Query tags
This feature is in Public Preview.
This page describes how to use query tags to group, filter, and attribute costs for SQL workloads on Databricks SQL warehouses.
Query tags are custom key-value pairs (for example, team:marketing or dbt_model_name:some_model_name) that you apply to SQL workloads. These tags appear in the system.query.history table and on the Query History page of the Databricks UI, and are returned in responses to the ListQueries API if non-empty. Query tags allow you to group queries by business context, attribute warehouse costs, and identify sources of long-running queries.
Tag data is stored as plain text and might be replicated globally. Don't use tag keys or values that contain passwords, personal information, or other sensitive data.
Requirements
Before using query tags, verify the following:
-
Confirm you can access the
system.query.historytable, specifically thequery_tagscolumn. If not, contact your account admin. See Query history system table reference. -
Minimum version requirements based on where you set query tags:
- dbt: dbt-databricks 1.11.0
- Power BI: October 2025 release
- Python Connector: v4.1.3
- Node.js Connector: v1.12.0
- Go Connector: v1.9.0
- JDBC driver (OSS): v3.0.3
Query tag scope
Query tags are scoped to Databricks SQL sessions. You can set them when creating a session as a configuration parameter, or within a session using the SET QUERY_TAGS SQL statement. After you set tags, all subsequent statements in the session are associated with those tags.
Set query tags
You can set query tags using session configuration parameters or SQL statements.
Use session configuration parameters
Set query tags using the query_tags configuration parameter (or ssp_query_tags in some drivers) when creating a session. The value is a serialized set of key-value pairs, with a colon (:) separating keys and values, and a comma (,) separating pairs. This string format is accepted by the client interfaces listed in Set query tags from tools and interfaces. For instructions on configuring sessions in your specific client, see the examples below.
If a colon (:), comma (,), or backslash (\) appears in a value, escape it with a leading backslash (\\:, \\,, or \\\\). Backslash (\) must be escaped in both keys and values.
The following example specifies tags team=eng, cost_center=701, a key-only tag exp, and a metadata tag with a JSON blob:
query_tags = team:eng,cost_center:701,exp,metadata:{"foo"\\:"bar"\\,"baz"\\:1}
Use SQL statements
Use the SET QUERY_TAGS statement to set, read, or remove query tags for the current session.
For syntax, parameters, and examples, see SET QUERY_TAGS.
Set query tags from tools and interfaces
Databricks UI
Use the SET QUERY_TAGS SQL statement anywhere you can submit SQL to a warehouse, including the SQL editor, notebooks, and dashboards. See SET QUERY_TAGS.
Databricks SQL Statement Execution API (SEA)
Include the query_tags field in the request body of POST /api/2.0/sql/statements to apply statement-level tags. Tags set this way apply only to that specific statement execution.
curl -X POST "https://${DATABRICKS_HOST}/api/2.0/sql/statements" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer ${DATABRICKS_TOKEN}" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"warehouse_id": "abc123",
"statement": "SELECT * FROM samples.nyctaxi.trips LIMIT 10",
"query_tags": [
{ "key": "team", "value": "engineering" },
{ "key": "env", "value": "prod" }
]
}'
dbt
Minimum version: dbt-databricks 1.11.0
The following reserved query tag keys are set automatically for all dbt runs and can't be overridden:
{
"dbt_model_name": "my_model",
"dbt_core_version": "1.10.7",
"dbt_databricks_version": "1.11.0",
"dbt_materialized": "incremental"
}
Default tags are subject to syntax limitations. Model names that include unescaped colons or commas result in tag_invalid: true in the system table.
You can add custom query tags at both project and model levels. Model configuration takes priority over connection configuration.
Project-level tag (~/.dbt/profiles.yml):
your_profile_name:
target: dev
outputs:
dev:
query_tags: '{"team": "marketing", "cost_center": "3000"}'
Model-level tag (~/.dbt/dbt_project.yml):
name: 'your_project'
version: '1.0.0'
config-version: 2
models:
your_model:
+query_tags: '{"team": "content-marketing"}'
Result with both configurations:
{
"team": "content-marketing",
"cost_center": "3000",
"dbt_model_name": "model.dev.your_model",
"dbt_core_version": "1.10.7",
"dbt_databricks_version": "1.11.0",
"dbt_materialized": "incremental"
}
Power BI
Minimum version: October 2025 release
- Configure the connection to the warehouse.
- Navigate to the Databricks settings dialog, as shown in the following image.
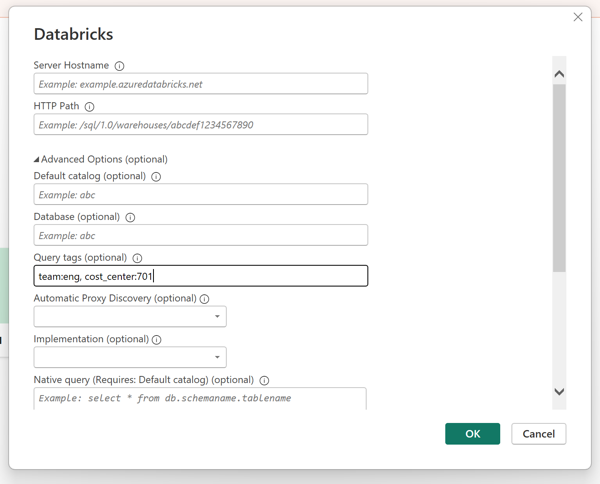
- In the Query tags text box, enter query tags using the session configuration parameter syntax.
- Click OK.
Changing query tags and clicking OK starts a new session. Previously set tags are discarded.
Tableau
- Configure the connection to the warehouse.
- Navigate to the Initial SQL tab.
- Enter query tags using the SET QUERY_TAGS. You can include Tableau parameters in the key or value.
