Rastreamento Anthropic
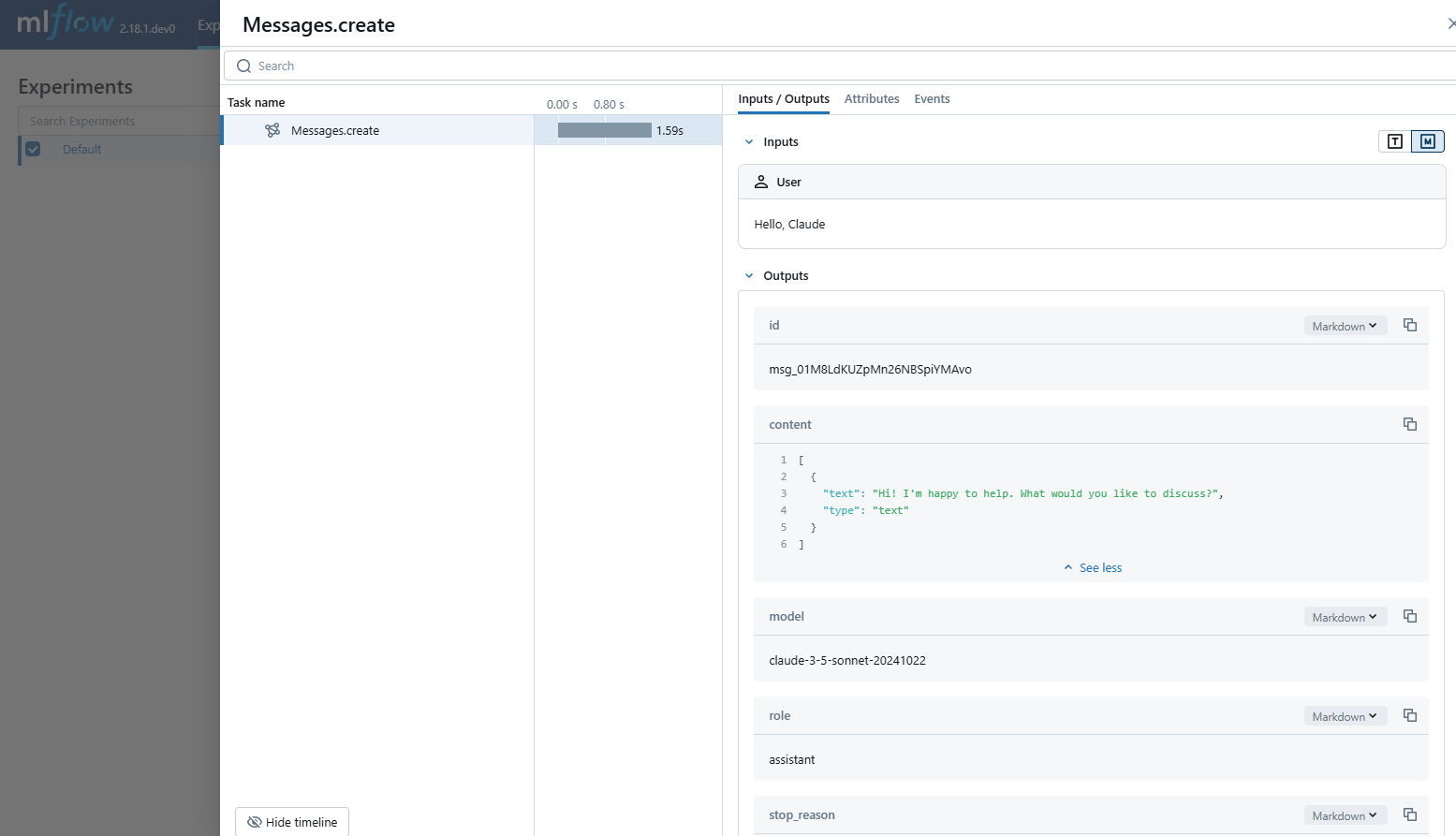
O MLflow Tracing oferece recursos de rastreamento automático para LLMs da Anthropic. Ao ativar o rastreamento automático
para Anthropic chamando a função mlflow.anthropic.autolog MLflow irá capturar rastreamentos aninhados e log á-los para o MLflow Experimento ativo após a invocação de Anthropic Python SDK.
