Get coding help from Databricks Assistant
This article describes how you can use Databricks Assistant to help you code and debug your notebooks, and provides tips on how to get the most out of the Assistant.
What can Databricks Assistant help with?
Databricks Assistant is a context-aware AI assistant that you can interact with using a conversational interface, making you more productive inside Databricks. You can describe your task in English and let the Assistant generate Python code or SQL queries, explain complex code, and automatically fix errors. The Assistant uses Unity Catalog metadata to understand your tables, columns, descriptions, and popular data assets across your company to provide personalized responses.
Databricks Assistant can help you with the following tasks:
- Generate code.
- Debug code, including identifying and suggesting fixes for errors.
- Transform, optimize, and refactor code.
- Explain code.
- Help you find relevant information in the Databricks documentation.
For information about the models that power Databricks Assistant, see Partner-powered AI features. For general information about Databricks Assistant, see What is Databricks Assistant?.
Run code in Assistant on serverless compute
You can run code directly from the Assistant side panel. The Assistant uses serverless compute by default, which is the default compute on Databricks.
If you’re on a page that already has a compute resource selected (for example, notebooks or the SQL editor), the Assistant will automatically use that compute instead. For information about compute types, see Compute.
If you don't have access to serverless compute, you must have a compute instance available to run code in the Assistant panel.
Assistant command shortcuts for notebooks
In a notebook, Databricks Assistant is available in the Assistant pane or inline in a code cell.
To use Databricks Assistant directly in a code cell, press Cmd+I on MacOS or Ctrl+I on Windows. A text box appears in the cell. You can type a question or comment in English and then press Enter (not Shift+Enter, like you would to run a cell) to have Assistant generate a response.
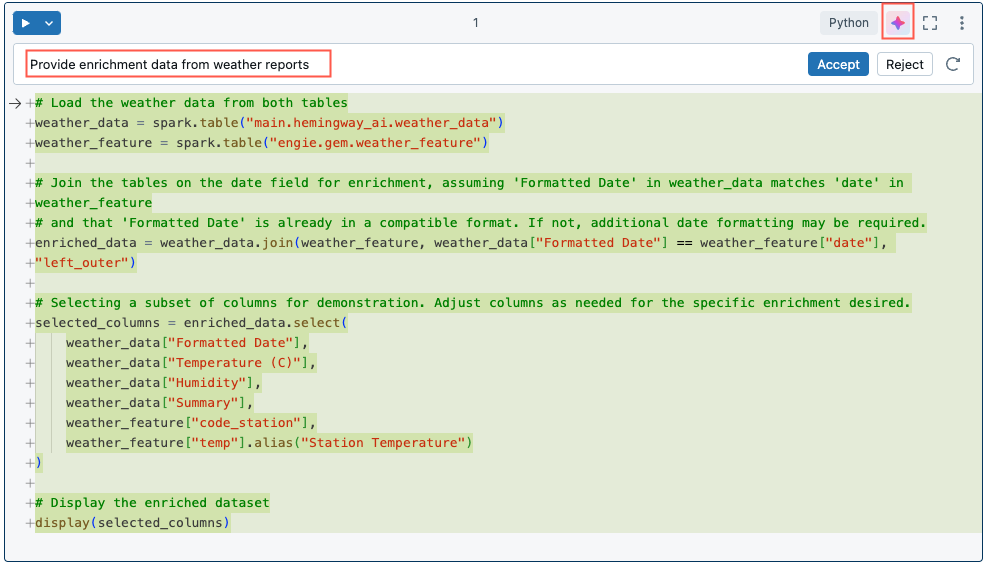
Use slash commands for prompts
Slash commands are a shortcut for creating common prompts.
Prompt text | What Assistant does |
|---|---|
| Displays common commands |
| Comments the code in a diff view |
| Provides an explanation of the code in a cell |
| Proposes a fix to any code errors in a diff view |
| Searches for relevant tables based on Unity Catalog metadata. To find features or feature tables, mention “features” or “feature tables” in the query. See Find features and feature tables using Databricks Assistant. |
| Searches for relevant queries based on Unity Catalog metadata. |
| Improves SQL and Python code. |
| Formats code for readability. |
| Suggests updated names to notebook cells and other elements, depending on the context. |
| Adjusts your notebook settings directly from Assistant. |
When you use /fix or /doc, in the diff window select Accept to accept the proposed changes or Reject to keep the original code. If you accept the proposed code, the code does not automatically run. You can review the code before running it. If the generated code is not what you wanted, try again by adding more details or information to your comment. See Tips to improve Databricks Assistant responses.
Get detailed explanations of code snippets. Use the /explain prompt and include terms like “be concise” or “explain code line-by-line” to request the level of detail that you want. You can also ask Databricks Assistant to add comments to the code.
For code autocomplete, performance may be better using the Assistant pane than in a notebook cell.
Assistant closes automatically if you Accept or Reject the code it generated.
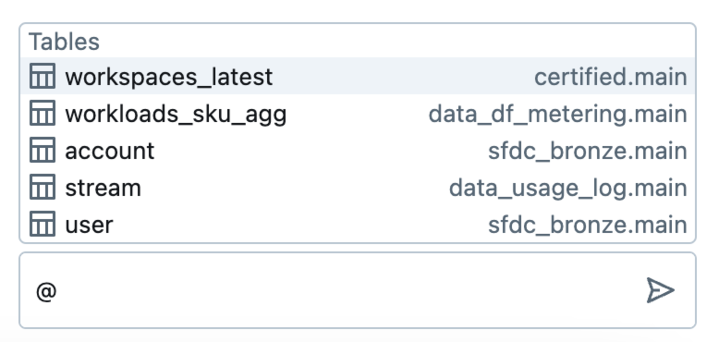
Reference tables in prompts using @
To quickly reference tables in Assistant prompts, use the @ (at) symbol.
