空の検索エンドポイントを特定して削除する
このページでは、空の検索エンドポイントを特定して削除する方法について説明します。 横断検索エンドポイントはワークスペース固有のリソースであるため、このプロセスをワークスペースごとに個別に繰り返す必要があります。
要件
- Python 用 Databricks SDK (
databricks-sdk)。 - Databricks ベクトル検索 Python SDK (
databricks-vectorsearch)。 - 認証が構成されています (OAuth、PAT、または構成プロファイル)。
CAN_MANAGE対象のワークスペースでの一括検索エンドポイントの許可。
Databricks ノートブックまたはローカル Python 環境に必要な SDK をインストールするには、次の手順を実行します。
# In a Databricks notebook
%pip install databricks-sdk databricks-vectorsearch
# In local Python environment
# pip install databricks-sdk databricks-vectorsearch
空のエンドポイントを識別する
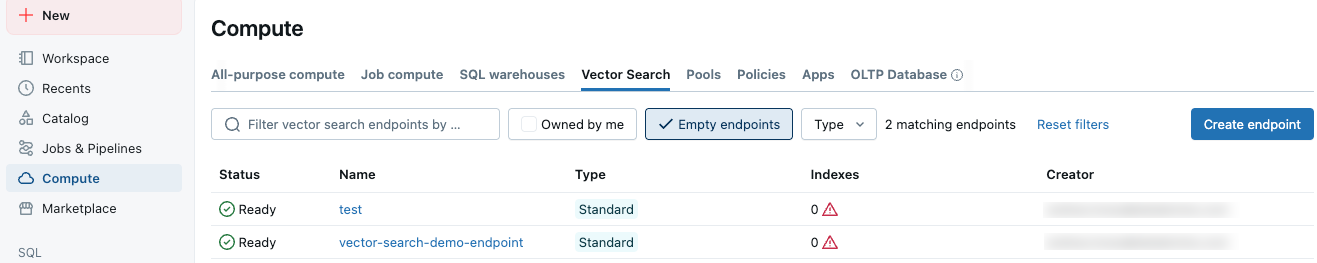
Databricks UI では、連続検索エンドポイント が コンピュート画面の 連続検索 タブに表示されます。 空のエンドポイント チェックボックスを切り替えると、インデックスが関連付けられていないエンドポイントが表示されます。空のエンドポイントには、図に示すように警告の三角形のアイコンも表示されます。
認証
このセクションでは認証オプションについて説明します。
オプション 1. Databricksノートブック内で実行する
Databricks ワークスペース ノートブックでコードを実行すると、認証は自動的に行われます。
from databricks.vector_search.client import VectorSearchClient
# Credentials are picked up automatically from notebook context
client = VectorSearchClient()
オプション2. 個人アクセストークン(PAT)
外部環境の場合は、明示的な資格情報を提供します。
from databricks.vector_search.client import VectorSearchClient
client = VectorSearchClient(
workspace_url="https://<your-instance>.cloud.databricks.com",
personal_access_token="dapiXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX"
)
オプション 3. 構成プロファイルを使用する (複数のワークスペースに推奨)
ホーム ディレクトリに.databrickscfgファイルを作成し、各ワークスペースのプロファイルを含めます。
[DEFAULT]
host = https://workspace1.cloud.databricks.com
token = dapiXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
[PRODUCTION]
host = https://workspace2.cloud.databricks.com
token = dapiYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYY
[DEVELOPMENT]
host = https://workspace3.cloud.databricks.com
token = dapiZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ
構成プロファイルを使用しない場合は、資格情報を直接指定できます。
# Define workspaces with explicit credentials
workspace_configs = [
{
'workspace_url': 'https://workspace1.cloud.databricks.com',
'token': 'dapiXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX'
},
{
'workspace_url': 'https://workspace2.cloud.databricks.com',
'token': 'dapiYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYY'
}
]
# Run cleanup, set `dry_run=False` to perform actual deletion
results = cleanup_multiple_workspaces(workspace_configs, dry_run=True)
単一のワークスペース内のエンドポイントを削除する
ベクトル検索エンドポイントはワークスペース固有です。 以下は、単一のワークスペース内の空のエンドポイントを見つけて削除するための基本的なスクリプトです。複数のワークスペースにわたる空のエンドポイントをクリーンアップするには、 「複数のワークスペースにわたるエンドポイントの削除」を参照してください。
エンドポイントの削除は元に戻せません。削除されるエンドポイントのリストを表示するには、オプションdry_run=Trueを使用します。リストが正しいことを確認したら、 dry_run=Falseを使用してスクリプトを実行します。
from databricks.vector_search.client import VectorSearchClient
def cleanup_empty_endpoints(client, dry_run=True):
"""
Find and delete empty Vector Search endpoints.
