Concepts: Generative AI on Databricks
A GenAI app is an application that uses generative AI models (such as large language models, image generation models, and text-to-speech models) to create new outputs, automate complex tasks, or engage in intelligent interactions based on user input.
A GenAI app can be powered by simple calls to LLMs or other GenAI models, or by complex AI agents. Read more about levels of complexity.
Agents, tools, evaluation, models, and other aspects of GenAI apps can be customized with your proprietary data. This data-driven customization leads to data intelligence, allowing you to go beyond the general intelligence offered by canned AI models.
GenAI applications
A user-facing GenAI application can take many forms, such as:
- A chat app, such as one deployed using Databricks Apps
- An API endpoint, such as an agent deployed to Model Serving
- A SQL function for analysts, such as an AI Function
Success with GenAI applications often requires two sets of skills: application development and AI evaluation. GenAI app development is much like developing non-AI applications, requiring software skills that depend on the type of application. However, evaluation for GenAI applications requires specialized tools and techniques to handle the complexity and open-ended responses from GenAI.
To learn about building industry-specific GenAI apps on Databricks, see:
- Databricks Solutions for Industry for use cases, customers, and other resources
- Databricks Solution Accelerators for example use case implementations that you can run and modify
GenAI evaluation
GenAI models, agents, and applications often have complex, open-ended behavior. Users can be allowed to enter any query. An AI agent can be allowed to gather text, images, and more during execution. The output can be arbitrary text, images, or other media, and there can be many "good" answers.
These complications make it challenging to evaluate GenAI. Proper evaluation requires:
- Automation using AI to evaluate AI
- Human feedback from experts and users to collect ground-truth and calibrate automated evaluation
- Deep-diving into complex agents to understand and debug behavior
Databricks-managed MLflow and related tooling provide the foundations for GenAI evaluation:
- Evaluate and monitor AI agents - Learn about evaluation, production monitoring, and human feedback.
- Get started: MLflow 3 for GenAI - Try tracing, evaluation, and collecting human feedback.
- MLflow Tracing - GenAI observability - Learn about MLflow Tracing to record and analyze agent behavior.
Agents
An agent or agent system is an AI-driven system that can autonomously perceive, decide, and act in an environment to achieve goals. Unlike a standalone GenAI model that only produces an output when prompted, an agent system possesses a degree of agency. Modern AI agents use a GenAI model as the "brain" of a system that:
- Receives user requests or messages from another agent.
- Reasons about how to proceed: which data to fetch, which logic to apply, which tools to call, or whether to request more input from the user.
- Executes a plan and possibly calls multiple tools or delegates to sub-agents.
- Returns an answer or prompts the user for additional clarification.
By bridging general intelligence (the GenAI model's pretrained capabilities) and data intelligence (the specialized knowledge and APIs specific to your business), agent systems enable high-impact enterprise use cases such as advanced customer service flows, data-rich analytics bots, and multi-agent orchestration for complex operational tasks.
There is a continuum from simple GenAI models to complex agents. To learn more, see Agent system design patterns.
Databricks provides a range of options for building agents, from fully guided to fully custom:
- AI Playground provides a UI for prototyping tool-calling agents, from which you can export generated agent code.
- Custom agents allows you to build and deploy agents using custom code or third-party agent authoring libraries.
Tools
AI agents can call tools to gather information or perform actions. Tools are single-interaction functions that an LLM can invoke to accomplish a well-defined task. The AI model typically generates parameters for each tool call, and the tool provides a straightforward input-output interaction.
Common tool categories include:
- Tools that retrieve or analyze data
- Semantic retrieval: Query a vector index to locate relevant text or other unstructured data.
- Structured retrieval: Run SQL queries or use APIs to retrieve structured information.
- Web search tool: Search the internet or an internal web corpus.
- Classic ML models: Invoke machine learning models to perform classification, regression, or other predictions.
- GenAI models: Generate specialized outputs such as code or images.
- Tools that modify the state of an external system
- API call: Call CRM endpoints, internal services, or other third-party integrations.
- Email or messaging app integration: Post a message or send a notification.
- Tools that run logic or perform a specific task
- Code execution: Run user-supplied or LLM-generated code in a sandbox.
Tools can be built into agentic logic or accessed using standardized interfaces like MCP.
Tools vs. agents:
- Tools perform a single, well-defined operation. Agents can perform more open-ended tasks.
- Tools are generally stateless and do not maintain ongoing context beyond each invocation. Agents maintain state as they iteratively solve tasks.
Tool error handling and safety:
Because each tool call is an external operation such as an API call, the system should handle failures gracefully. Time-outs, malformed responses, or invalid inputs should not cause the agent itself to fail completely. In production, limit the number of allowed tool calls, have a fallback response if tool calls fail, and apply guardrails to ensure the agent system does not repeatedly attempt the same failing action.
