Criar e gerenciar esquemas de rótulo
Os esquemas de rotulagem definem as perguntas específicas que os especialistas de domínio respondem ao rotular rastros existentes no aplicativo de revisão. Eles estruturam o processo de coleta de feedback, garantindo informações consistentes e relevantes para avaliar seu aplicativo GenAI.
Os esquemas de rotulagem aplicam-se apenas ao usar o aplicativo de revisão para rotular rastreamentos existentes. Eles não são usados para verificar o clima na interface de bate-papo do aplicativo de avaliações.
Como funcionam os esquemas de rótulos
Ao criar uma sessão de rótulo, você a associa a um ou mais esquemas de rótulo. Cada esquema representa uma avaliação associada a um traço. As avaliações são Feedback ou Expectation. Para mais detalhes, consulte o rótulo durante o desenvolvimento.
Os esquemas controlam:
- A questão apresentada aos revisores.
- O método de entrada (por exemplo, dropdown ou caixa de texto).
- Regras e restrições de validação.
- Instruções e comentários opcionais.
esquemas de rótulo para juízes LLM integrados
MLflow fornece nomes de esquema predefinidos para os juízes LLM integrados que usam expectativas. Você pode criar esquemas personalizados usando esses nomes para garantir compatibilidade com a funcionalidade de avaliação integrada.
A tabela a seguir mostra os esquemas de rótulos predefinidos e sua utilização.
Nome do esquema | Uso | Usado por esses juízes femininos |
|---|---|---|
| Reúne as instruções ideais que o aplicativo GenAI deve seguir para uma solicitação. | |
| Reúne declarações factuais que devem ser incluídas para garantir a correção. | |
| Reúne a resposta completa e verdadeira. |
Exemplos de esquemas de rótulo para juízes LLM integrados
Para obter detalhes, consulte a referência da API.
import mlflow.genai.label_schemas as schemas
from mlflow.genai.label_schemas import LabelSchemaType, InputTextList, InputText
# Schema for collecting expected facts
expected_facts_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name=schemas.EXPECTED_FACTS,
type=LabelSchemaType.EXPECTATION,
title="Expected facts",
input=InputTextList(max_length_each=1000),
instruction="Please provide a list of facts that you expect to see in a correct response.",
overwrite=True
)
# Schema for collecting guidelines
guidelines_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name=schemas.GUIDELINES,
type=LabelSchemaType.EXPECTATION,
title="Guidelines",
input=InputTextList(max_length_each=500),
instruction="Please provide guidelines that the model's output is expected to adhere to.",
overwrite=True
)
# Schema for collecting expected response
expected_response_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name=schemas.EXPECTED_RESPONSE,
type=LabelSchemaType.EXPECTATION,
title="Expected response",
input=InputText(),
instruction="Please provide a correct agent response.",
overwrite=True
)
Criar esquemas de rótulos personalizados
Para ter mais controle sobre o feedback que você coleta, crie um esquema de rótulos personalizado usando a interface do usuário ou API MLflow .
Os esquemas são definidos para experimentos, portanto, os nomes dos esquemas devem ser exclusivos dentro do seu experimento MLflow.
Os esquemas são de dois tipos:
feedbackAvaliações subjetivas, como classificações, preferências ou opiniões.expectationVerdade objetiva fundamental, como respostas corretas ou comportamento esperado.
Para mais detalhes, consulte o rótulo durante o desenvolvimento. Para definições de parâmetros, consulte a referência da API.
Crie esquemas personalizados usando a interface do usuário.
Para criar um esquema personalizado na interface do usuário do MLflow:
-
No workspace Databricks , na barra lateral esquerda, clique em Experimentos .
-
Clique no nome do seu experimento para abri-lo.
-
Clique em "rótulo schemas" na barra lateral.
-
Se um esquema de rótulo existente for exibido, você poderá editá-lo. Para criar ou adicionar um novo esquema de rótulo, clique em Adicionar esquema de rótulo e edite os campos.