Get help with code
Databricks Assistant helps with code, both SQL and Python:
- Edit mode, which works across a notebook to make fixes and updates to multiple cells.
- AI-based autocomplete in Databricks notebooks, the SQL editor, and the file editor.
- Data filtering with natural-language prompts.
- Code debugging with Diagnose Error.
Edit mode for suggestions across multiple notebook cells
Edit mode applies AI-generated suggestions across multiple cells in your notebook from a single prompt.
To use edit mode:
-
With a notebook open, click the Assistant icon
in the top right of the screen.
-
In the Assistant pane, click Edit at the bottom of the prompt box.
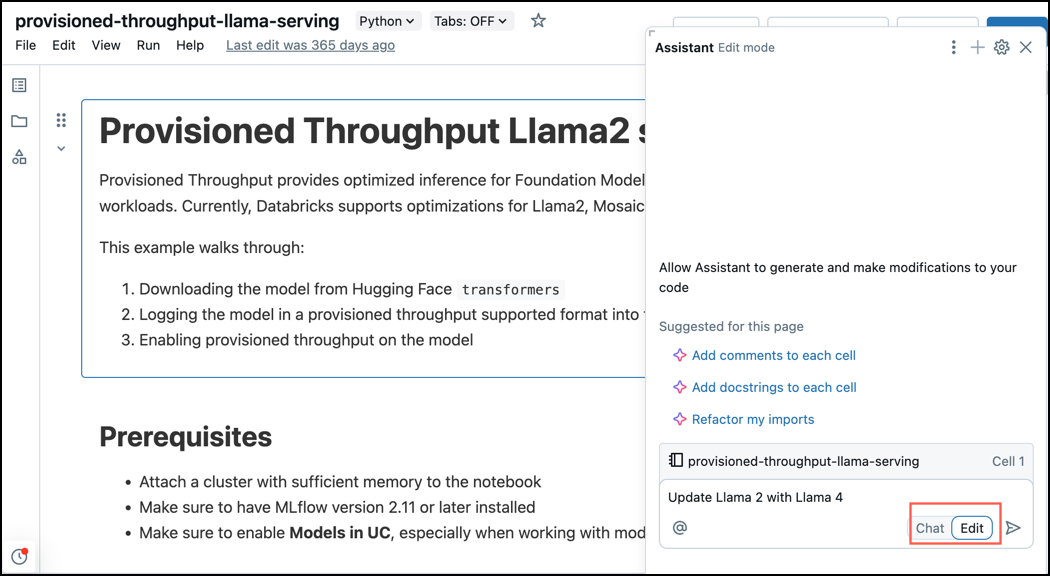
-
In edit mode, enter a prompt just as you would in chat mode.
Assistant analyzes your notebook and surfaces suggestions inline in the cells where changes are needed.