Learn more about AI tools in Databricks:
- AI agent tools - Guide to tool approaches
- Model Context Protocol (MCP) on Databricks - Managed, custom, and external MCP servers
GenAI models and LLMs
Large Language Models (LLMs) are AI models trained on massive text data sets that can understand, generate, and reason about human language. LLMs power applications like chatbots, code assistants, and content generation tools by predicting and producing contextually relevant text based on input prompts.
More generally, GenAI models or foundation models are trained on massive text, image, video, audio, or other data in order to learn about modes beyond text. Multi-modal models learn to connext human language with images, audio, and other media. LLMs are a type of GenAI or foundation model, though these terms are often used loosely and interchangeably.
GenAI models provide the intelligence behind GenAI agents and apps. Simple apps are often built using a single model customized with prompt engineering.
Learn about using GenAI models on Databricks:
- Get started: Query LLMs and prototype AI agents with no code
- Databricks-hosted foundation models available in Foundation Model APIs
- Learn about AI Gateway for governing GenAI models
Prompt engineering
GenAI models generally take prompts, or instructions telling the model how to handle user input. Prompts can be heavily customized with detailed steps, expert knowledge, data, and other information.
Databricks provides flexible ways to do prompt engineering. For example:
- AI Playground provides a UI for manual, interactive prompt engineering.
- MLflow Prompt Optimization and DSPy provide data-driven prompt optimization routines.
What is a GenAI platform?
GenAI requires a combined data + AI platform. For both developers and administrators, the key components for GenAI must be connected and governed in a simple, unified platform.
Key components include:
- AI assets such as models, agents, and apps
- Data assets such as files, tables, processing pipelines, vector indexes, and feature stores
- AI deployments such as endpoints for models and agents
- Tooling for building and deploying AI and data assets
Key governance capabilities include:
- Unified governance of AI and data assets. Learn more at What is Unity Catalog?.
- Unified governance of GenAI model endpoints. Learn more at AI Gateway.
- Unified security approach. Learn more at Databricks AI Security.
- Unified administration of AI and data tooling. Learn more at Administration.
Also see Databricks generative AI capabilities and Databricks architecture.
General intelligence vs. data intelligence
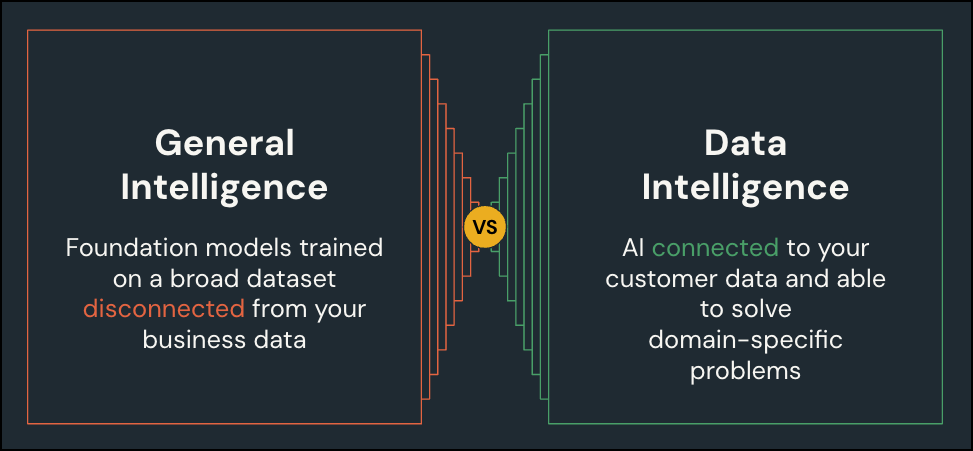
- General intelligence refers to what the LLM inherently knows from broad pretraining on diverse text. This is useful for language fluency and general reasoning.
- Data intelligence refers to your organization's domain-specific data and APIs. This might include customer records, product information, knowledge bases, or documents that reflect your unique business environment.
Agent systems blend these two sources of knowledge: They start with an LLM's broad, generic knowledge and then bring in real-time or domain-specific data to answer detailed questions or perform specialized actions. With Databricks, you can embed data intelligence into your GenAI apps at every level:
- Data sources like vector indexes and Genie
- Evaluation data and metrics
- Prompt optimization based on evaluation data
GenAI vs. ML vs. deep learning
The boundaries between generative artificial intelligence (GenAI), machine learning (ML), and deep learning (DL) can be fuzzy. This guide focuses on GenAI, but the following Databricks platform features support ML, deep learning, and GenAI:
- Model Serving supports ML, deep learning, and GenAI models. You might use it for GenAI batch inference and to deploy agents or fine-tuned models using custom model serving.
- GPU-enabled Databricks Runtime for Machine Learning can be used to train and fine-tune ML, deep learning, and GenAI models.
- MLflow experiment tracking can be used to track both classic ML and GenAI experiments and runs.
- Databricks Feature Store can be used to manage and serve structured data for both classic ML and GenAI.
Learn more
- Key challenges in building GenAI apps - Major challenges in GenAI, and solutions to them using Databricks
- Agent system design patterns - Simple to complex GenAI agents, plus practical advice
- AI on Databricks - Use cases, customers, and other resources for AI on Databricks