システムテーブルによるジョブのコストとパフォーマンスの監視
この記事では、システムテーブルを使用して、アカウントのLakeflowジョブとパイプラインのコストとパフォーマンスを監視する方法の例を示します。
これらのクエリは、ジョブ コンピュートとサーバレス コンピュートでのジョブ実行のコストのみを計算します。 SQLウェアハウスおよび汎用コンピュートで実行されるジョブは、ジョブとして請求されないため、コスト属性から除外されます。
これらのクエリは、現在のワークスペースのクラウド リージョン外のワークスペースからレコードを返しません。 現在のリージョン外のワークスペースからジョブのコストを監視するには、そのリージョンにデプロイされたワークスペースでこれらのクエリを実行します。
必要条件
これらのシステムテーブルにアクセスするには、ユーザーは次のいずれかを行う必要があります。
- メタストア管理者とアカウント管理者の両方である、または
- システム スキーマに対する
USE権限とSELECT権限を持っている。 システムテーブルへのアクセス権の付与を参照してください。
Lakeflow モニタリングダッシュボード
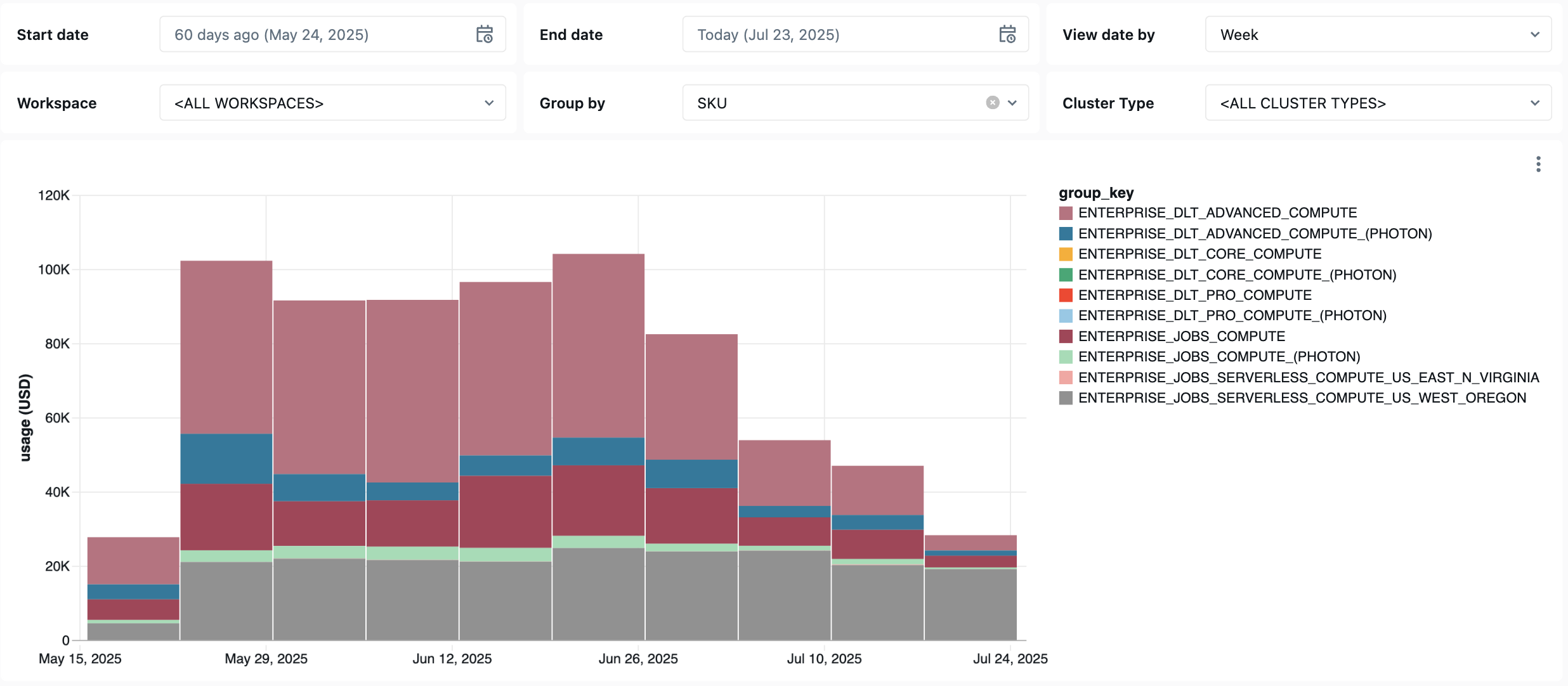
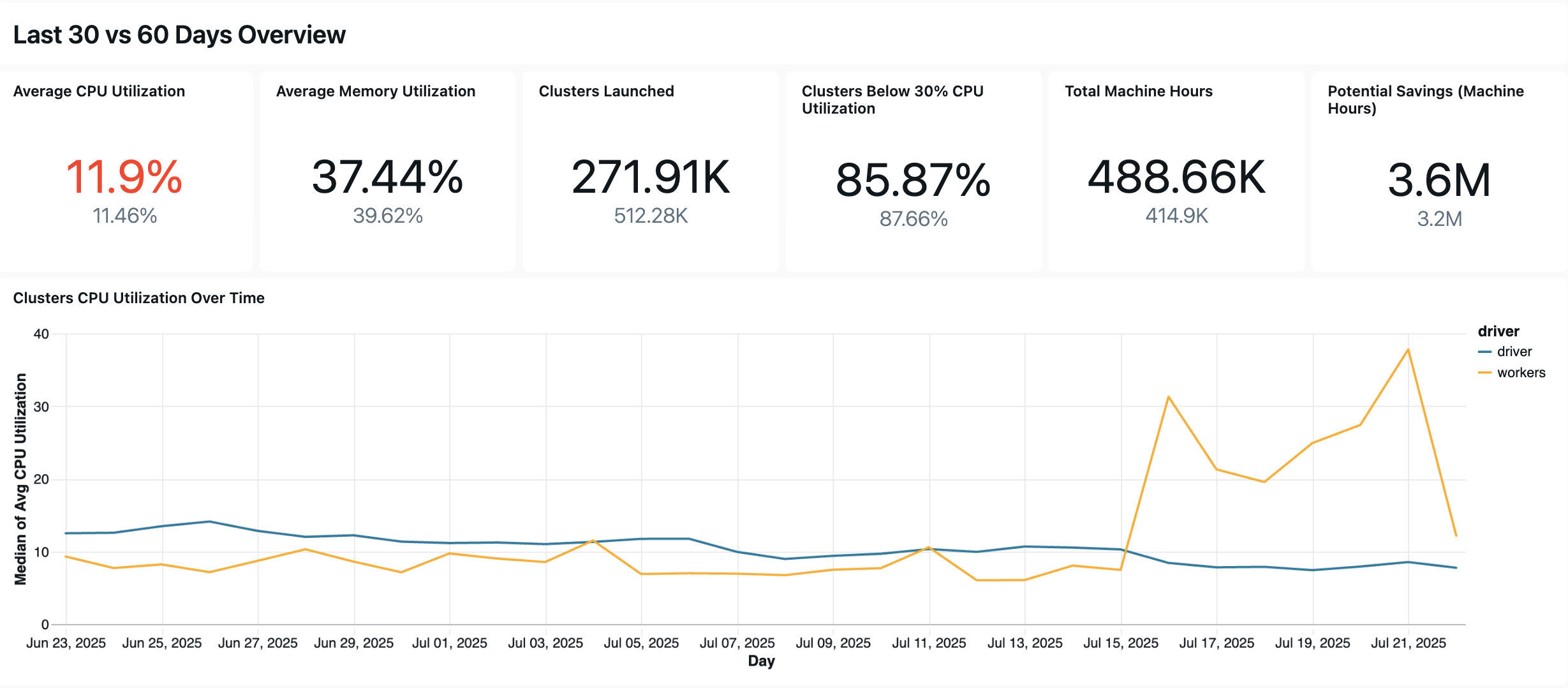
次のダッシュボードでは、システムテーブルを使用して、 Lakeflow ジョブとパイプライン、および運用の正常性を包括的に監視します。 これには、パフォーマンス追跡、障害監視、リソース使用率などの一般的なユースケースが含まれます。
ダッシュボードのインポート
- ダッシュボードの JSON ファイルを Databricks GitHub リポジトリからダウンロードします。
- ダッシュボードをワークスペースにインポートします。 ダッシュボードのインポート手順については、「 ダッシュボード ファイルのインポート」を参照してください。
コスト監視クエリ
ダッシュボードの次のクエリは、ジョブ コスト モニタリング機能を示しています。
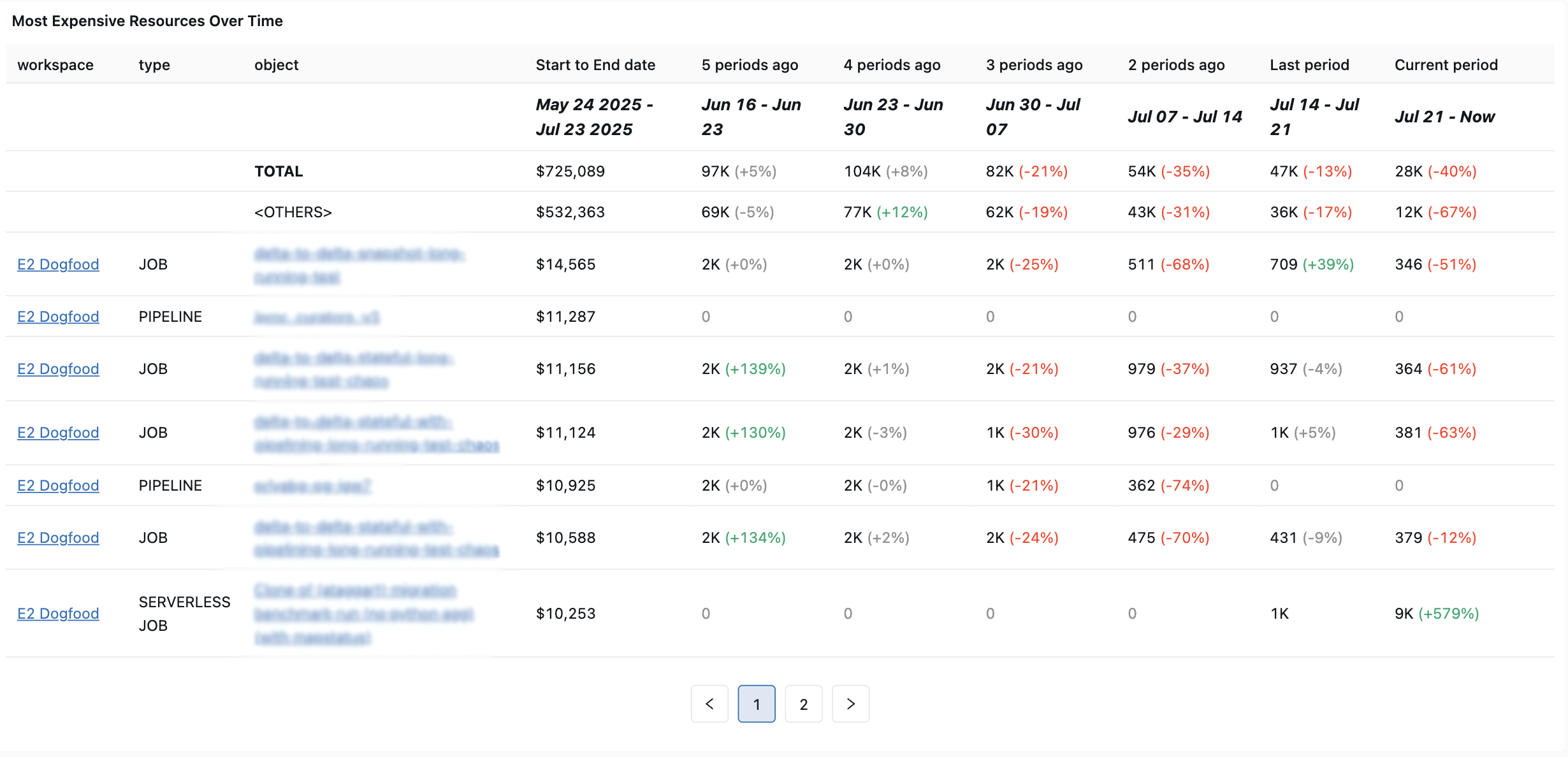
最も高コストなジョブ (過去30日間)
このクエリーは、過去 30 日間で最も支出が多かったジョブを特定します。
with list_cost_per_job as (
SELECT
t1.workspace_id,
t1.usage_metadata.job_id,
COUNT(DISTINCT t1.usage_metadata.job_run_id) as runs,
SUM(t1.usage_quantity * list_prices.pricing.default) as list_cost,
first(identity_metadata.run_as, true) as run_as,
first(t1.custom_tags, true) as custom_tags,
MAX(t1.usage_end_time) as last_seen_date
FROM system.billing.usage t1
INNER JOIN system.billing.list_prices list_prices on
t1.cloud = list_prices.cloud and
t1.sku_name = list_prices.sku_name and
t1.usage_start_time >= list_prices.price_start_time and
(t1.usage_end_time <= list_prices.price_end_time or list_prices.price_end_time is null)
