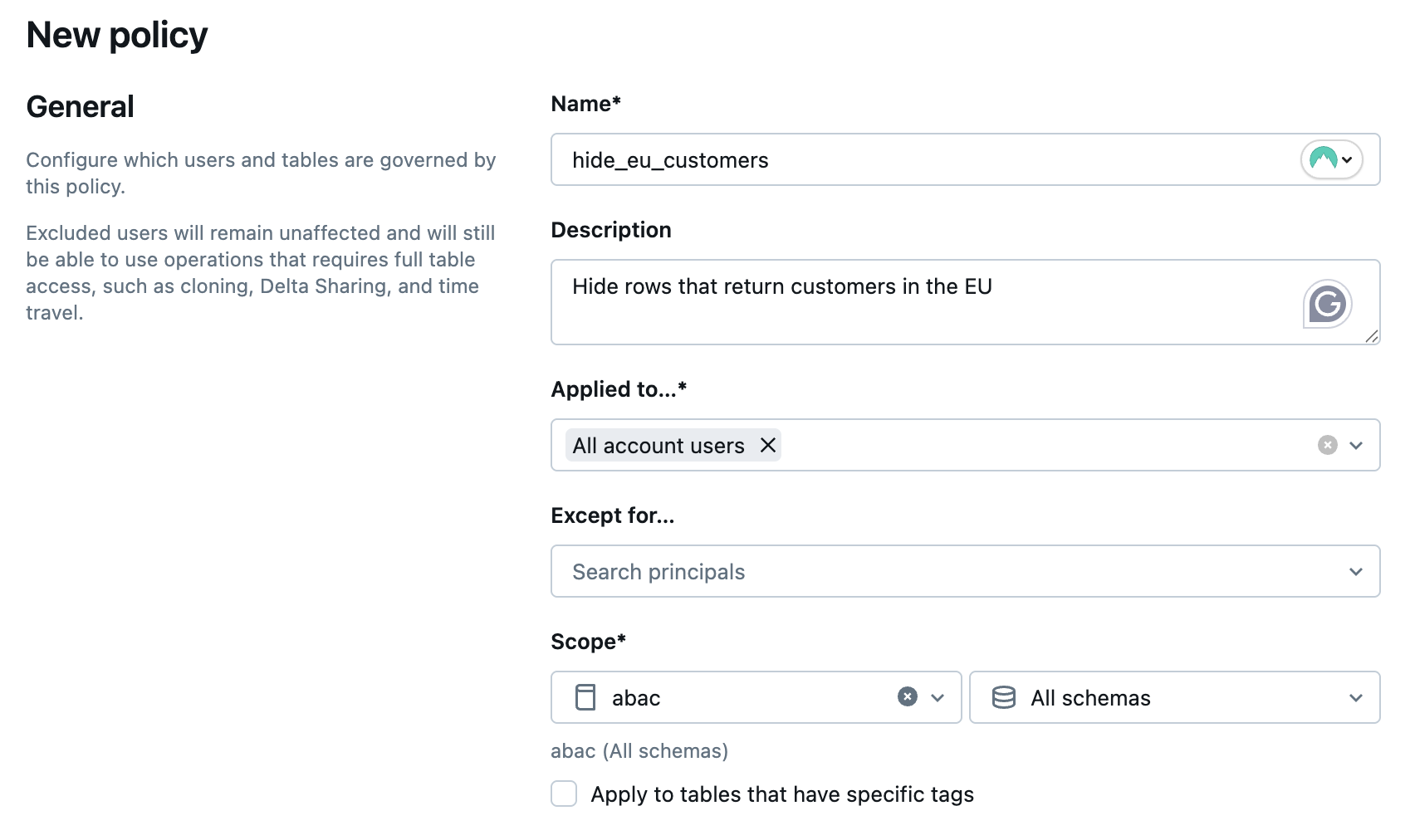
In General:
- For Name, enter a name for your policy.
- For Description, enter a description for your policy.
- For Applied to..., search for and select the principals that the policy applies to.
- For Except for..., add any principals you want to exclude from the policy.
- For Scope, choose the catalog, schemas, and tables you want the policy to apply to.
-
For Purpose, choose whether you want to mask columns or hide rows.
