Tracing OpenAI Agents
MLflow Tracing provides automatic tracing capability for OpenAI Agents SDK, a multi-agent framework developed by OpenAI. By enabling auto tracing
for OpenAI by calling the mlflow.openai.autolog function, MLflow will capture traces and log them to the active MLflow Experiment.
import mlflow
mlflow.openai.autolog()
On serverless compute clusters, autologging for genAI tracing frameworks is not automatically enabled. You must explicitly enable autologging by calling the appropriate mlflow.<library>.autolog() function for the specific integrations you want to trace.
Prerequisites
To use MLflow Tracing with the OpenAI Agents SDK, you need to install MLflow, the OpenAI SDK, and the openai-agents library.
- Development
- Production
For development environments, install the full MLflow package with Databricks extras, openai, and openai-agents:
pip install --upgrade "mlflow[databricks]>=3.1" openai openai-agents
The full mlflow[databricks] package includes all features for local development and experimentation on Databricks.
For production deployments, install mlflow-tracing, openai, and openai-agents:
pip install --upgrade mlflow-tracing openai openai-agents
The mlflow-tracing package is optimized for production use.
MLflow 3 is highly recommended for the best tracing experience with OpenAI Agents.
Before running the examples, you'll need to configure your environment:
For users outside Databricks notebooks: Set your Databricks environment variables:
export DATABRICKS_HOST="https://your-workspace.cloud.databricks.com"
export DATABRICKS_TOKEN="your-personal-access-token"
For users inside Databricks notebooks: These credentials are automatically set for you.