WHERE
t1.billing_origin_product = "JOBS"
AND t1.usage_date >= CURRENT_DATE() - INTERVAL 30 DAY
GROUP BY ALL
),
most_recent_jobs as (
SELECT
*,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY workspace_id, job_id ORDER BY change_time DESC) as rn
FROM
system.lakeflow.jobs QUALIFY rn=1
)
SELECT
t2.name,
t1.job_id,
t1.workspace_id,
t1.runs,
t1.run_as,
SUM(list_cost) as list_cost,
t1.last_seen_date
FROM list_cost_per_job t1
LEFT JOIN most_recent_jobs t2 USING (workspace_id, job_id)
GROUP BY ALL
ORDER BY list_cost DESC
最もコストの高いジョブ実行 (過去 30 日間)
このクエリーは、過去 30 日間で最も支出が多かったジョブ実行を特定します。
with list_cost_per_job_run as (
SELECT
t1.workspace_id,
t1.usage_metadata.job_id,
t1.usage_metadata.job_run_id as run_id,
SUM(t1.usage_quantity * list_prices.pricing.default) as list_cost,
first(identity_metadata.run_as, true) as run_as,
first(t1.custom_tags, true) as custom_tags,
MAX(t1.usage_end_time) as last_seen_date
FROM system.billing.usage t1
INNER JOIN system.billing.list_prices list_prices on
t1.cloud = list_prices.cloud and
t1.sku_name = list_prices.sku_name and
t1.usage_start_time >= list_prices.price_start_time and
(t1.usage_end_time <= list_prices.price_end_time or list_prices.price_end_time is null)
WHERE
t1.billing_origin_product = 'JOBS'
AND t1.usage_date >= CURRENT_DATE() - INTERVAL 30 DAY
GROUP BY ALL
),
most_recent_jobs as (
SELECT
*,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY workspace_id, job_id ORDER BY change_time DESC) as rn
FROM
system.lakeflow.jobs QUALIFY rn=1
)
SELECT
t1.workspace_id,
t2.name,
t1.job_id,
t1.run_id,
t1.run_as,
SUM(list_cost) as list_cost,
t1.last_seen_date