-
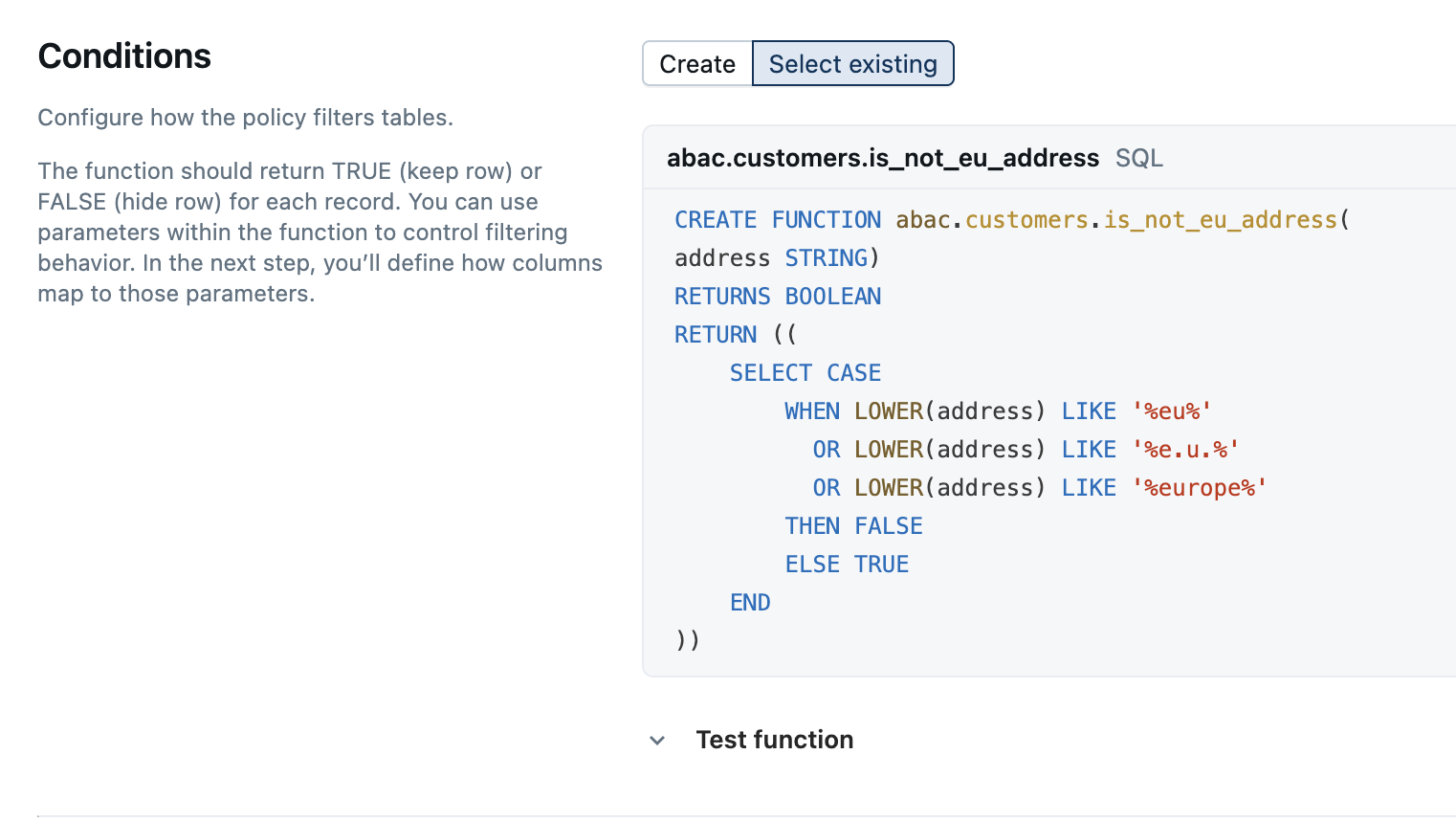
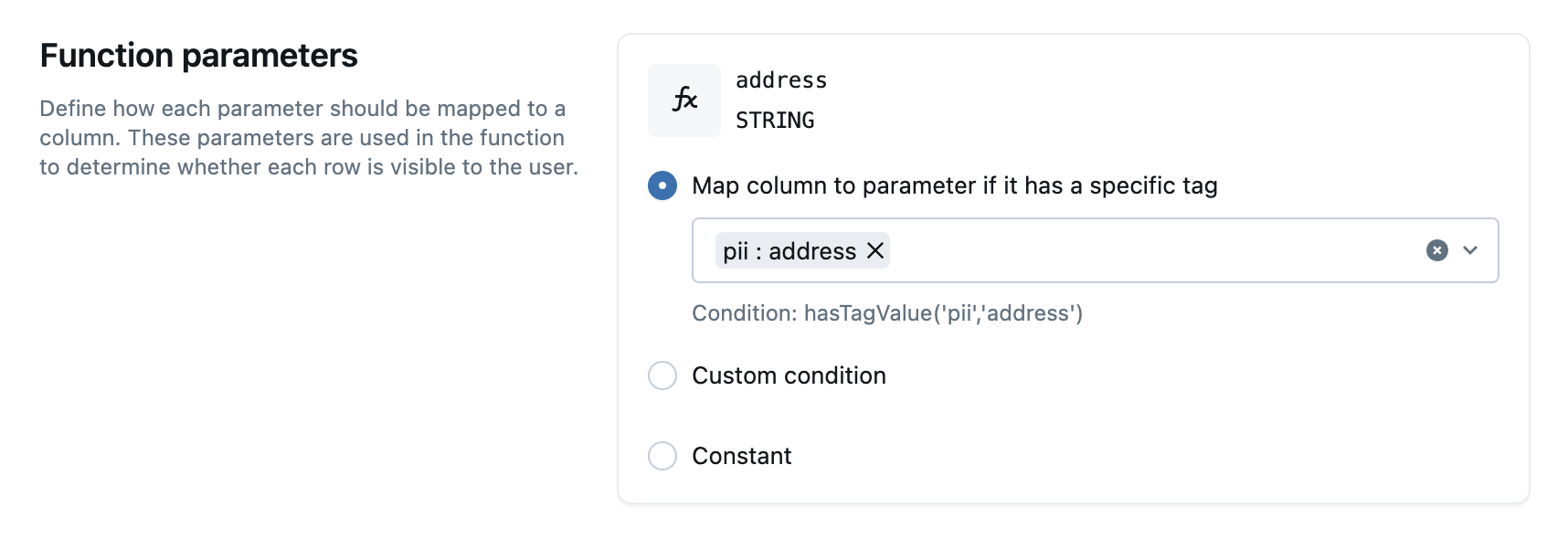
In the Conditions and Function parameters sections, configure how you want the policy to mask columns or hide rows. You do this by specifying a masking function, along with the conditions to apply the function.
-
Click Create policy.
The following is the general syntax for creating a policy:
CREATE POLICY <policy_name>
ON <securable_type> <securable_name>
COMMENT '<policy_description>'
-- One of the following:
ROW FILTER <udf_name>
| COLUMN MASK <udf_name> ON COLUMN <target_column>
TO `<principal_name>`[, `<principal_name>`, ...]
[EXCEPT `<principal_name>`[, `<principal_name>`, ...]]
FOR TABLES
[WHEN hasTag('<key>') OR hasTagValue('<key>', '<value>')]
MATCH COLUMNS hasTag('<key>') OR hasTagValue('<key>', '<value>') AS <alias>
USING COLUMNS <alias>[, <alias>, ...];
When you define table-level conditions (MATCH COLUMNS), the policy applies to the table only if every condition matches at least one column. If a condition doesn’t match any columns in the table, the policy doesn’t apply to the table, and Databricks skips any row filtering or column masking.
For example, if a policy defines MATCH COLUMNS condition1, condition2, condition3, the policy takes effect only if each of the three conditions matches at least one column in the table.
A policy can include up to three column conditions in its MATCH COLUMNS clause.
