Create and manage labeling schemas
Labeling schemas define the specific questions that domain experts answer when labeling existing traces in the Review App. They structure the feedback collection process, ensuring consistent and relevant information for evaluating your GenAI app.
Labeling schemas apply only when using the Review App to label existing traces. They are not used for vibe checks in the Review App Chat UI.
How labeling schemas work
When you create a labeling session, you associate it with one or more labeling schemas. Each schema represents an assessment that is attached to a trace. Assessments are either Feedback or Expectation. For details, see Label during development.
The schemas control:
- The question shown to reviewers.
- The input method (for example, dropdown or text box).
- Validation rules and constraints.
- Optional instructions and comments.
Labeling schemas for built-in LLM judges
MLflow provides predefined schema names for the built-in LLM Judges that use expectations. You can create custom schemas using these names to ensure compatibility with the built-in evaluation functionality.
The following table shows the predefined labeling schemas and their usage.
Schema name | Usage | Used by these built-in judges |
|---|---|---|
| Collects ideal instructions the GenAI app should follow for a request. | |
| Collects factual statements that must be included for correctness. | |
| Collects the complete ground-truth answer. |
Examples of labeling schemas for built-in LLM judges
For details, see the API reference.
import mlflow.genai.label_schemas as schemas
from mlflow.genai.label_schemas import LabelSchemaType, InputTextList, InputText
# Schema for collecting expected facts
expected_facts_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name=schemas.EXPECTED_FACTS,
type=LabelSchemaType.EXPECTATION,
title="Expected facts",
input=InputTextList(max_length_each=1000),
instruction="Please provide a list of facts that you expect to see in a correct response.",
overwrite=True
)
# Schema for collecting guidelines
guidelines_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name=schemas.GUIDELINES,
type=LabelSchemaType.EXPECTATION,
title="Guidelines",
input=InputTextList(max_length_each=500),
instruction="Please provide guidelines that the model's output is expected to adhere to.",
overwrite=True
)
# Schema for collecting expected response
expected_response_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name=schemas.EXPECTED_RESPONSE,
type=LabelSchemaType.EXPECTATION,
title="Expected response",
input=InputText(),
instruction="Please provide a correct agent response.",
overwrite=True
)
Create custom labeling schemas
For more control over the feedback you collect, create a custom labeling schema using the MLflow UI or API.
Schemas are scoped to experiments, so schema names must be unique within your MLflow experiment.
Schemas are one of two types:
feedback: Subjective assessments like ratings, preferences, or opinions.expectation: Objective ground truth like correct answers or expected behavior.
For details, see Label during development. For parameter definitions, see the API reference.
Create custom schemas using the UI
To create a custom schema in the MLflow UI:
-
In the Databricks workspace, in the left sidebar, click Experiments.
-
Click the name of your experiment to open it.
-
Click Labeling schemas in the sidebar.
-
If an existing labeling schema appears, you can edit it. To create or add a new labeling schema, click Add Label Schema, and edit the fields.
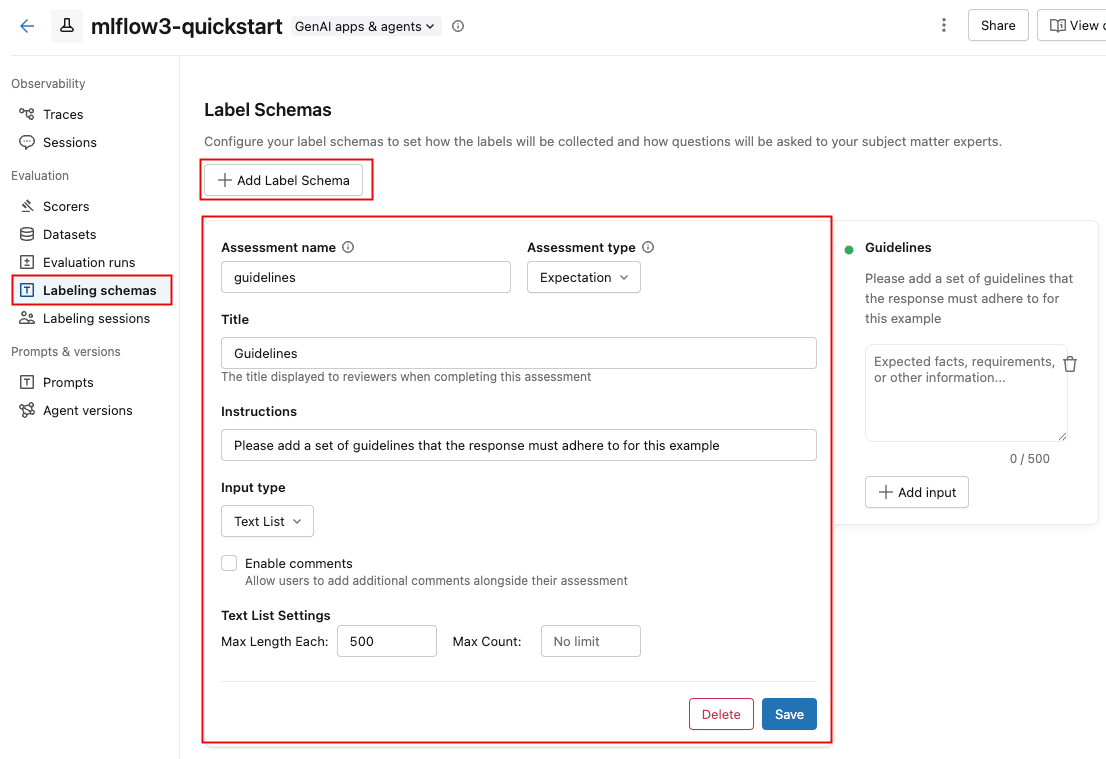
When you select the Input type, the fields below it change to let you specify detailed requirements, such as length limits for text, options for categorical choices, or a numeric range.