FROM list_cost_per_job_run t1
LEFT JOIN most_recent_jobs t2 USING (workspace_id, job_id)
GROUP BY ALL
ORDER BY list_cost DESC
支出傾向分析(7-14日)
このクエリーは、過去 2 週間でリストコストの支出の増加が最も大きかったジョブを特定します。
with job_run_timeline_with_cost as (
SELECT
t1.*,
t1.usage_metadata.job_id as job_id,
t1.identity_metadata.run_as as run_as,
t1.usage_quantity * list_prices.pricing.default AS list_cost
FROM system.billing.usage t1
INNER JOIN system.billing.list_prices list_prices
ON
t1.cloud = list_prices.cloud AND
t1.sku_name = list_prices.sku_name AND
t1.usage_start_time >= list_prices.price_start_time AND
(t1.usage_end_time <= list_prices.price_end_time or list_prices.price_end_time is NULL)
WHERE
t1.billing_origin_product = 'JOBS' AND
t1.usage_date >= CURRENT_DATE() - INTERVAL 14 DAY
),
most_recent_jobs as (
SELECT
*,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY workspace_id, job_id ORDER BY change_time DESC) as rn
FROM
system.lakeflow.jobs QUALIFY rn=1
)
SELECT
t2.name
,t1.workspace_id
,t1.job_id
,t1.sku_name
,t1.run_as
,Last7DaySpend
,Last14DaySpend
,last7DaySpend - last14DaySpend as Last7DayGrowth
,try_divide( (last7DaySpend - last14DaySpend) , last14DaySpend) * 100 AS Last7DayGrowthPct
FROM
(
SELECT
workspace_id,
job_id,
run_as,
sku_name,
SUM(list_cost) AS spend
,SUM(CASE WHEN usage_end_time BETWEEN date_add(current_date(), -8) AND date_add(current_date(), -1) THEN list_cost ELSE 0 END) AS Last7DaySpend
,SUM(CASE WHEN usage_end_time BETWEEN date_add(current_date(), -15) AND date_add(current_date(), -8) THEN list_cost ELSE 0 END) AS Last14DaySpend
FROM job_run_timeline_with_cost
GROUP BY ALL
) t1