This example defines a row filter policy that excludes rows for European customers from queries by US-based analysts:
CREATE POLICY hide_eu_customers
ON SCHEMA prod.customers
COMMENT 'Hide rows with European customers from sensitive tables'
ROW FILTER non_eu_region
TO `us_analysts`
FOR TABLES
MATCH COLUMNS
hasTag('geo_region') AS region
USING COLUMNS (region);
This example defines a column mask policy that hides social security numbers from US analysts, except for those with in the admins group:
CREATE POLICY mask_SSN
ON SCHEMA prod.customers
COMMENT 'Mask social security numbers'
COLUMN MASK mask_SSN
TO `us_analysts`
EXCEPT `admins`
FOR TABLES
MATCH COLUMNS
hasTagValue('pii', 'ssn') AS ssn
ON COLUMN ssn;
Tag data is stored as plain text and may be replicated globally. Do not use tag names, values, or descriptors that could compromise the security of your resources. For example, do not use tag names, values or descriptors that contain personal or sensitive information.
Edit a policy
Permissions required: MANAGE on the object or the owner of the object.
- Catalog Explorer
- SQL
- In your Databricks workspace, click
Catalog.
- Select the object that determines the policy scope, such as a catalog, schema, or table.
- Click the Policies tab.
- Select the policy and make edits.
- Click Update policy.
CREATE OR REPLACE POLICY <policy_name>
ON <securable_type> <securable_name>
COMMENT '<policy_description>'
-- One of the following:
ROW FILTER <udf_name>
| COLUMN MASK <udf_name> ON COLUMN <target_column>
TO `<principal_name>`[, `<principal_name>`, ...]
[EXCEPT `<principal_name>`[, `<principal_name>`, ...]]
FOR TABLES
[WHEN hasTag('<key>') OR hasTagValue('<key>', '<value>')]
MATCH COLUMNS hasTag('<key>') OR hasTagValue('<key>', '<value>') AS <alias>
USING COLUMNS <alias>[, <alias>, ...];
Delete a policy
Permissions required: MANAGE on the object or the owner of the object.
- Catalog Explorer
- SQL
- In your Databricks workspace, click
Catalog.
- Select the object that determines the policy scope, such as a catalog, schema, or table.
- Click the Policies tab.
- Select the policy.
- Click Delete policy.
DROP POLICY <policy_name> ON <securable_type> <securable_name>
Troubleshooting multiple filters or masks
When a user queries a table governed by ABAC, only one distinct row filter per table can resolve for each user. In addition, only one distinct column mask per column can resolve for each user. You can define multiple ABAC policies on a table provided they comply with these constraints. This prevents ambiguous results when multiple distinct filters or masks apply to the same user.
When Databricks detects multiple distinct filters or masks during policy evaluation for a given user, it throws an INVALID_PARAMETER_VALUE.UC_ABAC_MULTIPLE_ROW_FILTERS or COLUMN_MASKS_FEATURE_NOT_SUPPORTED.MULTIPLE_MASKS error. This behavior is by design and blocks access to the table until the conflict is resolved.
Understanding how multiple row filters or masks occur
Multiple filters or masks can arise in several ways:
-
A single policy generates multiple filters or masks.
This can happen when multiple columns match the policy conditions. For example, the following policy defines a row filter based on columns tagged withregion=EMEA:SQLCREATE OR REPLACE POLICY region_filter_policy
ON TABLE my_catalog.my_schema.customer_data
ROW FILTER my_catalog.my_schema.filter_by_region
TO `account users`
FOR TABLES
MATCH COLUMNS
hasTagValue('region', 'EMEA') AS region_cols
USING COLUMNS (region_cols);If the
customer_datatable has multiple columns tagged withregion=EMEA, this single policy generates one row filter per matching column. When Databricks evaluates the policy, it detects multiple row filters and throws the error. -
Multiple policies define filters or masks on the same table or column. If more than one ABAC policy applies to the same table or column, Databricks detects multiple effective filters or masks.
-
A table or column already has a manually applied filter or mask. Conflicts can also occur when a table or column includes both a manually applied (non-ABAC) row filter or column mask and one or more ABAC-defined filters or masks.
How to resolve the error
You can resolve the multiple row filters error with any of the following approaches:
-
Refine your policy's column matches: Update the
MATCH COLUMNSclause to be more specific, ensuring that it matches only one column. For example, combine multiple conditions to narrow down the match. -
Adjust your governed tags: Review which columns have the governed tags that trigger the policy. Remove or modify these tags if they shouldn't be included in the row filter.
-
Restructure your policies: Instead of relying on conditions that might match multiple columns, consider creating separate policies with explicit column targeting. This gives you more control over which columns trigger row filters.