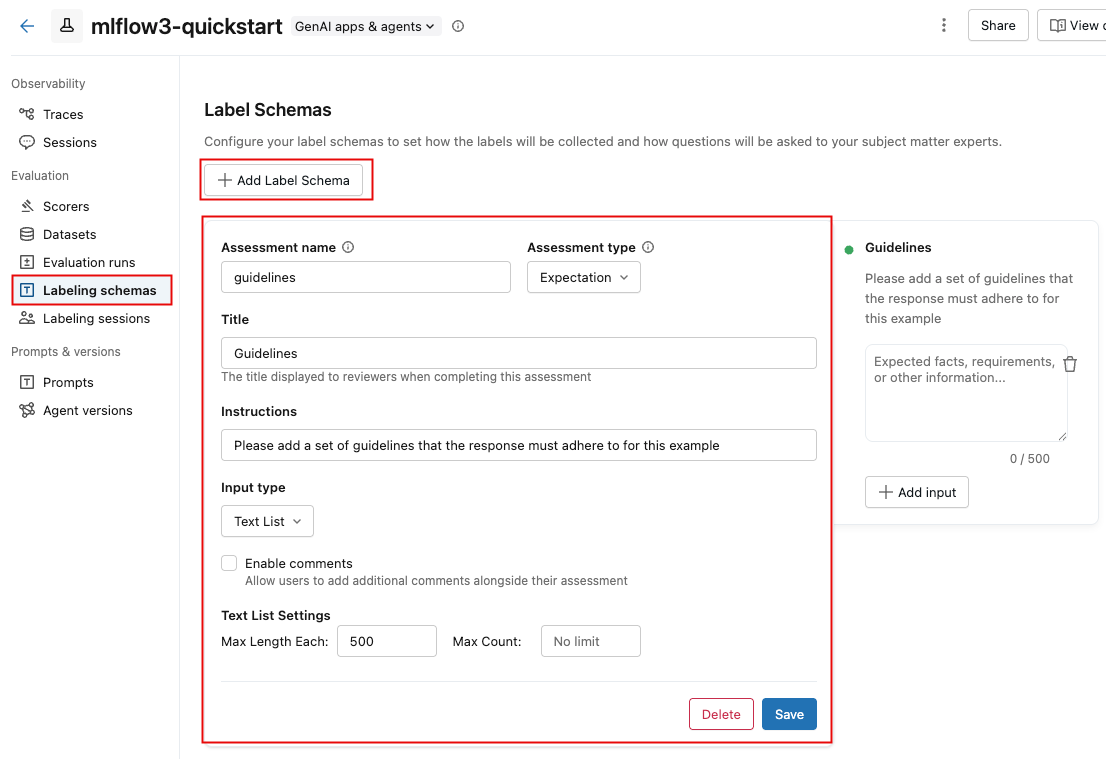
Ao selecionar o tipo de entrada , os campos abaixo dele mudam para permitir que você especifique requisitos detalhados, como limites de comprimento para texto, opções para escolhas categóricas ou um intervalo numérico.
À medida que você insere informações nos campos, a caixa à direita é atualizada para refletir o esquema que você está criando.
-
Quando terminar, clique em Salvar .
O vídeo a seguir mostra o processo.

Crie esquemas personalizados usando a API.
Você pode criar esquemas usando mlflow.genai.label_schemas.create_label_schema(). Todos os esquemas requerem um nome, tipo, título e especificação de entrada.
Exemplo de esquema básico
import mlflow.genai.label_schemas as schemas
from mlflow.genai.label_schemas import InputCategorical, InputText
# Create a feedback schema for rating response quality
quality_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name="response_quality",
type="feedback",
title="How would you rate the overall quality of this response?",
input=InputCategorical(options=["Poor", "Fair", "Good", "Excellent"]),
instruction="Consider accuracy, relevance, and helpfulness when rating."
)
Exemplo de feedback de esquema personalizado
import mlflow.genai.label_schemas as schemas
from mlflow.genai.label_schemas import InputCategorical, InputTextList
# Feedback schema for subjective assessment
tone_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name="response_tone",
type="feedback",
title="Is the response tone appropriate for the context?",
input=InputCategorical(options=["Too formal", "Just right", "Too casual"]),
enable_comment=True # Allow additional comments
)
Exemplo de expectativa de esquema personalizado
# Expectation schema for ground truth
facts_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name="required_facts",
type="expectation",
title="What facts must be included in a correct response?",
input=InputTextList(max_count=5, max_length_each=200),
instruction="List key facts that any correct response must contain."
