Configure a firewall for Azure deployments
This page describes how to configure a firewall for serverless compute using the SAP Databricks account console UI.
This page is applicable to Azure deployments only. For AWS deployments, see Configure a firewall for AWS deployments.
Overview of firewall enablement for serverless compute
An NCC defines network identities for Azure resources as default rules. When an NCC is attached to a workspace, serverless compute in that workspace uses one of those networks to connect to the Azure resource. You can allowlist these networks in your Azure resource firewalls. For non-storage Azure resource firewalls, contact your account team to learn about using stable NAT IPs.
What is a network connectivity configuration (NCC)?
Serverless network connectivity is managed with network connectivity configurations (NCC). NCCs are account-level regional constructs that are used to manage private endpoints creation and firewall enablement at scale.
Account admins create NCCs in the account console and an NCC can be attached to one or more workspaces to enable firewalls for resources. An NCC contains a list of stable IP addresses. When an NCC is attached to a workspace, serverless compute in that workspace uses one of those IP addresses to connect the cloud resource. You can allow list those networks on your resource firewall.
Cost implications of cross-region storage access
The firewall applies only when the Azure resources are in the same region as the SAP Databricks workspace. For cross-region traffic from SAP Databricks serverless compute (for example, workspace is in East US region and ADLS storage is in West Europe), SAP Databricks routes the traffic through an Azure NAT Gateway service.
Requirements
- You must be an SAP Databricks account admin.
- Each NCC can be attached to up to 50 workspaces.
- Each SAP Databricks account can have up to 10 NCCs per region. NCCs provide shared stable IP CIDR blocks rather than distinct IP blocks per configuration, and these IP ranges are region-specific.
- You must have
WRITEaccess to your Azure storage account's network rules.
Step 1: Create a network connectivity configuration and copy subnet IDs
