オンデマンド特徴量計算
この記事では、Databricks でオンデマンド特徴量を作成して使用する方法について説明します。
オンデマンド特徴量を使用するには、ワークスペースで Unity Catalog が有効になっている必要があり、Databricks Runtime 13.3 LTS ML 以降を使用する必要があります。
オンデマンド特徴量とは
「オンデマンド」とは、値が事前にわかっていないが、推論時に計算される特徴量を指します。 Databricks では、 Python ユーザー定義関数 (UDF) を使用して、オンデマンド特徴量の計算方法を指定します。 これらの関数は Unity Catalog によって管理され、 カタログエクスプローラ で検出できます。
ワークフロー
オンデマンドで特徴量を計算するには、特徴量の値の計算方法を記述する Python ユーザー定義関数 (UDF) を指定します。
- トレーニング中に、この関数とその入力バインディングを
create_training_setAPI のfeature_lookupsパラメーターで指定します。 - Feature Storeメソッド
log_modelを使用してトレーニング済みモデルをログに記録する必要があります。 これにより、モデルが推論に使用されたときに、オンデマンド特徴量が自動的に評価されます。 - バッチ スコアリングの場合、
score_batchAPI は、オンデマンド特徴量を含むすべての特徴量値を自動的に計算して返します。 - Mosaic AI Model Servingを使用してモデルを提供すると、モデルはスコアリング要求ごとに Python UDF から コンピュート オンデマンド特徴量を自動的に使用します。
Python UDF の作成
Python UDF は、SQL または Python コードを使用して作成できます。次の例では、カタログ main とスキーマ defaultに Python UDF を作成します。
- Python
- Databricks SQL
Pythonを使用するには、まず databricks-sdk[openai] パッケージをインストールする必要があります。%pip installは次のように使用します。
%pip install unitycatalog-ai[databricks]
dbutils.library.restartPython()
次に、次のようなコードを使用して Python UDF を作成します。
from unitycatalog.ai.core.databricks import DatabricksFunctionClient
client = DatabricksFunctionClient()
CATALOG = "main"
SCHEMA = "default"
def add_numbers(number_1: float, number_2: float) -> float:
"""
A function that accepts two floating point numbers, adds them,
and returns the resulting sum as a float.
Args:
number_1 (float): The first of the two numbers to add.
number_2 (float): The second of the two numbers to add.
Returns:
float: The sum of the two input numbers.
"""
return number_1 + number_2
function_info = client.create_python_function(
func=add_numbers,
catalog=CATALOG,
schema=SCHEMA,
replace=True
)
次のコードは、Databricks SQL を使用して Python UDF を作成する方法を示しています。
%sql
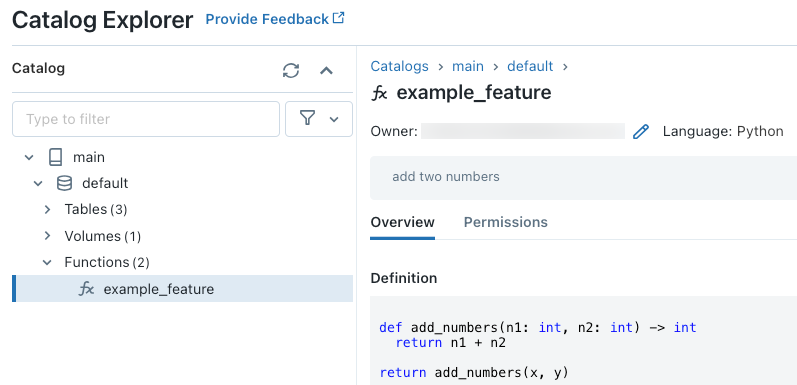
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION main.default.add_numbers(x INT, y INT)
RETURNS INT
LANGUAGE PYTHON
COMMENT 'add two numbers'
AS $$
def add_numbers(n1: int, n2: int) -> int:
return n1 + n2
return add_numbers(x, y)
$$
コードを実行した後、 カタログ エクスプローラー で 3 レベルの名前空間を移動して、関数定義を表示できます。
Python UDF の作成の詳細については、「 Python UDF を Unity Catalog に登録する 」と SQL 言語のマニュアルを参照してください。
欠落している特徴量の処理方法
Python UDF が FeatureLookup の結果に依存している場合、要求されたルックアップ キーが見つからない場合に返される値は環境によって異なります。 score_batchを使用する場合、返される値は Noneです。オンライン配信を使用する場合、返される値は float("nan")です。
次のコードは、両方のケースを処理する方法の例です。
%sql
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION square(x INT)
RETURNS INT
LANGUAGE PYTHON AS
$$
import numpy as np
if x is None or np.isnan(x):
return 0
return x * x
$$
オンデマンド特徴量を使用してモデルをトレーニングする
モデルをトレーニングするには、feature_lookups パラメーターで create_training_set API に渡される FeatureFunctionを使用します。
次のコード例では、前のセクションで定義した Python UDF main.default.example_feature を使用しています。
# Install databricks-feature-engineering first with:
# %pip install databricks-feature-engineering
# dbutils.library.restartPython()
from databricks.feature_engineering import FeatureEngineeringClient
from databricks.feature_engineering import FeatureFunction, FeatureLookup
from sklearn import linear_model
fe = FeatureEngineeringClient()