API Keys: Ensure your OpenAI API key is configured. For production environments, use Mosaic AI Gateway or Databricks secrets instead of hardcoded values for secure API key management.
export OPENAI_API_KEY="your-openai-api-key"
Basic Example
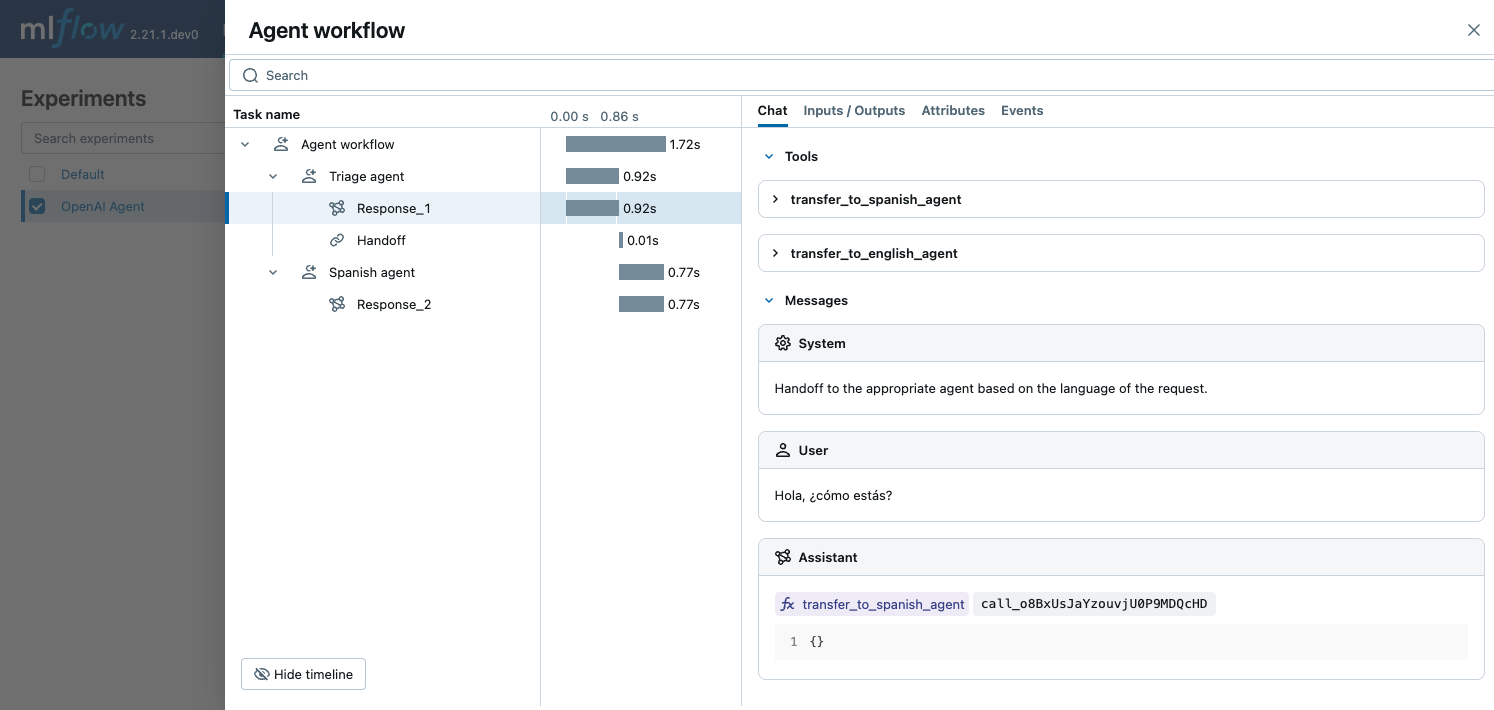
The following example demonstrates how to use the OpenAI Agents SDK with MLflow tracing for simple multi-language chat agents. The three agents collaborate to determine the language of the input and handoff to the appropriate sub-agent that speaks the language. MLflow captures how the agents interact with each other and make calls to the OpenAI API.
import mlflow
import asyncio
from agents import Agent, Runner
import os
# Ensure your OPENAI_API_KEY is set in your environment
# os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "your-openai-api-key" # Uncomment and set if not globally configured
# Enable auto tracing for OpenAI Agents SDK
mlflow.openai.autolog() # This covers agents if using openai module for LLM calls
# If agents have their own autolog, e.g., mlflow.agents.autolog(), prefer that.
# Set up MLflow tracking to Databricks
mlflow.set_tracking_uri("databricks")
mlflow.set_experiment("/Shared/openai-agent-demo")
# Define a simple multi-agent workflow
spanish_agent = Agent(
name="Spanish agent",
instructions="You only speak Spanish.",
)
english_agent = Agent(
name="English agent",
instructions="You only speak English",
)
triage_agent = Agent(
name="Triage agent",
instructions="Handoff to the appropriate agent based on the language of the request.",
handoffs=[spanish_agent, english_agent],
)
async def main():
