Use the Data Science Agent
This feature is in Public Preview.
This page introduces the Data Science Agent, an AI data agent available by selecting Agent Mode in Databricks Assistant. Designed specifically for Databricks notebooks and the SQL Editor, it explores data, generates and runs code, and fixes errors—all from a single prompt.
What is the Data Science Agent?
The Data Science Agent is a powerful capability in the Databricks Assistant’s Agent Mode that transforms the Assistant into an intelligent companion that can automate entire multi-step data science workflows in Databricks notebooks and the SQL Editor.
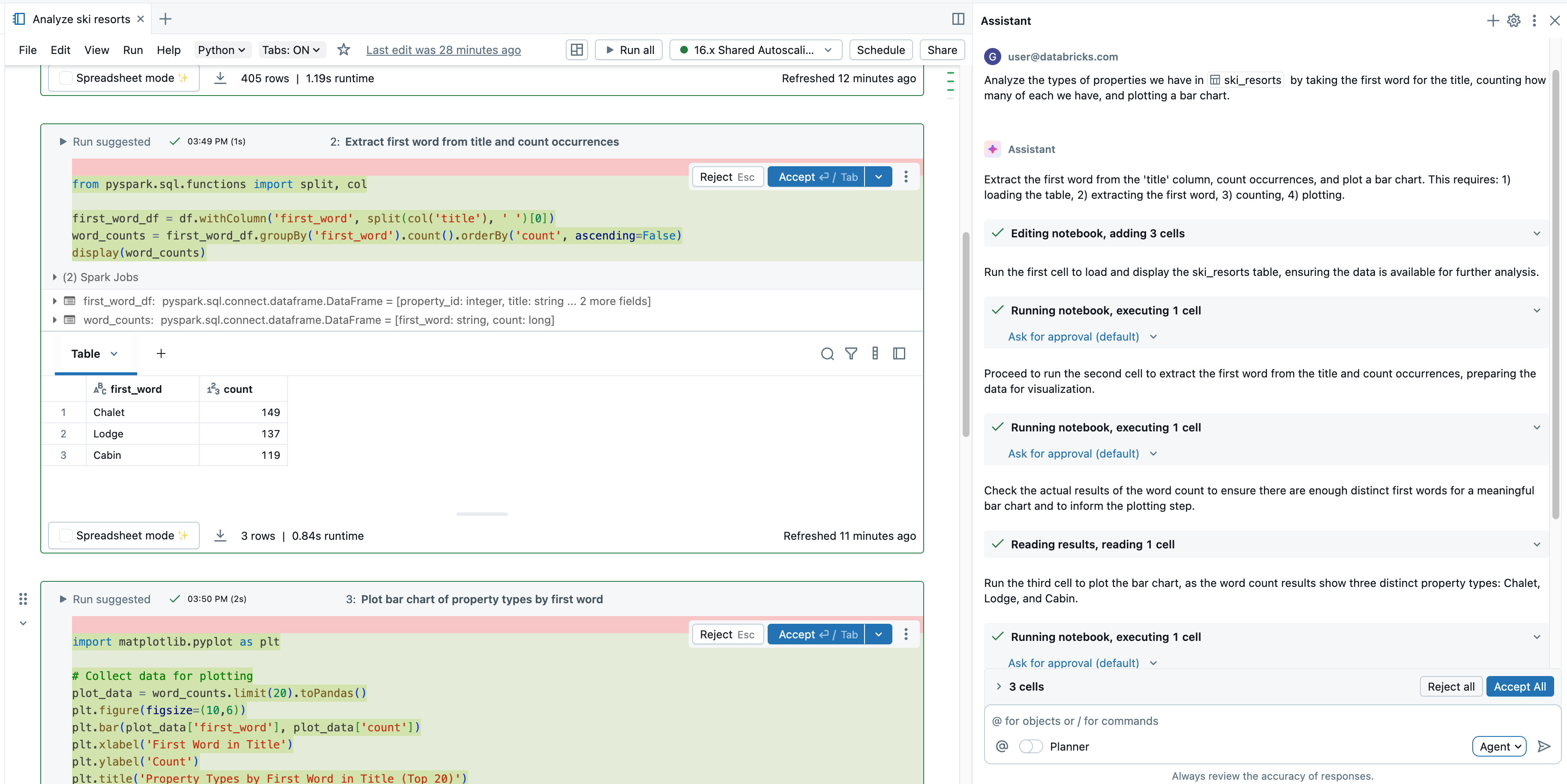
Compared to the Assistant Chat mode, Agent mode has expanded capabilities: planning a solution, retrieving relevant assets, running code, using cell outputs to improve results, fixing errors automatically, and more.
The Data Science Agent can plan and generate code to run in notebooks or queries to run in the SQL editor. The Agent works with you to approve its plans and confirm its next steps before proceeding. With your approval, the Data Science Agent can use tools to perform tasks like searching tables, editing a notebook, running cells, and reading cell outputs.