import mlflow
mlflow.anthropic.autolog()
MLflow O rastreamento captura automaticamente as seguintes informações sobre as chamadas do site Anthropic:
- Solicitações e respostas de conclusão
- Latências
- Nome do modelo
- Metadados adicionais, como
temperature,max_tokens, se especificados. - Chamada de função se retornada na resposta
- Qualquer exceção, se levantada
Em serverless compute clusters, o autologging não é ativado automaticamente. Você deve chamar explicitamente mlflow.anthropic.autolog() para ativar o rastreamento automático para essa integração.
Atualmente, a integração do MLflow Anthropic só oferece suporte ao rastreamento de chamadas síncronas para interações de texto. As APIs assíncronas não são rastreadas, e as entradas completas não podem ser registradas para entradas multimodais.
Pré-requisitos
Para usar o MLflow Tracing com o Anthropic, o senhor precisa instalar o MLflow e o Anthropic SDK.
- Development
- Production
Para ambientes de desenvolvimento, instale o pacote completo do MLflow com os extras do Databricks e anthropic:
pip install --upgrade "mlflow[databricks]>=3.1" anthropic
O pacote completo do mlflow[databricks] inclui todos os recursos para desenvolvimento local e experimentação no Databricks.
Para implantações de produção, instale mlflow-tracing e anthropic:
pip install --upgrade mlflow-tracing anthropic
O pacote mlflow-tracing é otimizado para uso na produção.
O MLflow 3 é altamente recomendado para obter a melhor experiência de rastreamento com o Anthropic.
Antes de executar os exemplos abaixo, o senhor precisará configurar seu ambiente:
Para usuários fora do Databricks Notebook : Defina seu Databricks variável de ambiente:
export DATABRICKS_HOST="https://your-workspace.cloud.databricks.com"
export DATABRICKS_TOKEN="your-personal-access-token"
Para usuários do Databricks Notebook : Essas credenciais são definidas automaticamente para o senhor.
API chave : Certifique-se de que seu Anthropic API key esteja configurado. Para uso em produção, recomendamos o uso de Mosaic AI Gateway ou Databricks secrets em vez de variável de ambiente:
export ANTHROPIC_API_KEY="your-anthropic-api-key"
APIs suportadas
O MLflow oferece suporte ao rastreamento automático para as seguintes APIs Anthropic:
Conclusão do bate-papo | Chamada de função | transmissão | Assíncrono | Imagem | Batch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
✅ | ✅ | ✅ (*1) |
(*1) O suporte a assíncrono foi adicionado no MLflow 2.21.0.
Para solicitar suporte para APIs adicionais, abra uma solicitação de recurso no GitHub.
Exemplo básico
import anthropic
import mlflow
import os
# Ensure your ANTHROPIC_API_KEY is set in your environment
# os.environ["ANTHROPIC_API_KEY"] = "your-anthropic-api-key" # Uncomment and set if not globally configured
# Enable auto-tracing for Anthropic
mlflow.anthropic.autolog()
# Set up MLflow tracking to Databricks
mlflow.set_tracking_uri("databricks")
mlflow.set_experiment("/Shared/anthropic-tracing-demo")
# Configure your API key.
client = anthropic.Anthropic(api_key=os.environ["ANTHROPIC_API_KEY"])
# Use the create method to create new message.
message = client.messages.create(
model="claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022",
max_tokens=1024,
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "Hello, Claude"},
],
)
Para ambientes de produção, sempre use Mosaic AI Gateay ou Databricks secrets em vez de valores codificados ou variáveis de ambiente.