features = [
# The feature 'on_demand_feature' is computed as the sum of the input value 'new_source_input'
# and the pre-materialized feature 'materialized_feature_value'.
# - 'new_source_input' must be included in base_df and also provided at inference time.
# - For batch inference, it must be included in the DataFrame passed to 'FeatureEngineeringClient.score_batch'.
# - For real-time inference, it must be included in the request.
# - 'materialized_feature_value' is looked up from a feature table.
FeatureFunction(
udf_name="main.default.example_feature", # UDF must be in Unity Catalog so uses a three-level namespace
input_bindings={
"x": "new_source_input",
"y": "materialized_feature_value"
},
output_name="on_demand_feature",
),
# retrieve the prematerialized feature
FeatureLookup(
table_name = 'main.default.table',
feature_names = ['materialized_feature_value'],
lookup_key = 'id'
)
]
# base_df includes the columns 'id', 'new_source_input', and 'label'
training_set = fe.create_training_set(
df=base_df,
feature_lookups=features,
label='label',
exclude_columns=['id', 'new_source_input', 'materialized_feature_value'] # drop the columns not used for training
)
# The training set contains the columns 'on_demand_feature' and 'label'.
training_df = training_set.load_df().toPandas()
# training_df columns ['materialized_feature_value', 'label']
X_train = training_df.drop(['label'], axis=1)
y_train = training_df.label
model = linear_model.LinearRegression().fit(X_train, y_train)
デフォルト値の指定
フィーチャのデフォルト値を指定するには、FeatureLookupのdefault_valuesパラメーターを使用します。
FeatureLookup(
table_name = 'main.default.table',
feature_names = ['materialized_feature_value'],
lookup_key = 'id',
default_values={
"materialized_feature_value": 0
}
)
rename_outputs パラメーターを使用してフィーチャ列の名前を変更する場合は、名前を変更したフィーチャ名を使用するdefault_values必要があります。
FeatureLookup(
table_name = 'main.default.table',
feature_names = ['materialized_feature_value'],
lookup_key = 'id',
rename_outputs={"materialized_feature_value": "feature_value"},
default_values={
"feature_value": 0
}
)
モデルをログに記録し、Unity Catalog に登録する
フィーチャ メタデータでパッケージ化されたモデルは、 Unity Catalog に登録できます。 モデルの作成に使用した特徴量テーブルは、 Unity Catalogに格納する必要があります。
モデルが推論に使用されたときにオンデマンド特徴量を自動的に評価するようにするには、レジストリURIを設定して、次のようにモデルをログに記録する必要があります。
import mlflow
mlflow.set_registry_uri("databricks-uc")
fe.log_model(
model=model,
artifact_path="main.default.model",
flavor=mlflow.sklearn,
training_set=training_set,
registered_model_name="main.default.recommender_model"
)
オンデマンド特徴量を定義する Python UDF が Python パッケージをインポートする場合は、引数 extra_pip_requirementsを使用してこれらのパッケージを指定する必要があります。 例えば:
import mlflow
mlflow.set_registry_uri("databricks-uc")
fe.log_model(
model=model,
artifact_path="model",
flavor=mlflow.sklearn,
training_set=training_set,
registered_model_name="main.default.recommender_model",
extra_pip_requirements=["scikit-learn==1.20.3"]
)
制限事項
- オンデマンド特徴量は、MapType と ArrayType を除く、Feature Store でサポートされているすべてのデータ タイプ を出力できます。
- 0.14.0 より前のバージョンの
databricks-feature-engineeringでは、ユーザー定義関数 ( UDF ) を使用してトレーニング セットを作成したり、 Feature Servingエンドポイントを作成したりするには、次のUnity Catalog権限が必要です。USE CATALOGsystemカタログに対する権限USE SCHEMAsystem.information_schemaスキーマに対する権限
ノートブックの例: オンデマンド特徴量
次のノートブックは、オンデマンド特徴量を使用するモデルをトレーニングしてスコアリングする方法の例を示しています。
基本的なオンデマンド特徴量のデモノートブック
次のノートブックは、レストランのレコメンデーション モデルの例を示しています。レストランの場所は、Databricks のオンラインテーブルから検索されます。ユーザーの現在地は、スコアリング要求の一部として送信されます。このモデルは、オンデマンド特徴量を使用して、ユーザーからレストランまでのリアルタイム距離をコンピュートします。 その後、その距離がモデルへの入力として使用されます。