What's coming?
Learn about features and behavioral changes in upcoming Databricks releases.
Behavioral change for the Auto Loader incremental directory listing option
The Auto Loader cloudFiles.useIncrementalListing option is deprecated. Although this note discusses a change to the options's default value and how to continue using it after this change, Databricks recommends against using this option in favor of file notification mode with file events.
In an upcoming Databricks Runtime release, the value of the deprecated Auto Loader cloudFiles.useIncrementalListing option will, by default, be set to false. Setting this value to false causes Auto Loader to perform a full directory listing each time it's run. Currently, the default value of the cloudFiles.useIncrementalListing option is auto, instructing Auto Loader to make a best-effort attempt at detecting if an incremental listing can be used with a directory.
To continue using the incremental listing feature, set the cloudFiles.useIncrementalListing option to auto. When you set this value to auto, Auto Loader makes a best-effort attempt to do a full listing once every seven incremental listings, which matches the behavior of this option before this change.
To learn more about Auto Loader directory listing, see Auto Loader streams with directory listing mode.
Behavior change when dataset definitions are removed from Lakeflow Declarative Pipelines
An upcoming release of Lakeflow Declarative Pipelines will change the behavior when a materialized view or streaming table is removed from a pipeline. With this change, the removed materialized view or streaming table will not be deleted automatically when the next pipeline update runs. Instead, you will be able to use the DROP MATERIALIZED VIEW command to delete a materialized view or the DROP TABLE command to delete a streaming table. After dropping an object, running a pipeline update will not recover the object automatically. A new object is created if a materialized view or streaming table with the same definition is re-added to the pipeline. You can, however, recover an object using the UNDROP command.
End of support timeline for legacy dashboards
- April 7, 2025: Official support for the legacy version of dashboards will end. Only critical security issues and service outages will be addressed.
- November 3, 2025: Databricks will begin archiving legacy dashboards that have not been accessed in the past six months. Archived dashboards will no longer be accessible, and the archival process will occur on a rolling basis. Access to actively used dashboards will remain unchanged.
Databricks will work with customers to develop migration plans for active legacy dashboards after November 3, 2025.
To help transition to AI/BI dashboards, upgrade tools are available in both the user interface and the API. For instructions on how to use the built-in migration tool in the UI, see Clone a legacy dashboard to an AI/BI dashboard. For tutorials about creating and managing dashboards using the REST API at Use Databricks APIs to manage dashboards.
The sourceIpAddress field in audit logs will no longer include a port number
Due to a bug, certain authorization and authentication audit logs include a port number in addition to the IP in the sourceIPAddress field (for example, "sourceIPAddress":"10.2.91.100:0"). The port number, which is logged as 0, does not provide any real value and is inconsistent with the rest of the Databricks audit logs. To enhance the consistency of audit logs, Databricks plans to change the format of the IP address for these audit log events. This change will gradually roll out starting in early August 2024.
If the audit log contains a sourceIpAddress of 0.0.0.0, Databricks might stop logging it.
External support ticket submission will soon be deprecated
Databricks is transitioning the support ticket submission experience from help.databricks.com to the help menu in the Databricks workspace. Support ticket submission via help.databricks.com will soon be deprecated. You'll continue to view and triage your tickets at help.databricks.com.
The in-product experience, which is available if your organization has a Databricks Support contract, integrates with Databricks Assistant to help address your issues quickly without having to submit a ticket.
To access the in-product experience, click your user icon in the top bar of the workspace, and then click Contact Support or type “I need help” into the assistant.
The Contact support modal opens.
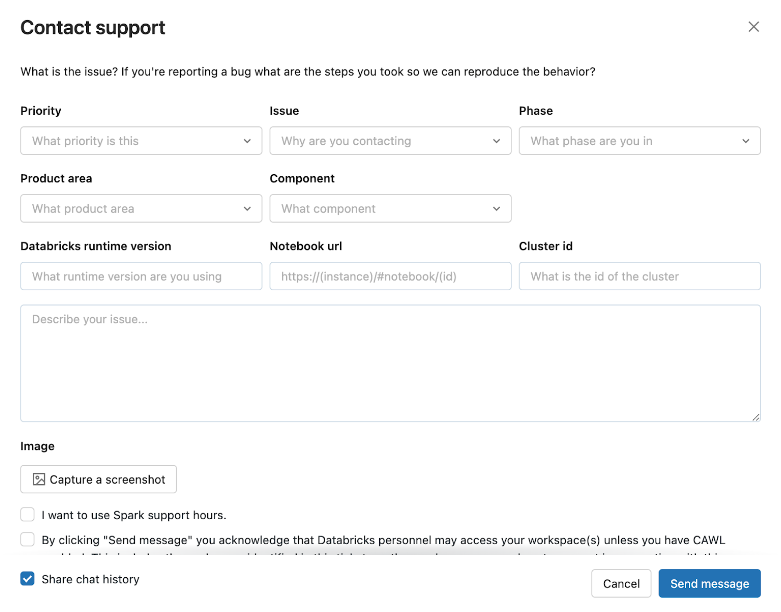
If the in-product experience is down, send requests for support with detailed information about your issue to help@databricks.com. For more information, see Get help.