As you enter information in the fields, the box at the right updates to reflect the schema you're creating.
-
When you are done, click Save.
The following video shows the process.

Create custom schemas using the API
You can create schemas using mlflow.genai.label_schemas.create_label_schema(). All schemas require a name, type, title, and input specification.
Basic schema example
import mlflow.genai.label_schemas as schemas
from mlflow.genai.label_schemas import InputCategorical, InputText
# Create a feedback schema for rating response quality
quality_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name="response_quality",
type="feedback",
title="How would you rate the overall quality of this response?",
input=InputCategorical(options=["Poor", "Fair", "Good", "Excellent"]),
instruction="Consider accuracy, relevance, and helpfulness when rating."
)
Custom schema feedback example
import mlflow.genai.label_schemas as schemas
from mlflow.genai.label_schemas import InputCategorical, InputTextList
# Feedback schema for subjective assessment
tone_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name="response_tone",
type="feedback",
title="Is the response tone appropriate for the context?",
input=InputCategorical(options=["Too formal", "Just right", "Too casual"]),
enable_comment=True # Allow additional comments
)
Custom schema expectation example
# Expectation schema for ground truth
facts_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name="required_facts",
type="expectation",
title="What facts must be included in a correct response?",
input=InputTextList(max_count=5, max_length_each=200),
instruction="List key facts that any correct response must contain."
)
Manage labeling schemas
Using the API, you can list, update, and delete labeling schemas.
List schemas
To get information about an existing schema, use the API get_label_schema. You must provide the name of the schema. as shown in the following example. For details, see the API reference: get_label_schema.
import mlflow.genai.label_schemas as schemas
# Get an existing schema
schema = schemas.get_label_schema("response_quality")
print(f"Schema: {schema.name}")
print(f"Type: {schema.type}")
print(f"Title: {schema.title}")
Update schemas
To update an existing schema, use the API create_label_schema and set the overwrite parameter to True. For details, see the API reference: create_label_schema.
import mlflow.genai.label_schemas as schemas
from mlflow.genai.label_schemas import InputCategorical
# Update by recreating with overwrite=True
updated_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name="response_quality",
type="feedback",
title="Rate the response quality (updated question)",
input=InputCategorical(options=["Excellent", "Good", "Fair", "Poor", "Very Poor"]),
instruction="Updated: Focus on factual accuracy above all else.",
overwrite=True # Replace existing schema
)
Delete schemas
The following example shows how to delete a labeling schema. For details, see the API reference: delete_label_schema.
import mlflow.genai.label_schemas as schemas
# Remove a schema that's no longer needed
schemas.delete_label_schema("old_schema_name")
Input types for custom schemas
MLflow supports the input types shown in the table for collecting different kinds of feedback. The following sections show examples for each type.