-
After generating suggestions, you can review them directly in the notebook or through the Assistant panel. Click any cell in the Assistant panel to jump to that part of the notebook.
-
Accept or reject edits individually, either inline in the notebook or from the Assistant panel. To apply all suggestions at once, click Accept All or Reject All.
Get inline code suggestions: Python and SQL examples
As you type, suggestions automatically appear. Press Tab to accept a suggestion. To manually trigger a suggestion, press Option+Shift+Space (on macOS) or Control+Shift+Space (on Windows).
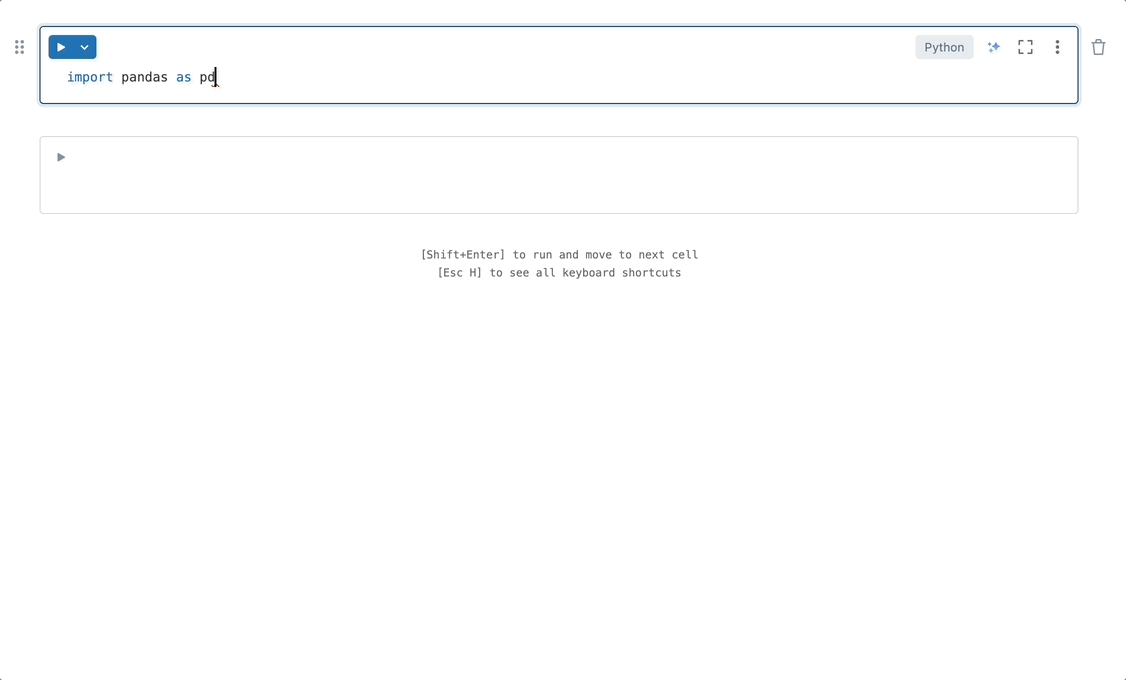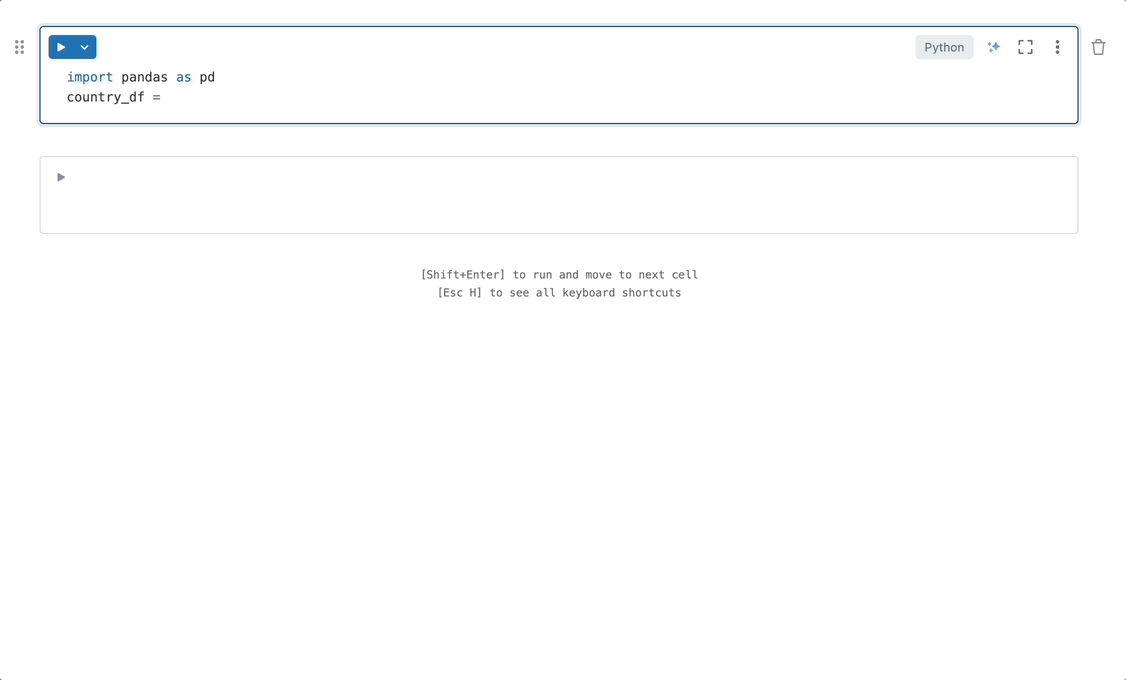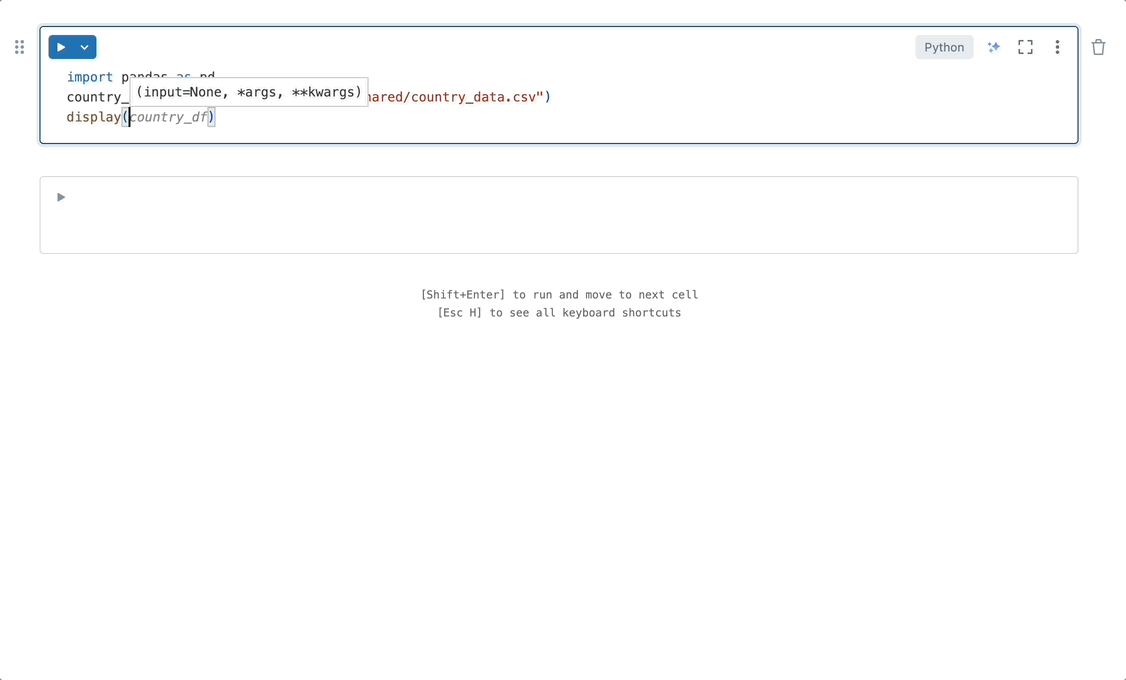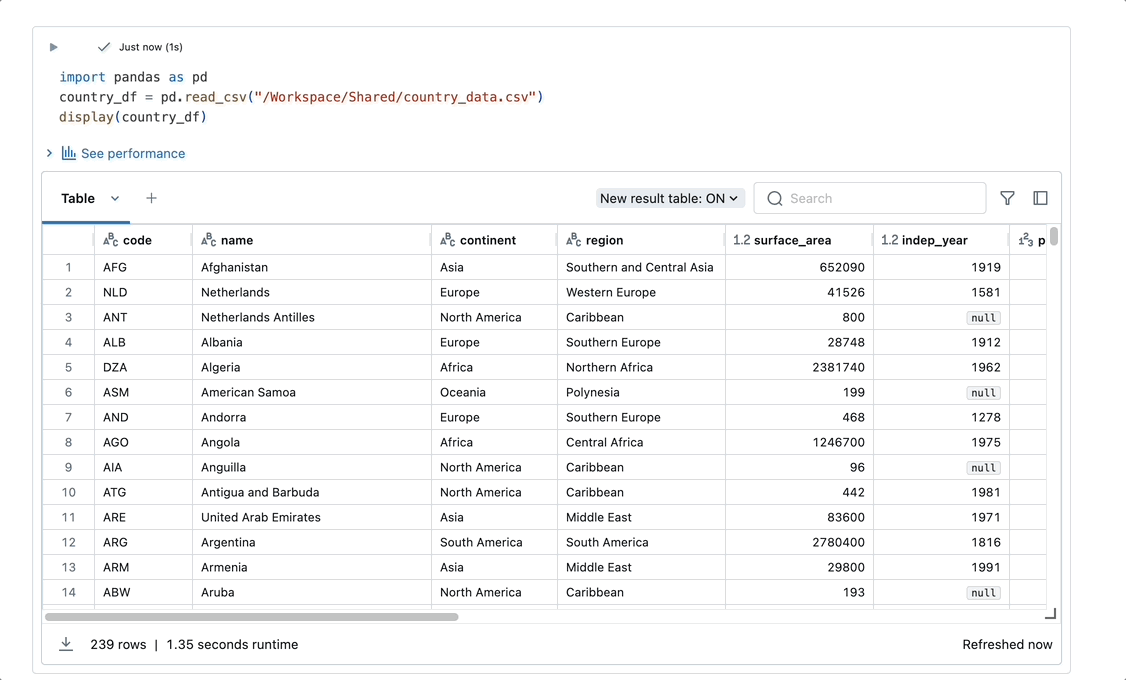
AI-based autocomplete can also generate code from comments:
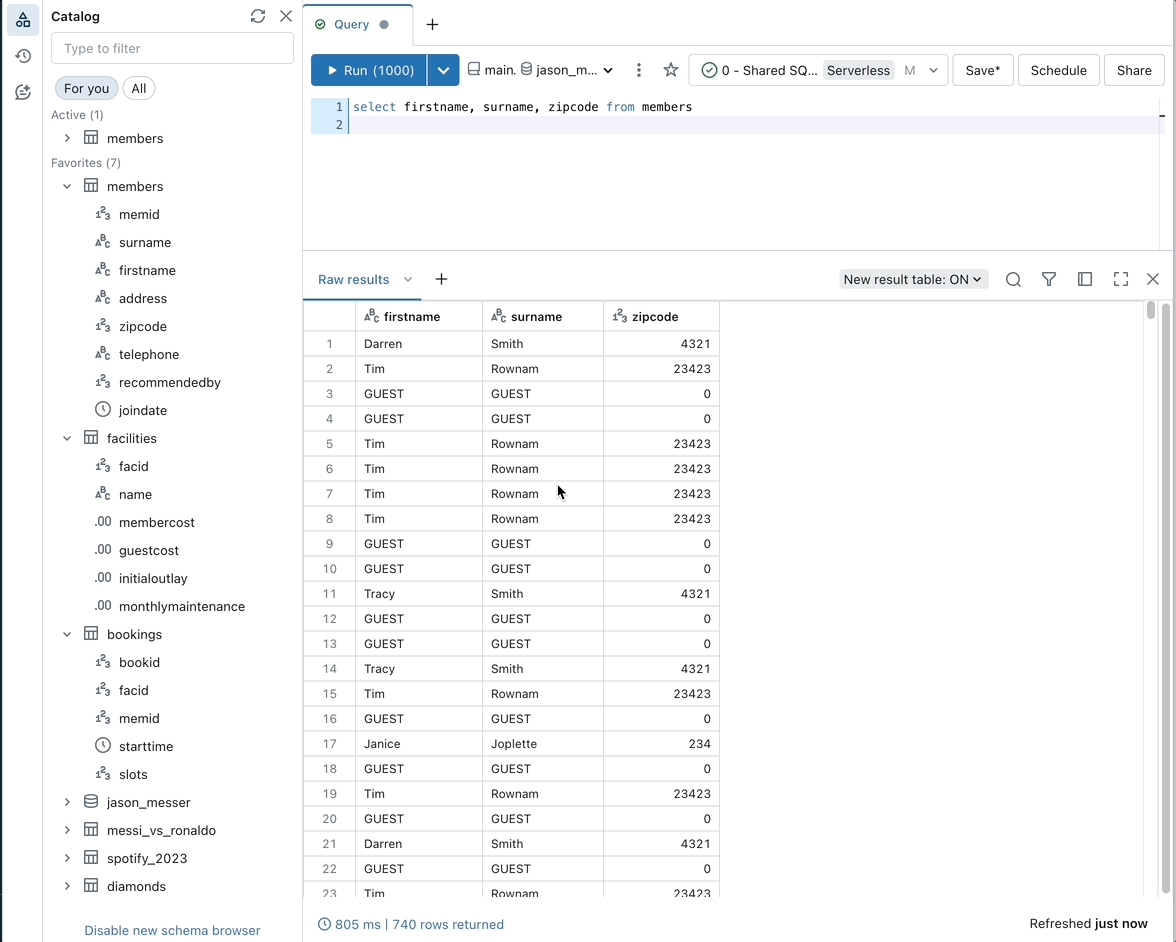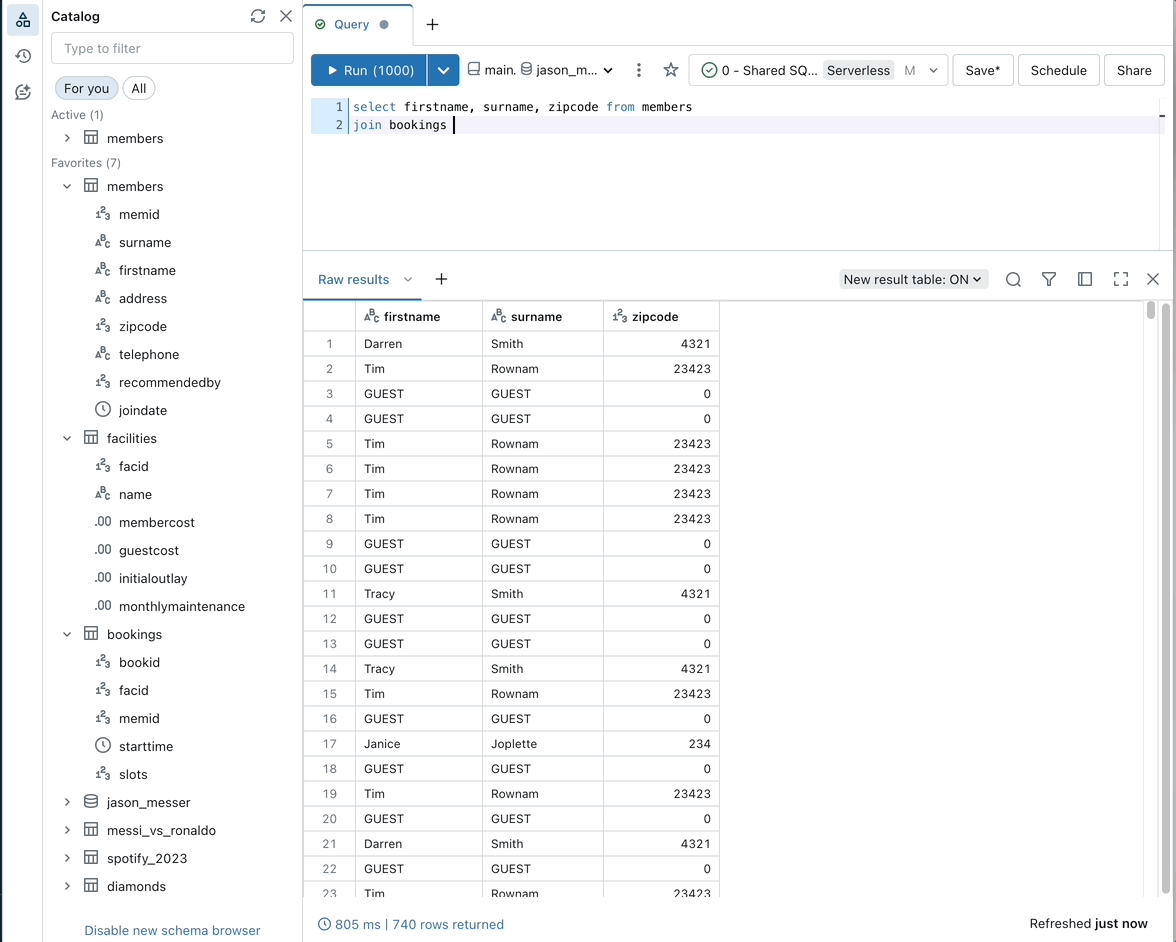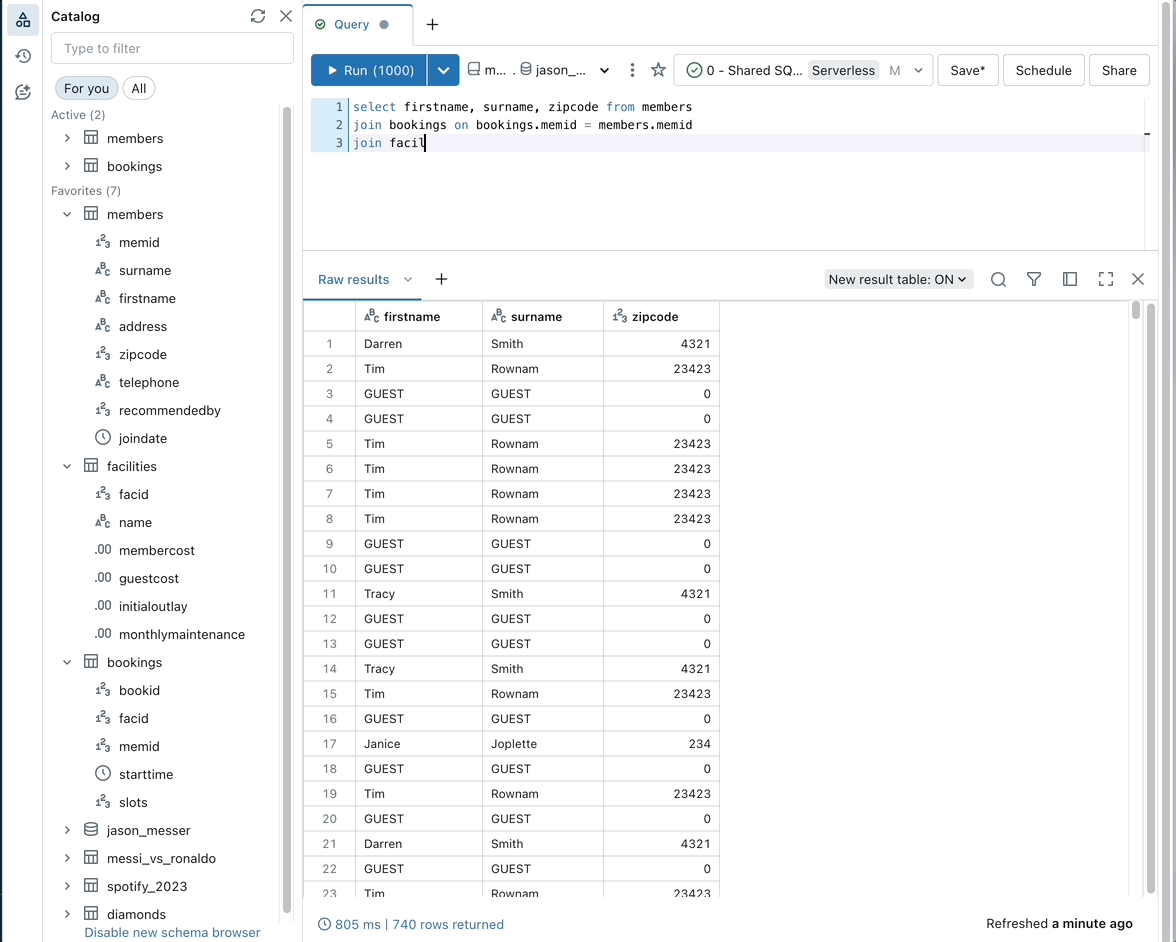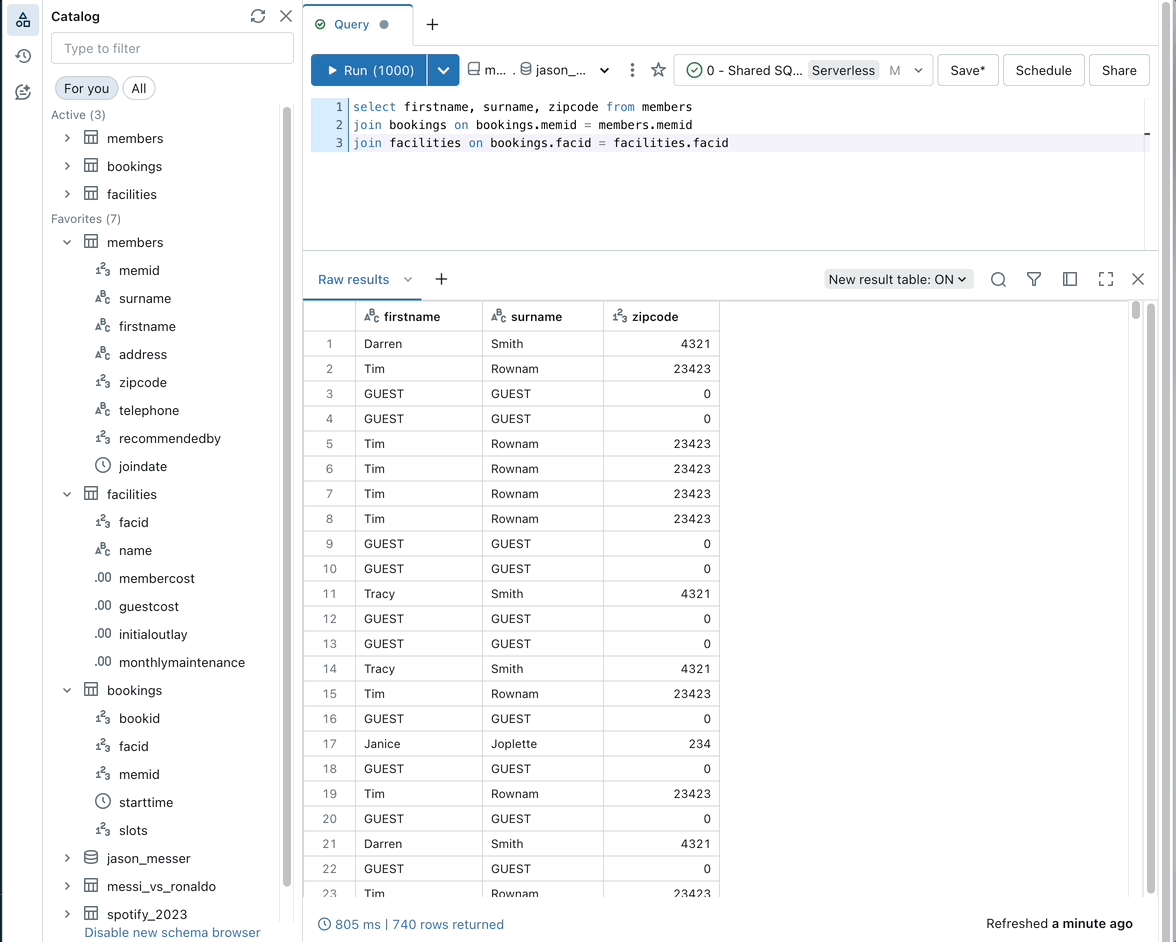
Filter data with natural language prompts
Use Databricks Assistant to filter data outputs with natural language prompts.
To filter outputs with natural language, click the Filter icon in the output table and enter a prompt. For example, as in the animated example following, you can prompt “Show me only males over 70.”