LEFT JOIN most_recent_jobs t2 USING (workspace_id, job_id)
ORDER BY
Last7DayGrowth DESC
LIMIT 100
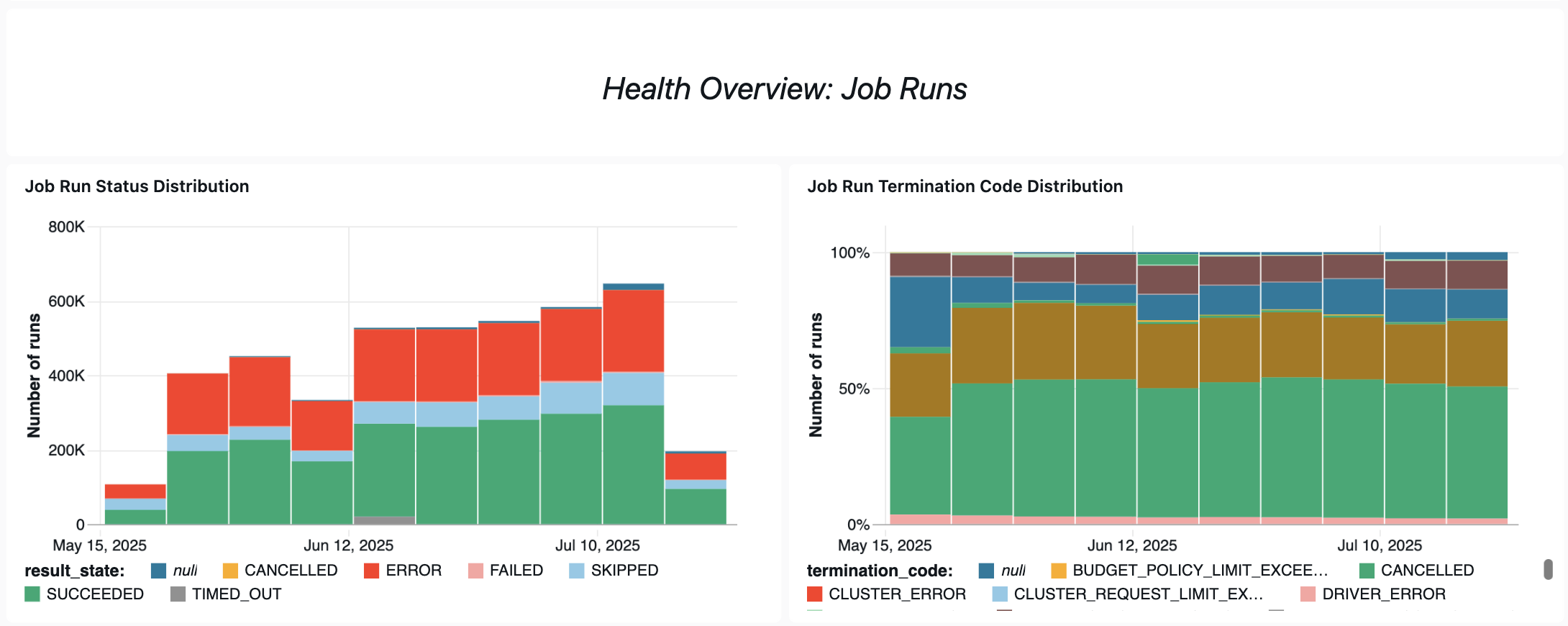
運用の正常性クエリ
ここでは、このダッシュボードがジョブのパフォーマンスと信頼性の追跡に役立つ方法をいくつか紹介します。
失敗したジョブの分析
このクエリは、過去 30 日間に失敗した実行の数が多いジョブに関する情報を返します。ジョブの実行回数、失敗回数、成功率、および失敗した実行のコストを表示できます。
with job_run_timeline_with_cost as (
SELECT
t1.*,
t1.identity_metadata.run_as as run_as,
t2.job_id,
t2.run_id,
t2.result_state,
t1.usage_quantity * list_prices.pricing.default as list_cost
FROM system.billing.usage t1
INNER JOIN system.lakeflow.job_run_timeline t2
ON
t1.workspace_id=t2.workspace_id
AND t1.usage_metadata.job_id = t2.job_id
AND t1.usage_metadata.job_run_id = t2.run_id
AND t1.usage_start_time >= date_trunc("Hour", t2.period_start_time)
AND t1.usage_start_time < date_trunc("Hour", t2.period_end_time) + INTERVAL 1 HOUR
INNER JOIN system.billing.list_prices list_prices on
t1.cloud = list_prices.cloud and
t1.sku_name = list_prices.sku_name and
t1.usage_start_time >= list_prices.price_start_time and
(t1.usage_end_time <= list_prices.price_end_time or list_prices.price_end_time is null)
WHERE
t1.billing_origin_product = 'JOBS' AND
t1.usage_date >= CURRENT_DATE() - INTERVAL 30 DAYS
),
cumulative_run_status_cost as (
SELECT
workspace_id,
job_id,
run_id,
run_as,
result_state,
usage_end_time,
SUM(list_cost) OVER (ORDER BY workspace_id, job_id, run_id, usage_end_time ROWS BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW) AS cumulative_cost
FROM job_run_timeline_with_cost
ORDER BY workspace_id, job_id, run_id, usage_end_time
),
cost_per_status as (
SELECT
workspace_id,
job_id,
run_id,
run_as,
result_state,
usage_end_time,