Input type | Description and usage |
|---|---|
| A single-select drop-down menu. Use for mutually exclusive options, such as ratings or classifications. |
| A multi-select drop-down menu. Use when multiple options can be selected. |
| A free-form text box. Use when the response is open-ended, such as detailed explanations or custom feedback. |
| Multiple free-form text boxes. Use for lists of text items, such as facts or requirements. |
| A numeric range. Use for numerical ratings or scores. |
InputCategorical
from mlflow.genai.label_schemas import InputCategorical
# Rating scale
rating_input = InputCategorical(
options=["1 - Poor", "2 - Below Average", "3 - Average", "4 - Good", "5 - Excellent"]
)
# Binary choice
safety_input = InputCategorical(options=["Safe", "Unsafe"])
# Multiple categories
error_type_input = InputCategorical(
options=["Factual Error", "Logical Error", "Formatting Error", "No Error"]
)
InputCategoricalList
from mlflow.genai.label_schemas import InputCategoricalList
# Multiple error types can be present
errors_input = InputCategoricalList(
options=[
"Factual inaccuracy",
"Missing context",
"Inappropriate tone",
"Formatting issues",
"Off-topic content"
]
)
# Multiple content types
content_input = InputCategoricalList(
options=["Technical details", "Examples", "References", "Code samples"]
)
InputText
from mlflow.genai.label_schemas import InputText
# General feedback
feedback_input = InputText(max_length=500)
# Specific improvement suggestions
improvement_input = InputText(
max_length=200 # Limit length for focused feedback
)
# Short answers
summary_input = InputText(max_length=100)
InputTextList
from mlflow.genai.label_schemas import InputTextList
# List of factual errors
errors_input = InputTextList(
max_count=10, # Maximum 10 errors
max_length_each=150 # Each error description limited to 150 chars
)
# Missing information
missing_input = InputTextList(
max_count=5,
max_length_each=200
)
# Improvement suggestions
suggestions_input = InputTextList(max_count=3) # No length limit per item
InputNumeric
from mlflow.genai.label_schemas import InputNumeric
# Confidence score
confidence_input = InputNumeric(
min_value=0.0,
max_value=1.0
)
# Rating scale
rating_input = InputNumeric(
min_value=1,
max_value=10
)
# Cost estimate
cost_input = InputNumeric(min_value=0) # No maximum limit
Complete examples
Customer service evaluation
Here's a comprehensive example for evaluating customer service responses:
import mlflow.genai.label_schemas as schemas
from mlflow.genai.label_schemas import (
InputCategorical,
InputCategoricalList,
InputText,
InputTextList,
InputNumeric
)
# Overall quality rating
quality_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name="service_quality",
type="feedback",
title="Rate the overall quality of this customer service response",
input=InputCategorical(options=["Excellent", "Good", "Average", "Poor", "Very Poor"]),
instruction="Consider helpfulness, accuracy, and professionalism.",
enable_comment=True
)
# Issues identification
issues_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name="response_issues",
type="feedback",
title="What issues are present in this response? (Select all that apply)",
input=InputCategoricalList(options=[
"Factually incorrect information",
"Unprofessional tone",
"Doesn't address the question",
"Too vague or generic",
"Contains harmful content",
"No issues identified"
]),
instruction="Select all issues you identify. Choose 'No issues identified' if the response is problem-free."
)
# Expected resolution steps
resolution_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name="expected_resolution",
type="expectation",
title="What steps should be included in the ideal resolution?",
input=InputTextList(max_count=5, max_length_each=200),
instruction="List the key steps a customer service rep should take to properly resolve this issue."
)
# Confidence in assessment
confidence_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name="assessment_confidence",
type="feedback",
title="How confident are you in your assessment?",
input=InputNumeric(min_value=1, max_value=10),
instruction="Rate from 1 (not confident) to 10 (very confident)"
)
Medical information review
Example for evaluating medical information responses:
import mlflow.genai.label_schemas as schemas
from mlflow.genai.label_schemas import InputCategorical, InputTextList, InputNumeric
# Safety assessment
safety_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name="medical_safety",
type="feedback",
title="Is this medical information safe and appropriate?",
input=InputCategorical(options=[
"Safe - appropriate general information",
"Concerning - may mislead patients",
"Dangerous - could cause harm if followed"
]),
instruction="Assess whether the information could be safely consumed by patients."
)
# Required disclaimers
disclaimers_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name="required_disclaimers",
type="expectation",
title="What medical disclaimers should be included?",
input=InputTextList(max_count=3, max_length_each=300),
instruction="List disclaimers that should be present (e.g., 'consult your doctor', 'not professional medical advice')."
)
# Accuracy of medical facts
accuracy_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name="medical_accuracy",
type="feedback",
title="Rate the factual accuracy of the medical information",
input=InputNumeric(min_value=0, max_value=100),
instruction="Score from 0 (completely inaccurate) to 100 (completely accurate)"
)
Integration with labeling sessions
The following example shows how to use your schemas in a labeling session:
import mlflow.genai.label_schemas as schemas
# Schemas are automatically available when creating labeling sessions
# The Review App will present questions based on your schema definitions
# Example: Using schemas in a session (conceptual - actual session creation
# happens through the Review App UI or other APIs)
session_schemas = [
"service_quality", # Your custom schema
"response_issues", # Your custom schema
schemas.EXPECTED_FACTS # Built-in schema
]
Best practices
Schema design
- Write questions as clear, specific prompts.
- Provide context to guide reviewers.
- Set reasonable limits on text length and list counts.
- For categorical inputs, ensure options are mutually exclusive and comprehensive.
Schema management
- Use descriptive, consistent names across your schemas.
- When updating schemas, consider the impact on existing sessions.
- Delete unused schemas to keep your workspace organized.
Next steps
- Label existing traces - Apply your schemas to collect structured feedback
- Create labeling sessions - Organize review workflows using your schemas
- Build evaluation datasets - Transform labeled data into test datasets