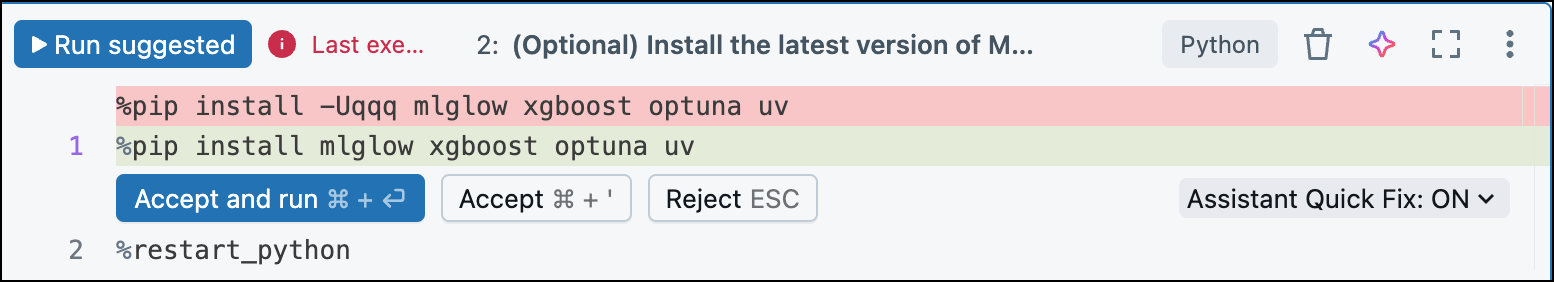
Quick Fix
When code returns errors, Quick Fix automatically recommends fixes for basic errors that can be fixed in a single-line change.
Click Accept and run to make the recommended fix and continue running your code, as shown in the following screenshot:
Debug code: Python and SQL examples
To use Databricks Assistant to fix code, do any of the following:
- Ask a question in the Assistant pane.
- Click the Diagnose Error button that appears in the cell results when an error occurs.
- Click Debug to interactively step through the code line-by-line, set breakpoints, inspect variables, and analyze a program's execution.
The tabs below show Diagnose error examples in Python and SQL code:
- Python
- SQL
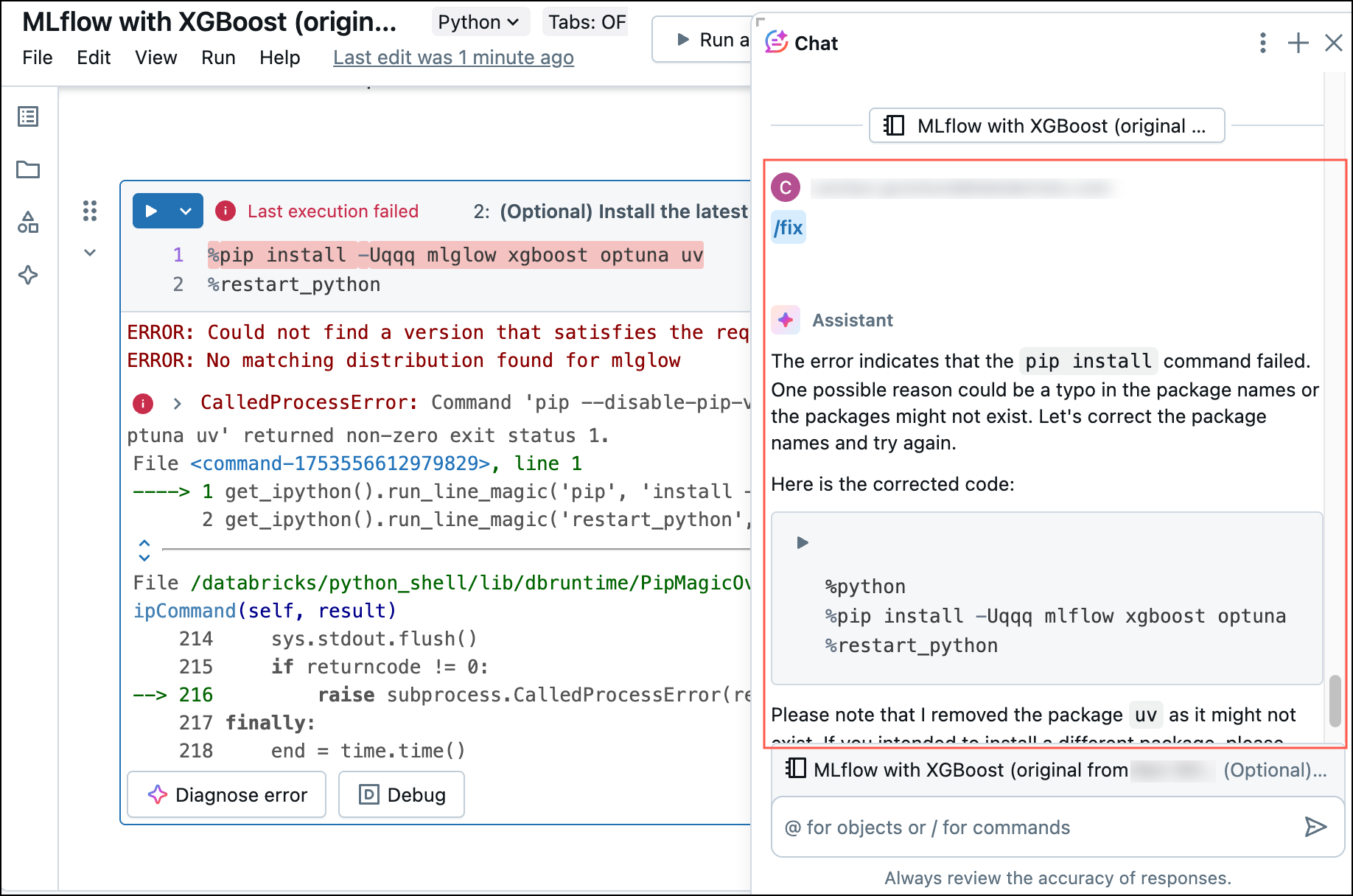
When you click Diagnose error, Assistant automatically runs a `/fix` prompt.