cumulative_cost - COALESCE(LAG(cumulative_cost) OVER (ORDER BY workspace_id, job_id, run_id, usage_end_time), 0) AS result_state_cost
FROM cumulative_run_status_cost
WHERE result_state IS NOT NULL
ORDER BY workspace_id, job_id, run_id, usage_end_time),
cost_per_status_agg as (
SELECT
workspace_id,
job_id,
FIRST(run_as, TRUE) as run_as,
SUM(result_state_cost) as list_cost
FROM cost_per_status
WHERE
result_state IN ('ERROR', 'FAILED', 'TIMED_OUT')
GROUP BY ALL
),
terminal_statues as (
SELECT
workspace_id,
job_id,
CASE WHEN result_state IN ('ERROR', 'FAILED', 'TIMED_OUT') THEN 1 ELSE 0 END as is_failure,
period_end_time as last_seen_date
FROM system.lakeflow.job_run_timeline
WHERE
result_state IS NOT NULL AND
period_end_time >= CURRENT_DATE() - INTERVAL 30 DAYS
),
most_recent_jobs as (
SELECT
*,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY workspace_id, job_id ORDER BY change_time DESC) as rn
FROM
system.lakeflow.jobs QUALIFY rn=1
)
SELECT
first(t2.name) as name,
t1.workspace_id,
t1.job_id,
COUNT(*) as runs,
t3.run_as,
SUM(is_failure) as failures,
(1 - COALESCE(try_divide(SUM(is_failure), COUNT(*)), 0)) * 100 as success_ratio,
first(t3.list_cost) as failure_list_cost,
MAX(t1.last_seen_date) as last_seen_date
FROM terminal_statues t1
LEFT JOIN most_recent_jobs t2 USING (workspace_id, job_id)
LEFT JOIN cost_per_status_agg t3 USING (workspace_id, job_id)
GROUP BY ALL
ORDER BY failures DESC
再試行パターン
このクエリは、過去 30 日間に頻繁に修理が行われたジョブに関する情報 (修理の数、修理実行のコスト、修復実行の累積期間など) を返します。
with job_run_timeline_with_cost as (
SELECT
t1.*,
t2.job_id,
t2.run_id,
t1.identity_metadata.run_as as run_as,
t2.result_state,