Databricks recommends sharing NCCs among workspaces in the same business unit and those sharing the same region and connectivity properties.
- As an account admin, go to the account console.
- In the sidebar, click Security.
- Click Network connectivity configurations.
- Click Add network configuration.
- Type a name for the NCC.
- Choose the region. This must match your workspace region.
- Click Add.
- In the list of NCCs, click on your new NCC.
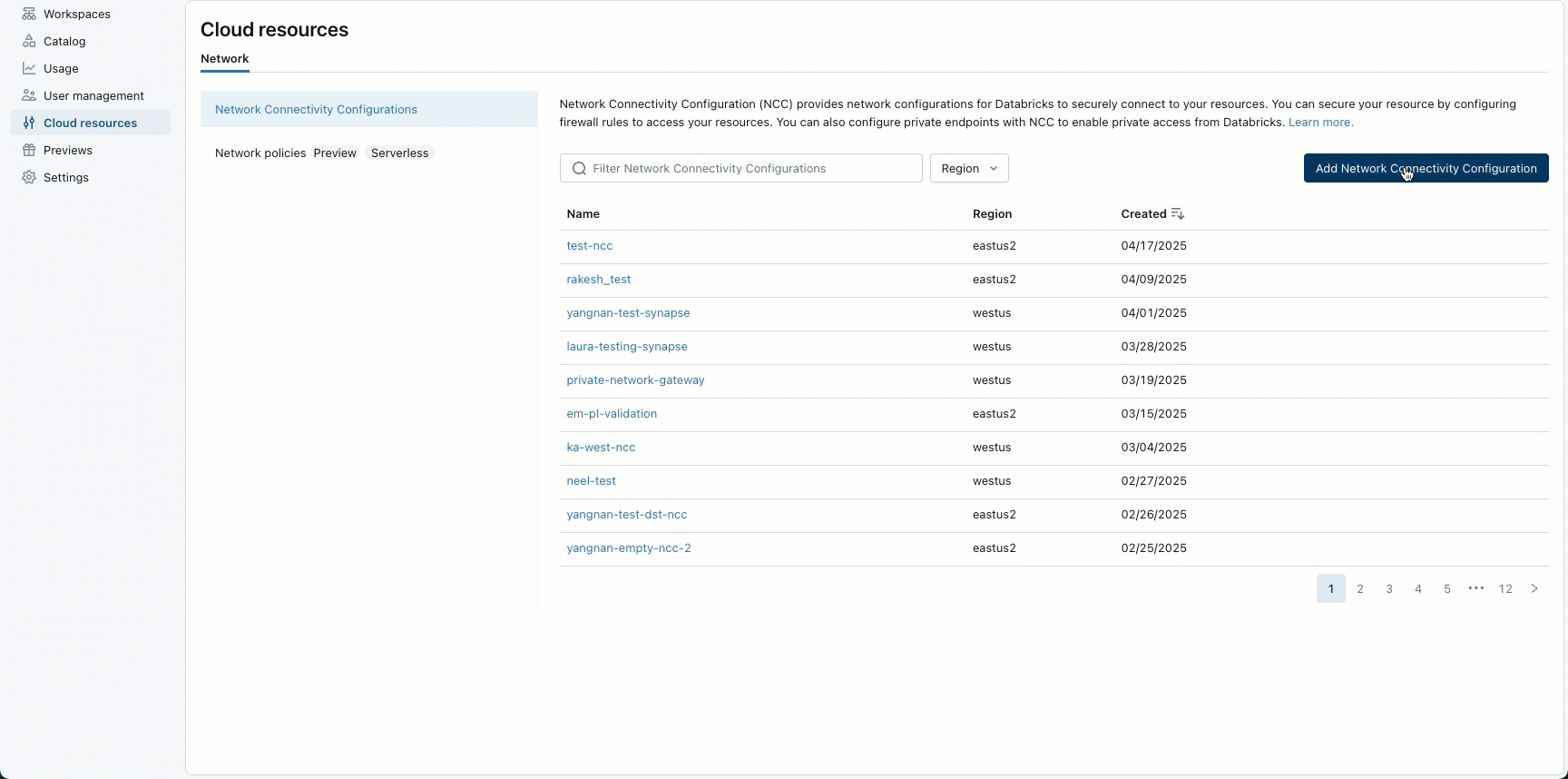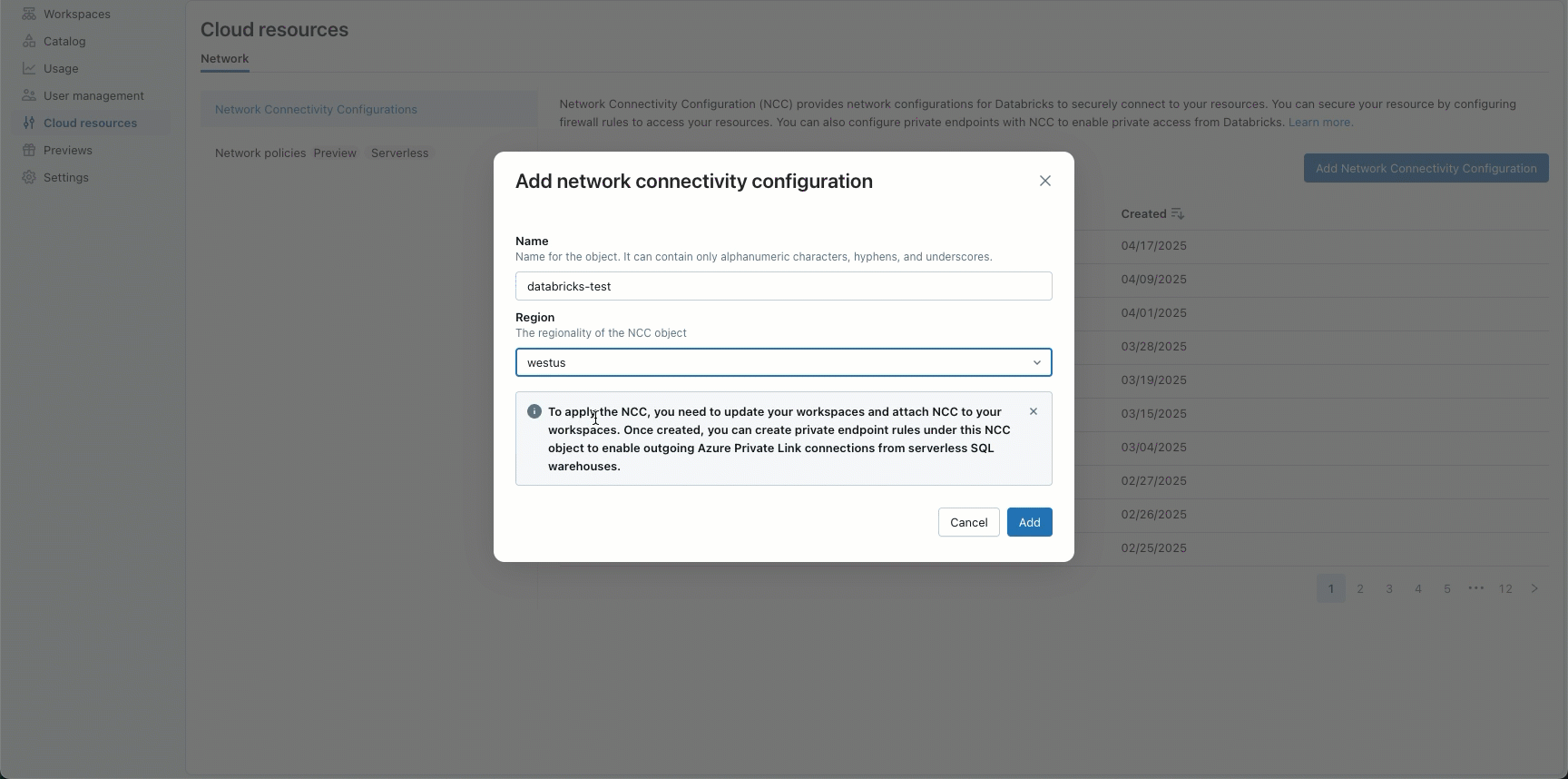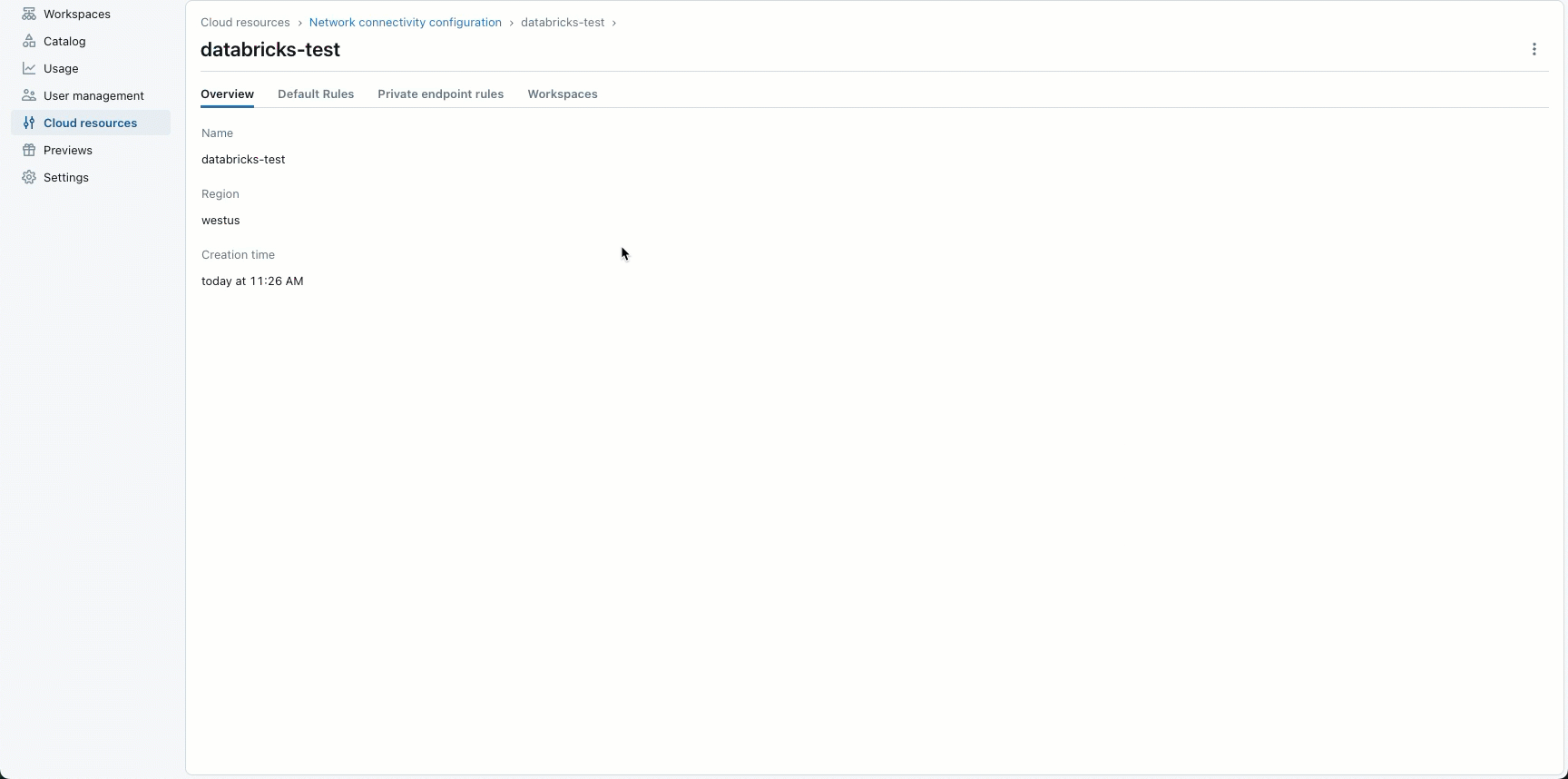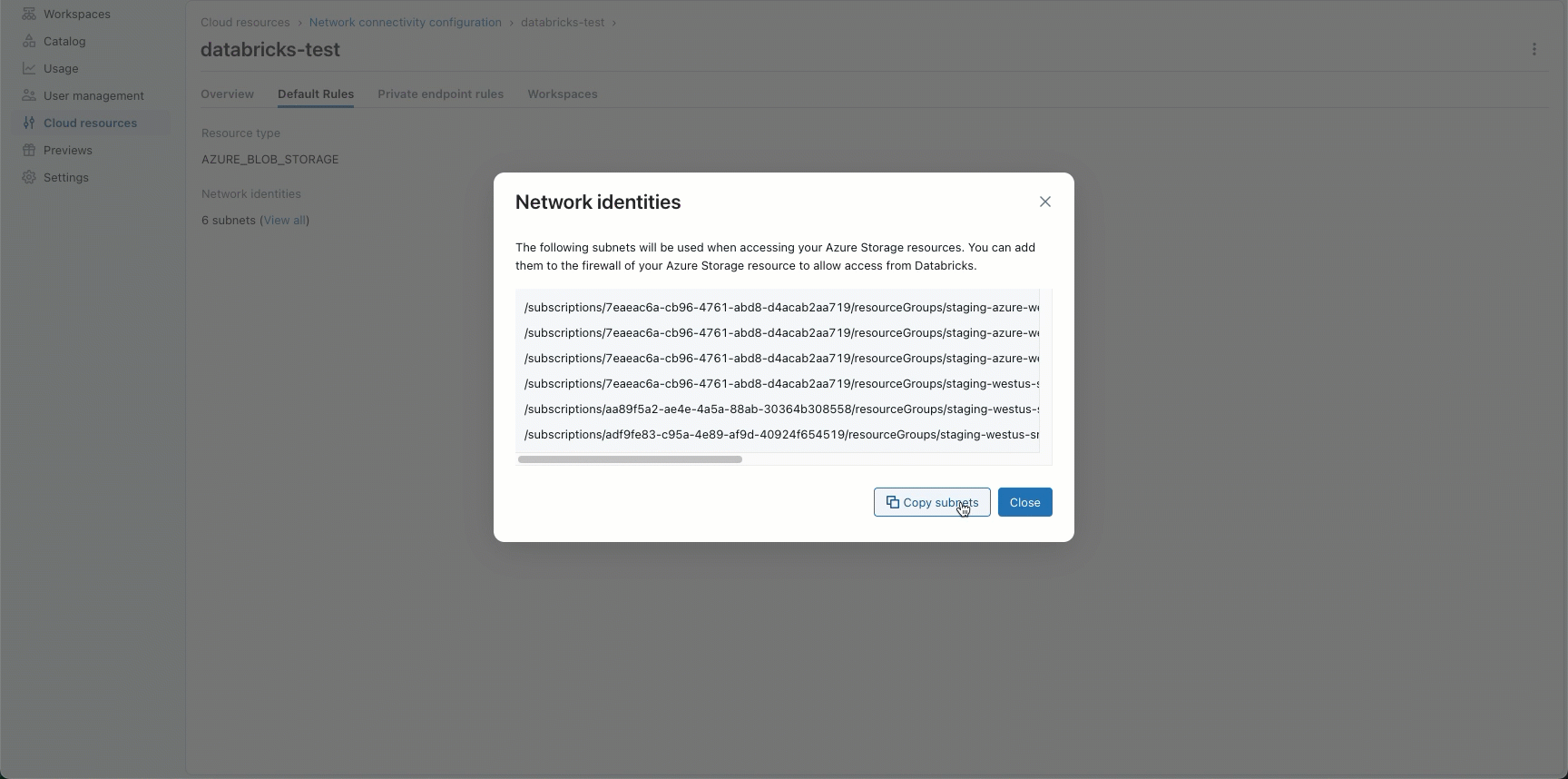
- In Default Rules under Network identities, click View all.
- In the dialog, click the Copy subnets button.
Step 2: Attach an NCC to workspaces
You can attach an NCC to up to 50 workspaces in the same region as the NCC.
- In the account console sidebar, click Workspaces.
- Click your workspace's name.
- Click Update workspace.
- In the Network connectivity configurations field, select your NCC. If it's not visible, confirm that you've selected the same region for both the workspace and the NCC.