)
gerenciar rótulo esquemas
Utilizando a API, você pode listar, atualizar e excluir esquemas de rótulos.
Listar esquemas
Para obter informações sobre um esquema existente, use a API get_label_schema. Você deve fornecer o nome do esquema. Conforme demonstrado no exemplo a seguir. Para obter detalhes, consulte a referência da API: get_label_schema.
import mlflow.genai.label_schemas as schemas
# Get an existing schema
schema = schemas.get_label_schema("response_quality")
print(f"Schema: {schema.name}")
print(f"Type: {schema.type}")
print(f"Title: {schema.title}")
Atualizar esquemas
Para atualizar um esquema existente, use a API create_label_schema e defina o parâmetro overwrite como True. Para obter detalhes, consulte a referência da API: create_label_schema.
import mlflow.genai.label_schemas as schemas
from mlflow.genai.label_schemas import InputCategorical
# Update by recreating with overwrite=True
updated_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name="response_quality",
type="feedback",
title="Rate the response quality (updated question)",
input=InputCategorical(options=["Excellent", "Good", "Fair", "Poor", "Very Poor"]),
instruction="Updated: Focus on factual accuracy above all else.",
overwrite=True # Replace existing schema
)
Excluir esquemas
O exemplo a seguir mostra como excluir um esquema de rótulo. Para obter detalhes, consulte a referência da API: delete_label_schema.
import mlflow.genai.label_schemas as schemas
# Remove a schema that's no longer needed
schemas.delete_label_schema("old_schema_name")
Tipos de entrada para esquemas personalizados
O MLflow suporta os tipos de entrada mostrados na tabela para coletar diferentes tipos de feedback. As seções a seguir mostram exemplos para cada tipo.
Tipo de entrada | Descrição e utilização |
|---|---|
| Um menu suspenso de seleção única. Utilize para opções mutuamente exclusivas, como classificações ou avaliações. |
| Um menu suspenso de seleção múltipla. Utilize esta opção quando for possível selecionar várias opções. |
| Uma caixa de texto livre. Utilize quando a resposta for aberta, como explicações detalhadas ou feedback personalizado. |
| Várias caixas de texto livre. Utilize para listas de itens de texto, como fatos ou requisitos. |
| Um intervalo numérico. Utilize para classificações ou pontuações numéricas. |
InputCategorical
from mlflow.genai.label_schemas import InputCategorical
# Rating scale
rating_input = InputCategorical(
options=["1 - Poor", "2 - Below Average", "3 - Average", "4 - Good", "5 - Excellent"]
)
# Binary choice
safety_input = InputCategorical(options=["Safe", "Unsafe"])
# Multiple categories
error_type_input = InputCategorical(
options=["Factual Error", "Logical Error", "Formatting Error", "No Error"]
)
InputCategoricalList
from mlflow.genai.label_schemas import InputCategoricalList
# Multiple error types can be present
errors_input = InputCategoricalList(
options=[
"Factual inaccuracy",
"Missing context",
"Inappropriate tone",
"Formatting issues",
"Off-topic content"
]
)
# Multiple content types
content_input = InputCategoricalList(
options=["Technical details", "Examples", "References", "Code samples"]
)
InputText
from mlflow.genai.label_schemas import InputText
# General feedback
feedback_input = InputText(max_length=500)
# Specific improvement suggestions
improvement_input = InputText(
max_length=200 # Limit length for focused feedback
)
# Short answers
summary_input = InputText(max_length=100)
InputTextList
from mlflow.genai.label_schemas import InputTextList
# List of factual errors
errors_input = InputTextList(
max_count=10, # Maximum 10 errors
max_length_each=150 # Each error description limited to 150 chars
)
# Missing information
missing_input = InputTextList(
max_count=5,
max_length_each=200
)
# Improvement suggestions
suggestions_input = InputTextList(max_count=3) # No length limit per item
InputNumeric
from mlflow.genai.label_schemas import InputNumeric
# Confidence score
confidence_input = InputNumeric(
min_value=0.0,
max_value=1.0
)
# Rating scale
rating_input = InputNumeric(
min_value=1,
max_value=10
)
# Cost estimate
cost_input = InputNumeric(min_value=0) # No maximum limit
Exemplos completos
Avaliação do atendimento ao cliente
Aqui está um exemplo abrangente para avaliar as respostas do atendimento ao cliente:
import mlflow.genai.label_schemas as schemas
from mlflow.genai.label_schemas import (
InputCategorical,
InputCategoricalList,
InputText,
InputTextList,
InputNumeric
)
# Overall quality rating
quality_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name="service_quality",
type="feedback",
title="Rate the overall quality of this customer service response",
input=InputCategorical(options=["Excellent", "Good", "Average", "Poor", "Very Poor"]),
instruction="Consider helpfulness, accuracy, and professionalism.",
enable_comment=True
)
# Issues identification
issues_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name="response_issues",
type="feedback",
title="What issues are present in this response? (Select all that apply)",
input=InputCategoricalList(options=[
"Factually incorrect information",
"Unprofessional tone",
"Doesn't address the question",
"Too vague or generic",
"Contains harmful content",
"No issues identified"
]),
instruction="Select all issues you identify. Choose 'No issues identified' if the response is problem-free."