Assíncrono
import anthropic
import mlflow
import os
# Ensure your ANTHROPIC_API_KEY is set in your environment
# os.environ["ANTHROPIC_API_KEY"] = "your-anthropic-api-key" # Uncomment and set if not globally configured
# Enable trace logging
mlflow.anthropic.autolog()
# Set up MLflow tracking to Databricks if not already configured
# mlflow.set_tracking_uri("databricks")
# mlflow.set_experiment("/Shared/anthropic-async-demo")
client = anthropic.AsyncAnthropic()
response = await client.messages.create(
model="claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022",
max_tokens=1024,
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "Hello, Claude"},
],
)
Exemplo avançado: Tool Calling Agent
O MLflow Tracing captura automaticamente a resposta de chamada de ferramenta dos modelos Anthropic. A instrução da função na resposta será destacada na interface do usuário de rastreamento. Além disso, o senhor pode anotar a função da ferramenta com o decorador @mlflow.trace para criar um intervalo para a execução da ferramenta.
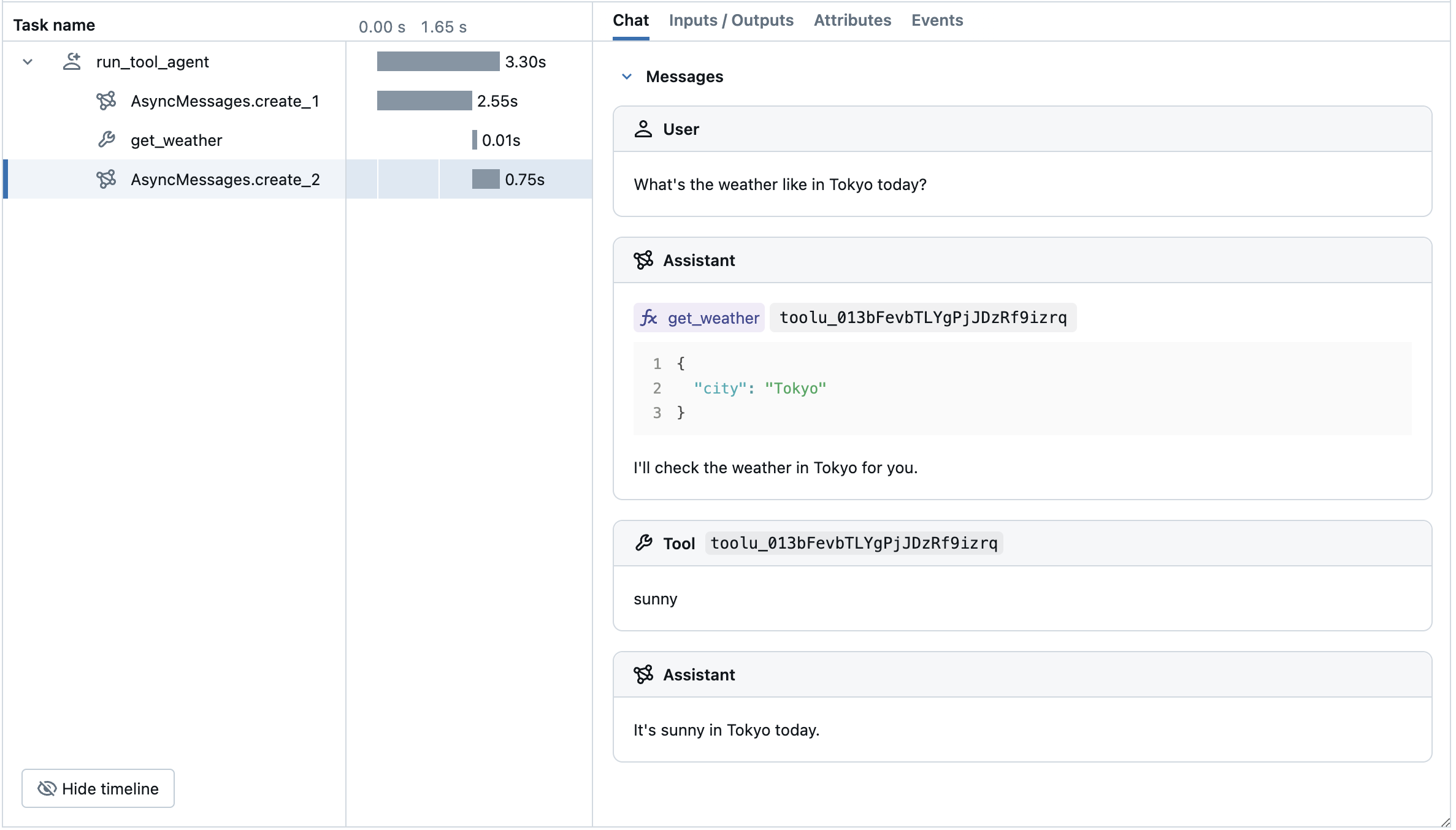
O exemplo a seguir implementa um agente de chamada de função simples usando o Anthropic Tool Calling e o MLflow Tracing for Anthropic. O exemplo também usa o Anthropic SDK assíncrono para que o agente possa lidar com invocações concorrentes sem bloqueio.
import json
import anthropic
import mlflow
import asyncio
from mlflow.entities import SpanType
import os
# Ensure your ANTHROPIC_API_KEY is set in your environment
# os.environ["ANTHROPIC_API_KEY"] = "your-anthropic-api-key" # Uncomment and set if not globally configured
# Set up MLflow tracking to Databricks if not already configured
# mlflow.set_tracking_uri("databricks")
# mlflow.set_experiment("/Shared/anthropic-tool-agent-demo")
# Assuming autolog is enabled globally or called earlier
# mlflow.anthropic.autolog()
client = anthropic.AsyncAnthropic()
model_name = "claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022"
# Define the tool function. Decorate it with `@mlflow.trace` to create a span for its execution.
@mlflow.trace(span_type=SpanType.TOOL)