The Data Science Agent’s access and actions are governed by the user’s permissions. It can only access data that you have access to and perform operations that you have permissions for.
Requirements
To use the Data Science Agent, your workspace needs the following:
- Partner-powered AI features enabled for both the account and workspace. See Partner-powered AI features.
- Databricks Assistant Agent Mode preview enabled. See Manage Databricks previews.
Use the Data Science Agent
To use the Data Science Agent:
-
From a Databricks notebook or the SQL Editor, open the Assistant side panel.
-
In the bottom right corner, select Agent. This toggles on the Assistant’s Agent mode, allowing you to interact with the Data Science Agent.
-
Enter a prompt for the Agent. For example, “Analyze
@sales_transactionsfrom samples.bakehouse to identify the top-selling product.”tipReference specific tables by using
@table_name. The agent will use that table and any associated metadata to curate its response. The agent respects the user’s Unity Catalog permissions, so it can only access the data that you have access to. -
As the Agent generates its response, it often pauses to get your input:
-
For more complex tasks, the agent may create a step-by-step plan and ask clarifying questions. Answer the Agent’s clarifying questions to help it hone its plan.
-
When the Agent needs to run code, it asks for your approval before proceeding. Allow or Decline its request. You can also select Allow in this thread (referring to the Assistant conversation thread) or Always allow.
importantThe Data Science Agent can generate and execute code in your notebook. While it has guardrails to prevent dangerous actions, there is still risk. You should only use it with code and data you trust
-
As the agent continues its work, you may be prompted to select Continue or Reject. Review the Agent’s existing work, then select Continue to allow the Agent to continue to its next steps or Reject to tell it to try something else.
-
To stop the Agent while it is working, click the red
.
-
The Agent can create new notebook cells (or queries), generate text and code, run the notebook cells, and access the cell output to interpret the results.
In order for the Data Science Agent to continue its work and take next steps, you need to stay on the current tab the Agent is working in.
Use cases
In Agent mode, the Assistant has expanded capabilities, such as finding data, interpreting outputs, and performing cell actions.
The Data Science Agent can help with complex data science tasks, including exploratory data analysis, forecasting, and machine learning. You can even use create a new data analysis notebook from scratch with the Data Science Agent. For better results, provide the agent with context by referencing tables, pipelines, notebooks, queries, and files with @<resource_name>. You can also click Add context to manually select context to provide. Each reference asset persists in the chat context.
Try the following prompts to get started:
- Data discovery:
- "Which table contains bakehouse transaction data?"
- "I want to see the weather data for the date 2025-01-01 in the city of Los Angeles, CA."
- "Find a table that contains New York City taxi data and show me the first 10 rows."
- Exploratory data analysis:
- "Help me parse the JSON string in column A."
- "Create a visualization of the data from this table."
- "Interpret this bar chart."
- "Describe the
@sales_transactionsdataset. Perform some EDA to help me understand the column statistics and visualize the distribution of values. Think like a data scientist." - “Analyze
@workload_insightsto find the top 5 customers for Databricks SQL workloads last week by revenue. Then plot how many users those customers had for Databricks SQL per week for the last 6 weeks.”
- Forecasting:
- "Using the
@incidentsdataset, build a forecast of the daily number of incidents for the next 2 weeks. When you’re done, give me a data table and an interactive chart to display the results." - "Using the
@website_trafficdataset, predict daily visitor counts for the upcoming month. Highlight any seasonal patterns." - "Generate a forecast of product demand for the next 6 months from the
@inventorydataset, including confidence intervals."
- "Using the
- Machine learning:
- "Perform some data preparation and feature engineering to prepare this dataset for model training."
- "Train a classification model on the
@customer_datadataset to predict churn. Evaluate the model with accuracy and AUC metrics." - "Perform hyperparameter tuning on a regression model using the
@housing_pricesdataset to improve prediction error." - "Build a clustering model on the
@sales_leadsdataset to identify customer segments and provide a summary of each cluster's characteristics."
- Notebook organization:
- "Create a new cell that summarizes the results from this notebook."
- "Give this notebook a relevant name."
Exploratory data analysis
Use the Data Science Agent to perform exploratory data analysis on a dataset. For example, try using the Agent to help you create a new notebook that analyzes the samples.bakehouse.sales_transactions dataset.
In an empty notebook tab, open the Assistant panel, select Agent mode, and enter the following prompt: "Describe the dataset, @sales_transactions from samples.bakehouse. I want to do some EDA so I can understand the column statistics and visualize the distribution of values. Think like a data scientist."
The agent creates a plan to answer your prompt and might ask clarifying questions. With your approval, it generates new notebook cells that include code to explore the data and text that explains its process and findings.