)
# Expected resolution steps
resolution_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name="expected_resolution",
type="expectation",
title="What steps should be included in the ideal resolution?",
input=InputTextList(max_count=5, max_length_each=200),
instruction="List the key steps a customer service rep should take to properly resolve this issue."
)
# Confidence in assessment
confidence_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name="assessment_confidence",
type="feedback",
title="How confident are you in your assessment?",
input=InputNumeric(min_value=1, max_value=10),
instruction="Rate from 1 (not confident) to 10 (very confident)"
)
Revisão de informações médicas
Exemplo de avaliação de respostas de informações médicas:
import mlflow.genai.label_schemas as schemas
from mlflow.genai.label_schemas import InputCategorical, InputTextList, InputNumeric
# Safety assessment
safety_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name="medical_safety",
type="feedback",
title="Is this medical information safe and appropriate?",
input=InputCategorical(options=[
"Safe - appropriate general information",
"Concerning - may mislead patients",
"Dangerous - could cause harm if followed"
]),
instruction="Assess whether the information could be safely consumed by patients."
)
# Required disclaimers
disclaimers_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name="required_disclaimers",
type="expectation",
title="What medical disclaimers should be included?",
input=InputTextList(max_count=3, max_length_each=300),
instruction="List disclaimers that should be present (e.g., 'consult your doctor', 'not professional medical advice')."
)
# Accuracy of medical facts
accuracy_schema = schemas.create_label_schema(
name="medical_accuracy",
type="feedback",
title="Rate the factual accuracy of the medical information",
input=InputNumeric(min_value=0, max_value=100),
instruction="Score from 0 (completely inaccurate) to 100 (completely accurate)"
)
Integração com sessões de rótulo
O exemplo a seguir mostra como usar seus esquemas em uma sessão de rótulo:
import mlflow.genai.label_schemas as schemas
# Schemas are automatically available when creating labeling sessions
# The Review App will present questions based on your schema definitions
# Example: Using schemas in a session (conceptual - actual session creation
# happens through the Review App UI or other APIs)
session_schemas = [
"service_quality", # Your custom schema
"response_issues", # Your custom schema
schemas.EXPECTED_FACTS # Built-in schema
]
Melhores práticas
Projeto de esquema
- Elabore perguntas como instruções claras e específicas.
- Forneça contexto aos revisores do guia.
- Defina limites razoáveis para o tamanho do texto e a quantidade de itens na lista.
- Para entradas categóricas, assegure-se de que as opções sejam mutuamente exclusivas e abrangentes.
Gerenciamento de esquemas
- Use nomes descritivos e consistentes em todos os seus esquemas.
- Ao atualizar esquemas, considere o impacto nas sessões existentes.
- Exclua esquemas não utilizados para manter seu workspace organizado.
Próximos passos
- rótulo traços existentes - Aplique seus esquemas para coletar feedback estruturado
- Criar sessões de rótulo - Organizar o fluxo de trabalho de revisão usando seus esquemas
- Criar um conjunto de dados de avaliação - Transformar os dados do rótulo em um conjunto de dados de teste