- Click Update.
- Wait 10 minutes for the change to take effect.
- Restart any running serverless compute resources in the workspace.
If you are using this feature to connect to the workspace storage account, your configuration is complete. The network rules are automatically added to the workspace storage account. For additional storage accounts, continue to the next step.
Step 3: Lock down your storage account
If you haven't already limited access to the Azure storage account to only allow-listed networks, do so now. You do not need to do this step for the workspace storage account.
Creating a storage firewall also affects connectivity from classic compute plane to your resources. You must also add network rules to connect to your storage accounts from classic compute resources.
- Go to the Azure portal.
- Navigate to your storage account for the data source.
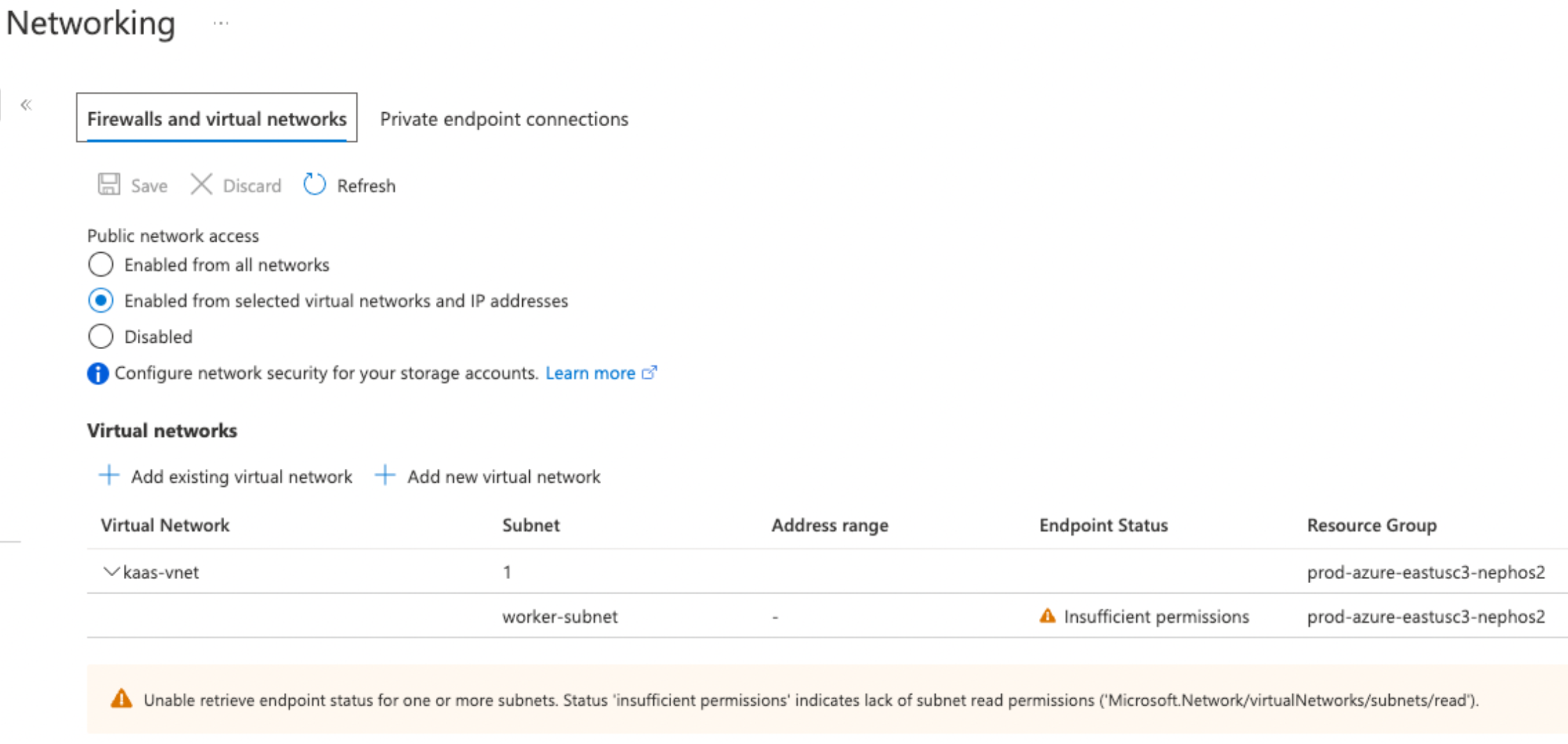
- In the left nav, click Networking.
- In the field Public network access, check the value. By default, the value is Enabled from all networks. Change this to Enabled from selected virtual networks and IP addresses.
