Common pipeline maintenance tasks
Learn how to perform ongoing operations for managed ingestion pipelines.
Restart the ingestion pipeline
Applies to: SaaS connectors
Database connectors
Restart the ingestion pipeline when a pipeline run fails unexpectedly or hangs. This can fix transient failures such as temporary network issues, source database timeouts, or configuration errors that have been corrected.
Interface | Instructions |
|---|---|
Lakehouse UI | |
Pipelines API | |
Databricks CLI |
Restart the ingestion gateway
Applies to: Database connectors
To decrease the load on the source database, the ingestion gateway only checks for new tables periodically. It might take up to six hours to discover new tables. To speed up this process, restart the gateway.
Interface | Instructions |
|---|---|
Lakehouse UI | |
Pipelines API | |
Databricks CLI |
Run a full refresh to reingest data
Applies to: SaaS connectors
Database connectors
A full refresh clears existing data and reingests all records. Fully refresh target tables when data is inconsistent, incomplete, or needs to be reprocessed from the source.
For more information about full refresh behavior, see Fully refresh target tables.
Interface | Instructions |
|---|---|
Lakehouse UI | |
Pipelines API | |
Databricks CLI |
Update the pipeline schedule
Applies to: SaaS connectors
Database connectors
Adjust how frequently data is ingested from the source to balance data freshness requirements with source system load.
Interface | Instructions |
|---|---|
Lakehouse UI | |
Jobs API | |
Databricks CLI |
ALTER destination streaming tables
Applies to: SaaS connectors
Database connectors
You can use ALTER SQL statements to modify managed ingestion pipeline datasets. For complete syntax and examples, see ALTER STREAMING TABLE.
You can't modify the schedule or trigger of a managed ingestion pipeline dataset with an ALTER statement. See Update the pipeline schedule.
Set up alerts and notifications
Applies to: SaaS connectors
Database connectors
Lakeflow Connect automatically sets up notifications for ingestion pipelines and scheduling jobs so that you can track pipeline health and receive timely alerts about failures. You can customize notifications if needed.
Interface | Instructions |
|---|---|
Lakehouse UI | |
Pipelines API | |
Databricks CLI |
Remove unused staging files
Applies to: Database connectors
For ingestion pipelines created after January 6, 2025, Databricks automatically schedules volume staging data for deletion after 25 days and physically removes it after 30 days. An ingestion pipeline that has not completed successfully for 25 days or longer might result in data gaps in the destination tables. To avoid gaps, you must trigger a full refresh of the target tables.
For ingestion pipelines created before January 6, 2025, contact Databricks Support to request manual enablement of automatic retention management for staging CDC data.
The following data is automatically cleaned up:
- CDC data files
- Snapshot files
- Staging table data
Specify tables to ingest
Applies to: SaaS connectors
Database connectors
The Pipelines API provides two methods to specify tables to ingest in the objects field of the ingestion_definition:
- Table specification: Ingests an individual table from the specified source catalog and schema to the specified destination catalog and schema.
- Schema specification: Ingests all tables from the specified source catalog and schema into the specified catalog and schema.
If you choose to ingest an entire schema, review the limitations on the number of tables per pipeline for your connector.
Interface | Instructions |
|---|---|
Pipelines API | |
Databricks CLI |
Verify successful data ingestion
Applies to: Database connectors
The list view on the pipeline details page shows the number of records processed as data is ingested. These numbers refresh automatically.
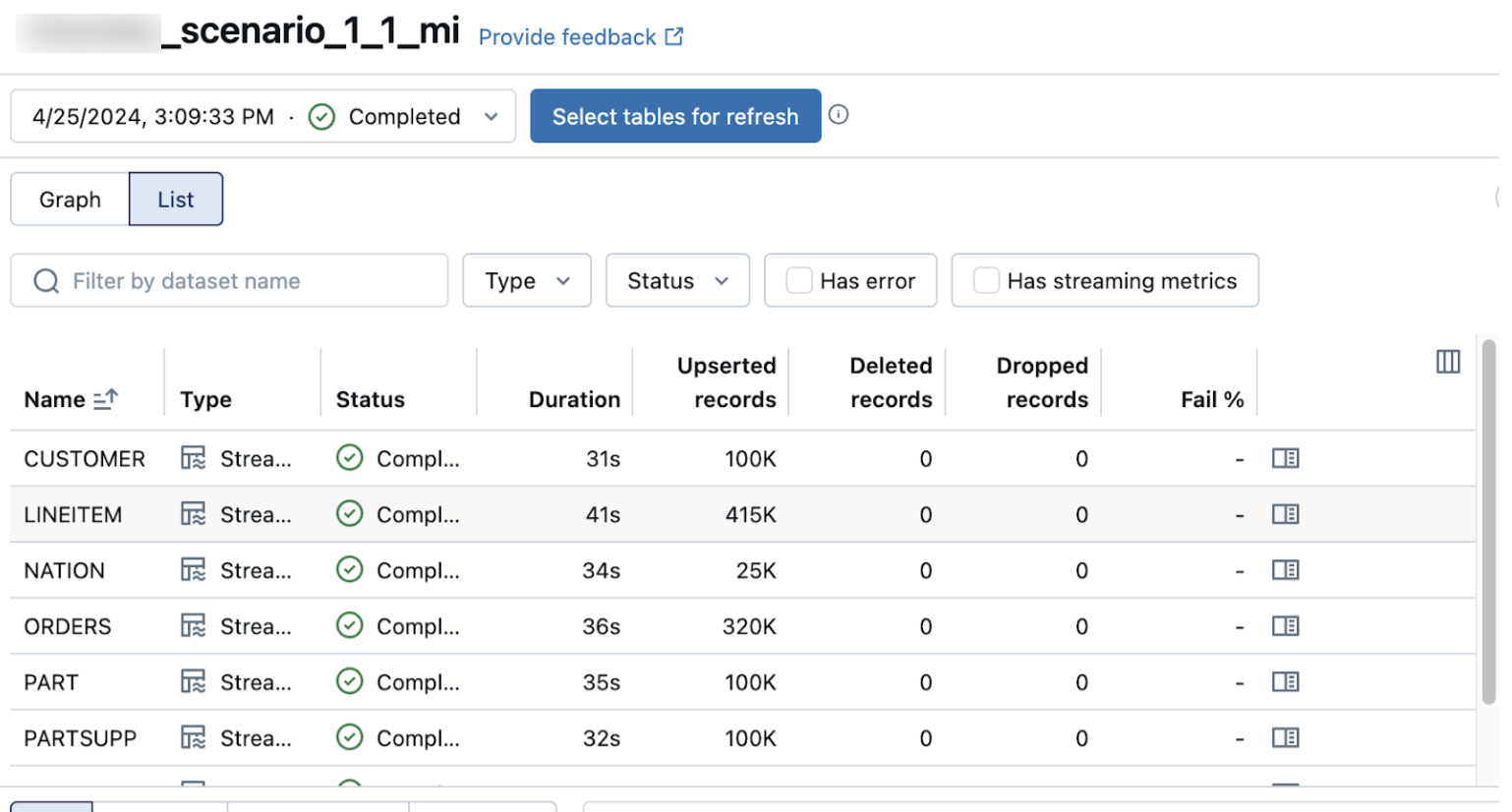
The Upserted records and Deleted records columns are not shown by default. You can enable them by clicking on the columns configuration button and selecting them.