async def get_weather(city: str) -> str:
if city == "Tokyo":
return "sunny"
elif city == "Paris":
return "rainy"
return "unknown"
tools = [
{
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "Returns the weather condition of a given city.",
"input_schema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {"city": {"type": "string"}},
"required": ["city"],
},
}
]
_tool_functions = {"get_weather": get_weather}
# Define a simple tool calling agent
@mlflow.trace(span_type=SpanType.AGENT)
async def run_tool_agent(question: str):
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": question}]
# Invoke the model with the given question and available tools
ai_msg = await client.messages.create(
model=model_name,
messages=messages,
tools=tools,
max_tokens=2048,
)
messages.append({"role": "assistant", "content": ai_msg.content})
# If the model requests tool call(s), invoke the function with the specified arguments
tool_calls = [c for c in ai_msg.content if c.type == "tool_use"]
for tool_call in tool_calls:
if tool_func := _tool_functions.get(tool_call.name):
tool_result = await tool_func(**tool_call.input)
else:
raise RuntimeError("An invalid tool is returned from the assistant!")
messages.append(
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "tool_result",
"tool_use_id": tool_call.id,
"content": tool_result,
}
],
}
)
# Send the tool results to the model and get a new response
response = await client.messages.create(
model=model_name,
messages=messages,
max_tokens=2048,
)
return response.content[-1].text
# Run the tool calling agent
cities = ["Tokyo", "Paris", "Sydney"]
questions = [f"What's the weather like in {city} today?" for city in cities]
answers = await asyncio.gather(*(run_tool_agent(q) for q in questions))
for city, answer in zip(cities, answers):
print(f"{city}: {answer}")
Desativar o rastreamento automático
O rastreamento automático para o Anthropic pode ser desativado globalmente chamando mlflow.anthropic.autolog(disable=True) ou mlflow.autolog(disable=True).