- Click Sign In to save and authenticate.
Changing the Initial SQL and clicking Sign In starts a new session. Previously set tags are discarded.
Python Connector
Minimum version: v4.1.3
from databricks import sql
import os
with sql.connect(
server_hostname = os.getenv("DATABRICKS_SERVER_HOSTNAME"),
http_path = os.getenv("DATABRICKS_HTTP_PATH"),
access_token = os.getenv("DATABRICKS_TOKEN"),
session_configuration = {
'query_tags': 'team:engineering,dashboard:abc123'
}
) as connection:
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
cursor.execute("SELECT * FROM samples.nyctaxi.trips LIMIT 10")
result = cursor.fetchall()
Node.js Connector
Minimum version: v1.12.0
const { DBSQLClient } = require('@databricks/sql');
const client = new DBSQLClient();
client
.connect({
host: process.env.DATABRICKS_SERVER_HOSTNAME,
path: process.env.DATABRICKS_HTTP_PATH,
token: process.env.DATABRICKS_TOKEN,
})
.then(async (client) => {
const session = await client.openSession({
configuration: {
query_tags: 'team:engineering,env:prod',
},
});
const queryOperation = await session.executeStatement('SELECT * FROM samples.nyctaxi.trips LIMIT 10');
const result = await queryOperation.fetchAll();
await queryOperation.close();
await session.close();
await client.close();
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
});
Go Connector
Minimum version: v1.9.0
DSN connection string:
package main
import (
"database/sql"
"fmt"
_ "github.com/databricks/databricks-sql-go"
)
func main() {
dsn := "token:dapi1234@myworkspace.cloud.databricks.com:443/sql/1.0/endpoints/abc123?query_tags=team:engineering,env:prod"
db, err := sql.Open("databricks", dsn)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer db.Close()
rows, err := db.Query("SELECT * FROM samples.nyctaxi.trips LIMIT 10")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer rows.Close()
}
NewConnector with WithSessionParams:
package main
import (
"database/sql"
"os"
dbsql "github.com/databricks/databricks-sql-go"
)
func main() {
connector, err := dbsql.NewConnector(
dbsql.WithAccessToken(os.Getenv("DATABRICKS_ACCESS_TOKEN")),
dbsql.WithServerHostname(os.Getenv("DATABRICKS_HOST")),
dbsql.WithPort(443),
dbsql.WithHTTPPath(os.Getenv("DATABRICKS_HTTP_PATH")),
dbsql.WithSessionParams(map[string]string{
"query_tags": "team:engineering,env:prod",
}),
)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
db := sql.OpenDB(connector)
defer db.Close()
rows, err := db.Query("SELECT * FROM samples.nyctaxi.trips LIMIT 10")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer rows.Close()
}
JDBC driver (OSS)
Minimum version: v3.0.3
Connection URL:
String url = "jdbc:databricks://myworkspace.cloud.databricks.com:443/default;" +
"httpPath=/sql/1.0/endpoints/abc123;" +
"query_tags=team:engineering,env:prod;" +
"AuthMech=3;UID=token;PWD=dapi1234";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url);
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM samples.nyctaxi.trips LIMIT 10");
Properties object:
String url = "jdbc:databricks://myworkspace.cloud.databricks.com:443/default";
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("httpPath", "/sql/1.0/endpoints/abc123");
properties.put("query_tags", "team:engineering,env:prod");
properties.put("AuthMech", "3");
properties.put("UID", "token");
properties.put("PWD", "dapi1234");
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, properties);
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM samples.nyctaxi.trips LIMIT 10");
JDBC driver (Simba)
Connection URL:
String url = "jdbc:databricks://myworkspace.cloud.databricks.com:443;" +
"httpPath=/sql/1.0/endpoints/abc123;" +
"ssp_query_tags=team:engineering,env:prod;" +
"AuthMech=3;UID=token;PWD=dapi1234";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url);
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM samples.nyctaxi.trips LIMIT 10");
Properties object:
String url = "jdbc:databricks://myworkspace.cloud.databricks.com:443";
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("httpPath", "/sql/1.0/endpoints/abc123");
properties.put("ssp_query_tags", "team:engineering,env:prod");
properties.put("AuthMech", "3");
properties.put("UID", "token");
properties.put("PWD", "dapi1234");
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, properties);
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM samples.nyctaxi.trips LIMIT 10");
ODBC driver
Include the ssp_query_tags parameter in your ODBC connection configuration.
Limitations
- Maximum of 20 user-specified tags per query. When using non-SQL interfaces (session configuration parameters), additional tags are discarded and a sentinel tag
tag_truncated: trueis added. - Tag keys and values must not exceed 128 characters. When using non-SQL interfaces (session configuration parameters), tags that are not valid are discarded and
tag_invalidis added. - Tag keys must not contain the characters
,,:,-,/,=, or.. When using non-SQL interfaces (session configuration parameters), tags that are not valid are discarded andtag_invalidis added. SQL statements with invalid tag keys fail with an error at execution time. - Query tags are only supported for Databricks SQL workloads. The
query_tagscolumn is not populated for other compute types. - Databricks may use keys starting with
@@internally. Some connectors already use this prefix. Avoid this prefix to prevent conflicts.
View query tags
Query the system.query.history table to view query tags. You can group and filter by specific keys or key-value pairs.
SELECT statement_id, query_tags, executed_by, start_time
FROM system.query.history
WHERE MAP_CONTAINS_KEY(query_tags, 'team')
AND query_tags['team'] = 'engineering'
ORDER BY start_time DESC
LIMIT 100;
Key-only tags appear with a null value. To filter for them:
WHERE MAP_CONTAINS_KEY(query_tags, 'key') AND query_tags['key'] IS NULL
For more information, see Query history system table reference.