result = await Runner.run(triage_agent, input="Hola, ¿cómo estás?")
print(result.final_output)
# If you are running this code in a Jupyter notebook, replace this with `await main()`.
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
Function Calling
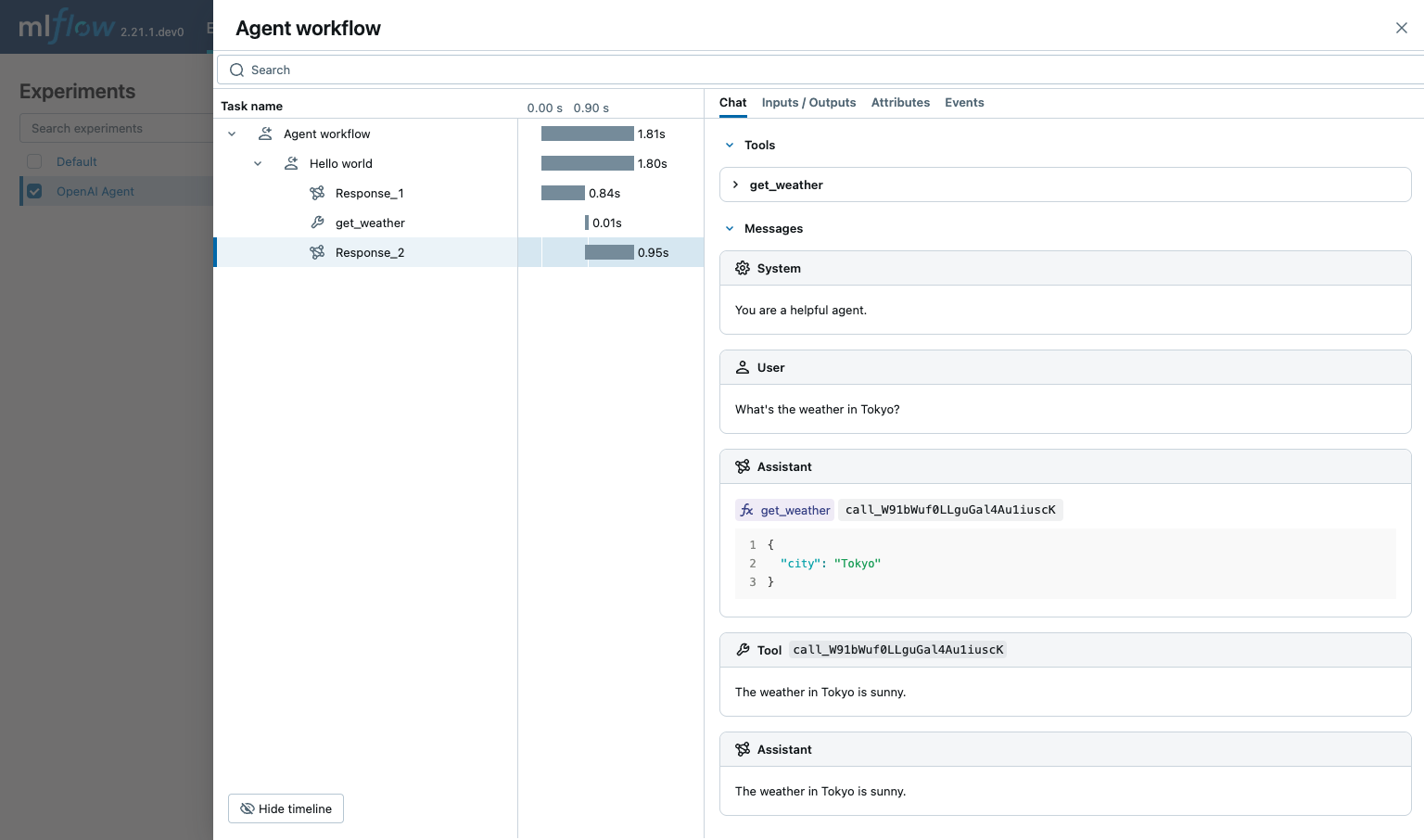
OpenAI Agents SDK support defining functions that can be called by the agent. MLflow captures the function calls and display what functions are available to the agent, which of them are called, and the inputs and outputs of the function calls.
import asyncio
from agents import Agent, Runner, function_tool
import mlflow
import os
# Ensure your OPENAI_API_KEY is set in your environment
# os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "your-openai-api-key" # Uncomment and set if not globally configured
# Enable auto tracing for OpenAI Agents SDK
mlflow.openai.autolog() # Assuming underlying LLM calls are via OpenAI
# Set up MLflow tracking to Databricks if not already configured
# mlflow.set_tracking_uri("databricks")
# mlflow.set_experiment("/Shared/openai-agent-function-calling-demo")
@function_tool
def get_weather(city: str) -> str:
return f"The weather in {city} is sunny."
agent = Agent(
name="Hello world",
instructions="You are a helpful agent.",
tools=[get_weather],
)
async def main():
result = await Runner.run(agent, input="What's the weather in Tokyo?")
print(result.final_output)
# The weather in Tokyo is sunny.
# If you are running this code in a Jupyter notebook, replace this with `await main()`.
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
For production environments, use Mosaic AI Gateway or Databricks secrets instead of hardcoded values for secure API key management.