t1.usage_quantity * list_prices.pricing.default as list_cost
FROM system.billing.usage t1
INNER JOIN system.lakeflow.job_run_timeline t2
ON
t1.workspace_id=t2.workspace_id
AND t1.usage_metadata.job_id = t2.job_id
AND t1.usage_metadata.job_run_id = t2.run_id
AND t1.usage_start_time >= date_trunc("Hour", t2.period_start_time)
AND t1.usage_start_time < date_trunc("Hour", t2.period_end_time) + INTERVAL 1 HOUR
INNER JOIN system.billing.list_prices list_prices on
t1.cloud = list_prices.cloud and
t1.sku_name = list_prices.sku_name and
t1.usage_start_time >= list_prices.price_start_time and
(t1.usage_end_time <= list_prices.price_end_time or list_prices.price_end_time is null)
WHERE
t1.billing_origin_product = 'JOBS' AND
t1.usage_date >= CURRENT_DATE() - INTERVAL 30 DAYS
),
cumulative_run_status_cost as (
SELECT
workspace_id,
job_id,
run_id,
run_as,
result_state,
usage_end_time,
SUM(list_cost) OVER (ORDER BY workspace_id, job_id, run_id, usage_end_time ROWS BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW) AS cumulative_cost
FROM job_run_timeline_with_cost
ORDER BY workspace_id, job_id, run_id, usage_end_time
),
cost_per_status as (
SELECT
workspace_id,
job_id,
run_id,
run_as,
result_state,
usage_end_time,
cumulative_cost - COALESCE(LAG(cumulative_cost) OVER (ORDER BY workspace_id, job_id, run_id, usage_end_time), 0) AS result_state_cost
FROM cumulative_run_status_cost
WHERE result_state IS NOT NULL
ORDER BY workspace_id, job_id, run_id, usage_end_time),
cost_per_unsuccesful_status_agg as (
SELECT
workspace_id,
job_id,
run_id,
first(run_as, TRUE) as run_as,
SUM(result_state_cost) as list_cost
FROM cost_per_status
WHERE