Args:
client: VectorSearchClient instance
dry_run: If True, only print what would be deleted without actually deleting
Returns:
List of deleted endpoint names
"""
deleted_endpoints = []
# List all Vector Search endpoints
endpoints = client.list_endpoints()
for endpoint in endpoints["endpoints"]:
# List indexes in this endpoint
indexes = list(client.list_indexes(name=endpoint["name"])['vector_indexes'])
if len(indexes) == 0:
if dry_run:
print(f"[DRY RUN] Would delete empty endpoint: '{endpoint["name"]}'")
else:
print(f"Deleting empty endpoint: '{endpoint["name"]}'")
try:
client.delete_endpoint(endpoint["name"])
deleted_endpoints.append(endpoint["name"])
print(f"✓ Successfully deleted: {endpoint["name"]}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"✗ Failed to delete {endpoint["name"]}: {str(e)}")
else:
print(f"Endpoint '{endpoint["name"]}' has {len(indexes)} indexes - keeping")
return deleted_endpoints
# Example usage
client = VectorSearchClient() # Uses default authentication
# Set `dry_run=False` when you are ready to delete endpoints
deleted = cleanup_empty_endpoints(client, dry_run=True)
print(f"\nTotal endpoints deleted: {len(deleted)}")
複数のワークスペースにわたるエンドポイントを削除する
複数のワークスペースにわたって空のエンドポイントをクリーンアップするには、構成プロファイルを反復処理します。
-
エンドポイントの削除は元に戻せません。削除されるエンドポイントのリストを表示するには、オプション
dry_run=Trueを使用します。リストが正しいことを確認したら、dry_run=Falseを使用してスクリプトを実行します。 -
多数のワークスペースを処理する場合は、API レート制限に注意してください。必要に応じて遅延を追加します。
Pythonimport time
for config in workspace_configs:
# Set `dry_run=False` to perform actual deletion
result = cleanup_workspace(**config, dry_run=True)
time.sleep(2) # Add delay between workspaces
from databricks.sdk import WorkspaceClient
from databricks.vector_search.client import VectorSearchClient
import logging
# Configure logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
def cleanup_workspace(profile_name=None, workspace_url=None, token=None, dry_run=True):
"""
Clean up empty endpoints in a specific workspace.
Args:
profile_name: Name of configuration profile to use
workspace_url: Direct workspace URL (if not using profile)
token: PAT token (if not using profile)
dry_run: If True, only show what would be deleted
Returns:
Dict with cleanup results
"""
try:
# Initialize client based on authentication method
if profile_name:
# Use Databricks SDK to get credentials from profile
w = WorkspaceClient(profile=profile_name)
workspace_url = w.config.host
client = VectorSearchClient(
workspace_url=workspace_url,
personal_access_token=w.config.token
)
logger.info(f"Connected to workspace using profile '{profile_name}': {workspace_url}")
elif workspace_url and token:
client = VectorSearchClient(
workspace_url=workspace_url,
personal_access_token=token
)
logger.info(f"Connected to workspace: {workspace_url}")
else:
# Use default authentication (notebook context)
client = VectorSearchClient()
logger.info("Connected using default authentication")
# Perform cleanup
deleted = cleanup_empty_endpoints(client, dry_run=dry_run)
return {
'workspace': workspace_url or 'default',
'success': True,
'deleted_count': len(deleted),
'deleted_endpoints': deleted
}
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Failed to process workspace: {str(e)}")
return {
'workspace': workspace_url or profile_name or 'default',
'success': False,
'error': str(e)
}
def cleanup_multiple_workspaces(workspace_configs, dry_run=True):
"""
Clean up empty endpoints across multiple workspaces.