Step 4: Add Azure storage account network rules
You do not need to do this step for the workspace storage account.
-
In a text editor, copy and paste the following script, replacing the parameters with values for your Azure account:
PowerShell# Define parameters
$subscription = `<YOUR_SUBSCRIPTION_ID>` # Replace with your Azure subscription ID or name
$resourceGroup = `<YOUR_RESOURCE_GROUP>` # Replace with your Azure resource group name
$accountName = `<YOUR_STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME>` # Replace with your Azure storage account name
$subnets = `<SUBNET_NAME_1>` # Replace with your actual subnet names
# Add network rules for each subnet
foreach ($subnet in $subnets) {
az storage account network-rule add --subscription $subscription `
--resource-group $resourceGroup `
--account-name $accountName `
--subnet $subnet
} -
Launch Azure Cloud Shell.
-
In Azure Cloud Shell, using an editor, create a new file that ends with the
.ps1extension:vi ncc.ps1 -
Paste the script from step 1 into your editor and then press
Esc, type:wq, and pressEnter. -
Run the following command to execute your script:
./ncc.ps1 -
After running all the commands, you can use the Azure portal to view your storage account and confirm that there is an entry in the Virtual Networks table that represents the new subnet.
tip- When you add storage account network rules, use the Network Connectivity API to retrieve the latest subnets.
- Avoid storing NCC information locally.
- Ignore the mention of “Insufficient permissions” in the endpoint status column or the warning below the network list. They indicate only that you do not have permission to read the SAP Databricks subnets but it does not interfere with the ability for that SAP Databricks serverless subnet to contact your Azure storage.
-
To confirm that your storage account uses these settings from the Azure portal, navigate to Networking in your storage account. Confirm that the Public network access is set to Enabled from selected virtual networks and IP addresses and allowed networks are listed in the Virtual Networks section.