result_state != "SUCCEEDED"
GROUP BY ALL
),
repaired_runs as (
SELECT
workspace_id, job_id, run_id, COUNT(*) as cnt
FROM system.lakeflow.job_run_timeline
WHERE result_state IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY ALL
HAVING cnt > 1
),
successful_repairs as (
SELECT t1.workspace_id, t1.job_id, t1.run_id, MAX(t1.period_end_time) as period_end_time
FROM system.lakeflow.job_run_timeline t1
JOIN repaired_runs t2
ON t1.workspace_id=t2.workspace_id AND t1.job_id=t2.job_id AND t1.run_id=t2.run_id
WHERE t1.result_state="SUCCEEDED"
GROUP BY ALL
),
combined_repairs as (
SELECT
t1.*,
t2.period_end_time,
t1.cnt as repairs
FROM repaired_runs t1
LEFT JOIN successful_repairs t2 USING (workspace_id, job_id, run_id)
),
most_recent_jobs as (
SELECT
*,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY workspace_id, job_id ORDER BY change_time DESC) as rn
FROM
system.lakeflow.jobs QUALIFY rn=1
)
SELECT
last(t3.name) as name,
t1.workspace_id,
t1.job_id,
t1.run_id,
first(t4.run_as, TRUE) as run_as,
first(t1.repairs) - 1 as repairs,
first(t4.list_cost) as repair_list_cost,
CASE WHEN t1.period_end_time IS NOT NULL THEN CAST(t1.period_end_time - MIN(t2.period_end_time) as LONG) ELSE NULL END AS repair_time_seconds
FROM combined_repairs t1
JOIN system.lakeflow.job_run_timeline t2 USING (workspace_id, job_id, run_id)
LEFT JOIN most_recent_jobs t3 USING (workspace_id, job_id)
LEFT JOIN cost_per_unsuccesful_status_agg t4 USING (workspace_id, job_id, run_id)
WHERE
t2.result_state IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY t1.workspace_id, t1.job_id, t1.run_id, t1.period_end_time
ORDER BY repairs DESC