Args:
workspace_configs: List of workspace configurations
dry_run: If True, only show what would be deleted
Returns:
Summary of cleanup results
"""
results = []
for config in workspace_configs:
logger.info(f"\n{'='*60}")
result = cleanup_workspace(**config, dry_run=dry_run)
results.append(result)
logger.info(f"{'='*60}\n")
# Print summary
total_deleted = sum(r['deleted_count'] for r in results if r['success'])
successful = sum(1 for r in results if r['success'])
failed = sum(1 for r in results if not r['success'])
logger.info("\n" + "="*60)
logger.info("CLEANUP SUMMARY")
logger.info("="*60)
logger.info(f"Workspaces processed: {len(results)}")
logger.info(f"Successful: {successful}")
logger.info(f"Failed: {failed}")
logger.info(f"Total endpoints deleted: {total_deleted}")
if failed > 0:
logger.warning("\nFailed workspaces:")
for r in results:
if not r['success']:
logger.warning(f" - {r['workspace']}: {r['error']}")
return results
# Example: Clean up using configuration profiles
workspace_configs = [
{'profile_name': 'DEFAULT'},
{'profile_name': 'PRODUCTION'},
{'profile_name': 'DEVELOPMENT'}
]
# Set `dry_run=False` to do actual deletion.
results = cleanup_multiple_workspaces(workspace_configs, dry_run=True)
カスタムフィルタリング
次のように、特定のエンドポイントを削除から除外するカスタム ロジックを追加できます。
def should_delete_endpoint(endpoint, indexes):
"""
Custom logic to determine if an endpoint should be deleted.
Args:
endpoint: Endpoint object
indexes: List of indexes in the endpoint
Returns:
Boolean indicating if endpoint should be deleted
"""
# Don't delete if it has indexes
if len(indexes) > 0:
return False
# Don't delete endpoints with specific naming patterns
protected_patterns = ['prod-', 'critical-', 'do-not-delete']
for pattern in protected_patterns:
if pattern in endpoint.name.lower():
logger.warning(f"Skipping protected endpoint: {endpoint.name}")
return False
# Add more custom logic as needed
return True
結果をエクスポート
監査用にクリーンアップ結果をファイルに保存するには:
import json
from datetime import datetime
def export_results(results, filename=None):
"""Export cleanup results to JSON file."""
if not filename:
timestamp = datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d_%H%M%S')
filename = f'vector_search_cleanup_{timestamp}.json'
with open(filename, 'w') as f:
json.dump({
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat(),
'results': results
}, f, indent=2)
logger.info(f"Results exported to: {filename}")
トラブルシューティング
認証の問題
- PAT トークンが有効であり、期限切れでないことを確認します。
- 構成プロファイルが正しくフォーマットされていることを確認します。
- トークンに必要な権限があることを確認してください。
権限エラー
ユーザーまたはサービスプリンシパルに、連続検索エンドポイントに対するCAN_MANAGE権限があることを確認してください。
ネットワークの問題
プロキシ要件のある環境では、SDK を適切に構成します。
import os
os.environ['HTTPS_PROXY'] = 'http://your-proxy:po
次のステップ
- Lakeflowジョブを使用して、このスクリプトを定期的に実行するようにスケジュールします。
- Infrastructure-as-Codeと統合します。
- クリーンアップの概要に関する電子メールまたは Slack 通知を追加します。
- ワークスペース全体のエンドポイントの使用状況を追跡するためのダッシュボードを作成します。