Guardrails
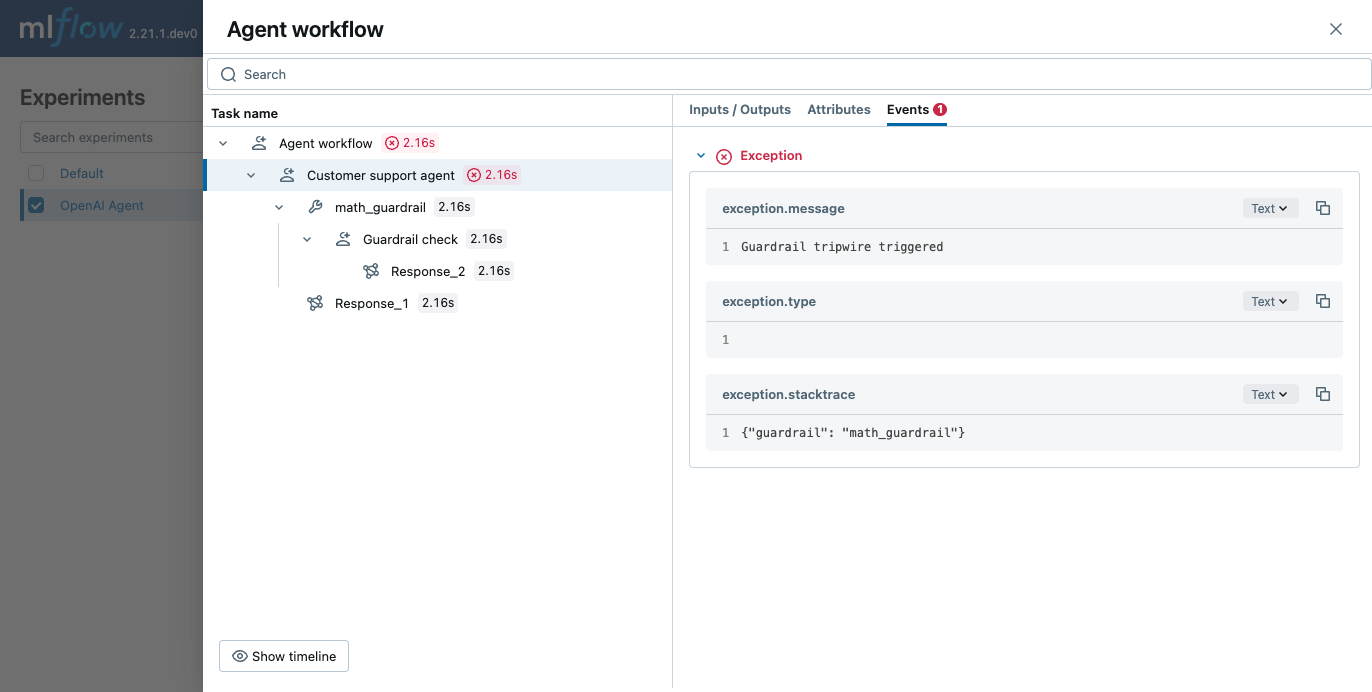
OpenAI Agents SDK support defining guardrails that can be used to check the input and output of the agent. MLflow captures the guardrail checks and display the reasoning behind the guardrail check and whether the guardrail was tripped.
from pydantic import BaseModel
from agents import (
Agent,
GuardrailFunctionOutput,
InputGuardrailTripwireTriggered,
RunContextWrapper,
Runner,
TResponseInputItem,
input_guardrail,
)
import mlflow
import os
# Ensure your OPENAI_API_KEY is set in your environment
# os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "your-openai-api-key" # Uncomment and set if not globally configured
# Enable auto tracing for OpenAI Agents SDK
mlflow.openai.autolog() # Assuming underlying LLM calls are via OpenAI
# Set up MLflow tracking to Databricks if not already configured
# mlflow.set_tracking_uri("databricks")
# mlflow.set_experiment("/Shared/openai-agent-guardrails-demo")
class MathHomeworkOutput(BaseModel):
is_math_homework: bool
reasoning: str
guardrail_agent = Agent(
name="Guardrail check",
instructions="Check if the user is asking you to do their math homework.",
output_type=MathHomeworkOutput,
)
@input_guardrail
async def math_guardrail(
ctx: RunContextWrapper[None], agent: Agent, input
) -> GuardrailFunctionOutput:
result = await Runner.run(guardrail_agent, input, context=ctx.context)
return GuardrailFunctionOutput(
output_info=result.final_output,
tripwire_triggered=result.final_output.is_math_homework,
)
agent = Agent(
name="Customer support agent",
instructions="You are a customer support agent. You help customers with their questions.",
input_guardrails=[math_guardrail],
)
async def main():
# This should trip the guardrail
try:
await Runner.run(agent, "Hello, can you help me solve for x: 2x + 3 = 11?")
print("Guardrail didn't trip - this is unexpected")
except InputGuardrailTripwireTriggered:
print("Math homework guardrail tripped")
# If you are running this code in a Jupyter notebook, replace this with `await main()`.
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
Disable auto-tracing
Auto tracing for OpenAI Agents SDK can be disabled globally by calling mlflow.openai.autolog(disable=True) or mlflow.autolog(disable=True).