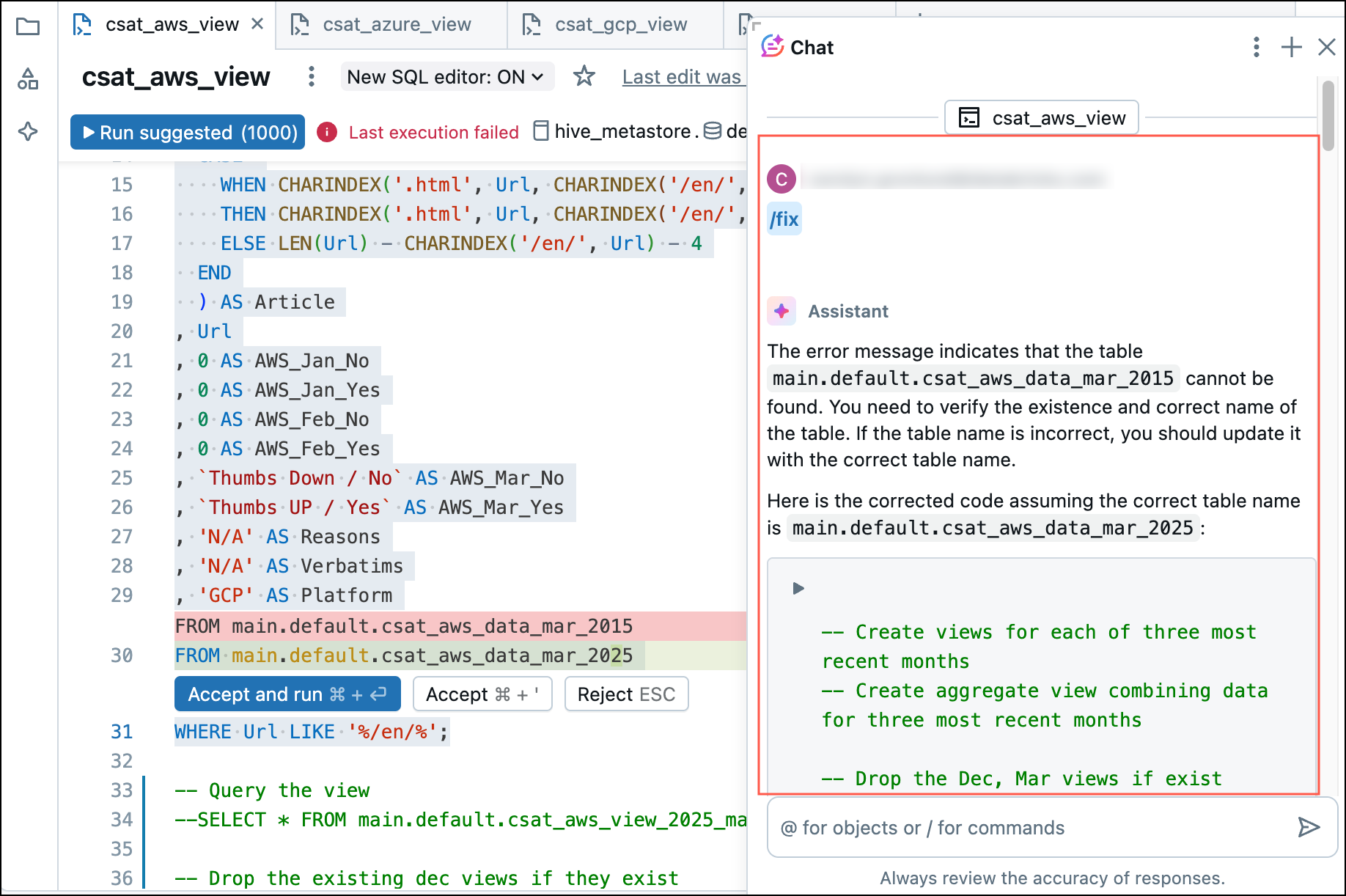
When you click Diagnose error, Assistant automatically runs /fix.
Debug environment errors
The Assistant can help diagnose and suggest fixes for environment failures, including library installation errors.
When there is an installation failure in the environment side panel, the Assistant icon appears in the bottom right. Click
to open the Assistant pane, where the Assistant runs
/repairEnvironment to help diagnose and fix the issue.
You can also open the pip logs and then click Diagnose error to run the /repairEnvironment command in the Assistant pane.
Optimize Python, PySpark, and SQL code
Using the slash prompt /optimize, evaluate and optimize Python, PySpark, and SQL code.
- In a notebook cell or the SQL editor, click the
Assistant icon.
- In the prompt box, type
/optimize, and click the Generate button. - To use the optimization suggestions from Assistant, click Accept.

Here's how /optimize helps with code:
- Pre-run warnings: Yellow underlines highlight opportunities to optimize your query before execution, such as when you are not filtering on a partition column. Hover over the underlined text to view optimization suggestions.
- Post-run analysis: After you run the code, click the Optimize button.
- Table-level suggestions: For example, when users create a table, they receive a hint recommending
CREATE TABLE CLUSTER BY AUTO.
Additional information
The following articles contain additional information about using Databricks Assistant: