Unity Catalog privileges and securable objects
This page describes the Unity Catalog securable objects and the privileges that apply to them. To learn how to grant privileges in Unity Catalog, see Show, grant, and revoke privileges.
This article refers to the Unity Catalog privileges and inheritance model in Privilege Model version 1.0. If you created your Unity Catalog metastore during the public preview (before August 25, 2022), you might be on an earlier privilege model that doesn't support the current inheritance model. You can upgrade to Privilege Model version 1.0 to get privilege inheritance. See Upgrade to privilege inheritance.
Securable objects in Unity Catalog
A securable object is an object defined in the Unity Catalog metastore on which privileges can be granted to a principal (user, service principal, or group). Securable objects in Unity Catalog are hierarchical.
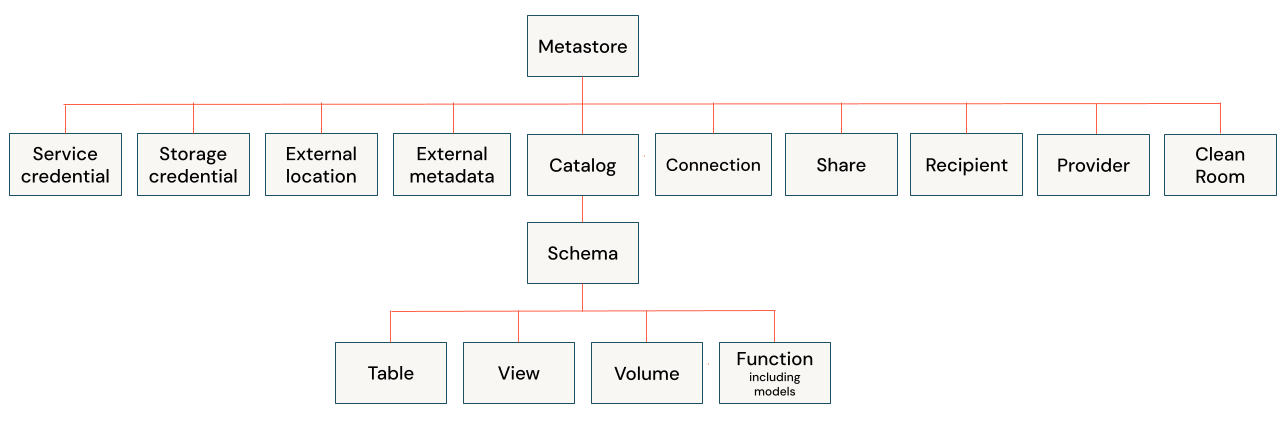
The securable objects are:
-
METASTORE: The top-level container for metadata. Each Unity Catalog metastore exposes a three-level namespace (
catalog.schema.table) that organizes your data.When you manage privileges on a metastore, you do not include the metastore name in a SQL command. Unity Catalog grants or revokes the privilege on the metastore attached to your workspace. For example, the following command grants a group named engineering the ability to create a catalog in the metastore attached to the workspace:
SQLGRANT CREATE CATALOG ON METASTORE TO engineering -
CATALOG: The first layer of the object hierarchy, used to organize your data assets. A foreign catalog is a special catalog type that mirrors a database in an external data system in a Lakehouse Federation scenario.
-
SCHEMA: Also known as databases, schemas are the second layer of the object hierarchy and contain tables and views.
-
TABLE: At the lowest level in the object hierarchy, tables managed tables, external tables, foreign tables, streaming tables, online tables, and feature tables. See Databricks tables.
-
VIEW: A read-only object created from a query on one or more tables that is contained within a schema.
-
MATERIALIZED VIEW: An object created from a query on one or more tables that is contained within a schema. Its results reflect the state of data when it was last refreshed.
-
METRIC VIEW: A read-only object that defines a set of metric definitions, including dimensions and measures, based on one or more data sources, which can be tables, views, or SQL queries. See Unity Catalog metric views.
-
VOLUME: A logical volume of unstructured data. Can be external (stored in external locations in your cloud storage of choice) or managed (stored in a storage container in your cloud storage that you create expressly for Databricks).
-
FUNCTION: A user-defined function or an MLflow registered model that is contained within a schema.
-
Model: An MLflow registered model is a specific type of function. Models are listed separately from other functions in Catalog Explorer, but when you grant a privilege on a model using SQL, you use
GRANT ON FUNCTION. -
EXTERNAL LOCATION: An object that contains a reference to a storage credential and a cloud storage path that is contained within a Unity Catalog metastore.
-
EXTERNAL METADATA: An object that contains metadata for an entity in an external system, such as a Tableau dashboard or Salesforce object, so that it can be added to custom data lineage configurations. See Bring your own data lineage.
-
SERVICE CREDENTIAL: An object that encapsulates a long-term cloud credential that provides access to an external service. Contained in a Unity Catalog metastore.
-
STORAGE CREDENTIAL: An object that encapsulates a long-term cloud credential that provides access to cloud storage that is contained within a Unity Catalog metastore.
-
CONNECTION: An object that specifies a path and credentials for accessing an external database system in a Lakehouse Federation scenario.
-
SHARE: A logical grouping for the tables you intend to share using Delta Sharing. A share is contained within a Unity Catalog metastore.
-
RECIPIENT: An object that identifies an organization or group of users that can have data shared with them using Delta Sharing. These objects are contained within a Unity Catalog metastore.
-
PROVIDER: An object that represents an organization that has made data available for sharing using Delta Sharing. These objects are contained within a Unity Catalog metastore.
-
CLEAN ROOM: An object that represents a secure and privacy-protecting environment, managed by Databricks, where multiple parties can collaborate without direct access to each other's data.
Privilege types by securable object in Unity Catalog
The following table lists the privilege types that apply to each securable object in Unity Catalog. To learn how to grant privileges in Unity Catalog, see Show, grant, and revoke privileges.
Securable | Privileges |
|---|---|
Metastore |
|
Catalog |
All users have The following privilege types apply to securable objects in a catalog. You can grant these privileges at the catalog level to apply them to current and future objects in the catalog.
|
Schema |
The following privilege types apply to securable objects within a schema. You can grant these privileges at the schema level to apply them to current and future objects within the schema.
|
Table |
|
Materialized view |
|
View |
|
Volume |
|
External location |
|
External metadata |
|
Service credential |
|
Storage credential |
|
Connection |
|
Function |
|
Procedure |
|
Model | Registered models are a type of function. |
Share |
|
Recipient | None |
Provider | None |
Clean room |
|
General Unity Catalog privilege types
This section provides details about the privilege types that apply generally to Unity Catalog. To learn how to grant privileges in Unity Catalog, see Show, grant, and revoke privileges.
ALL PRIVILEGES
Applicable object types: CATALOG, EXTERNAL LOCATION, EXTERNAL METADATA, SERVICE CREDENTIAL, STORAGE CREDENTIAL, SCHEMA, FUNCTION (including models), PROCEDURE, TABLE, MATERIALIZED VIEW, VIEW, VOLUME
Used to grant or revoke all privileges applicable to the securable object and its child objects without explicitly specifying them.
When ALL PRIVILEGES is granted on an object, it does not individually grant the user each applicable privilege at the time of the grant. Instead, it expands to all available privileges at the time permissions checks are made. This means that as Databricks releases new privileges and new securable objects, an existing ALL PRIVILEGES grant automatically includes any new privileges applicable to the securable object, its existing child objects, and any new child objects.
To avoid accidental data exfiltration or privilege escalation, ALL PRIVILEGES does not include the EXTERNAL USE SCHEMA, EXTERNAL USE LOCATION, or MANAGE privileges.
When ALL PRIVILEGES is revoked, both the ALL PRIVILEGES grant and any individual privileges implied by it are removed. Privileges that are not part of ALL PRIVILEGES, such as MANAGE, EXTERNAL USE LOCATION, and EXTERNAL USE SCHEMA, are not affected.
This privilege is powerful when applied at higher levels in the hierarchy. For example, GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON CATALOG main TO analysts grants the analyst team all existing and future privileges on every existing and future securable object in the catalog.
ACCESS
Applicable object types: SERVICE CREDENTIAL
Allows a user to use a service credential to access an external service or services.
APPLY TAG
Applicable object types: CATALOG, SCHEMA, TABLE, VOLUME, MATERIALIZED VIEW, VIEW, models that are registered as a FUNCTION
Allows a user to add and edit tags on an object. Granting APPLY TAG to a table or view also enables column tagging. Granting APPLY TAG to a registered model also enables model version tagging.
The user must also have the USE CATALOG privilege on the parent catalog and USE SCHEMA on the parent schema.
To apply a governed tag to Unity Catalog securable objects, you must also have the ASSIGN permission on the governed tag. See Manage permissions on governed tags.
BROWSE
Applicable object types: CATALOG, CLEAN ROOM, EXTERNAL METADATA, EXTERNAL LOCATION
Allows a user to view an object's metadata using Catalog Explorer, the schema browser, search results, the lineage graph, information_schema, and the REST API. This visibility enables users to discover objects and request access to them.
The user does not require the USE CATALOG privilege on the parent catalog or USE SCHEMA on the parent schema.
All users are granted the BROWSE privilege by default on new catalogs that are created using Catalog Explorer. You can revoke the privilege if you prefer. Catalogs created using SQL statements, the REST API, or the Databricks CLI do not grant the BROWSE privilege by default. You must grant it overtly.
Databricks recommends granting BROWSE on catalogs to the All account users group to make objects discoverable and allow all users to request access to objects.
Users with only the BROWSE privilege on an object have limited ability to explore metadata using SQL.
CREATE CATALOG
Applicable object types: Unity Catalog metastore
Allows a user to create a catalog in a Unity Catalog metastore. To create a foreign catalog, you must also have the CREATE FOREIGN CATALOG privilege on the connection that contains the foreign catalog or on the metastore.
CREATE CLEAN ROOM
Applicable object types: Unity Catalog metastore
Allows a user to create a clean room for securely collaborating on projects with other organizations without sharing underlying data.
CREATE CONNECTION
Applicable object types: Unity Catalog metastore, SERVICE CREDENTIAL
Allows a user to create a connection to an external database in a Lakehouse Federation scenario. To use a service credential to create a connection, the user must have this privilege on both the metastore and the service credential.
CREATE EXTERNAL LOCATION
Applicable object types: Unity Catalog metastore, STORAGE CREDENTIAL
To create an external location, the user must have this privilege on both the metastore and the storage credential that is being referenced in the external location.
CREATE EXTERNAL METADATA
Applicable object types: Unity Catalog metastore
Allows a user to create an external metadata securable for use in custom lineage. To add lineage relationships to the external metadata object, the user must have the MODIFY privilege on the external metadata object, along with privileges on the Unity Catalog object that they are specifying the relationship with.
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE
Applicable object types: EXTERNAL LOCATION, STORAGE CREDENTIAL
Allows a user to create external tables directly in your cloud tenant using an external location or storage credential. Databricks recommends granting this privilege on an external location rather than storage credential (since it's scoped to a path, it allows more control over where users can create external tables in your cloud tenant).
CREATE EXTERNAL VOLUME
Applicable object types: EXTERNAL LOCATION
Allows a user to create external volumes using an external location.
CREATE FOREIGN CATALOG
Applicable object types: CONNECTION
Allows a user to create foreign catalogs using a connection to an external database in a Lakehouse Federation scenario.
CREATE FOREIGN SECURABLE
Applicable object types: EXTERNAL LOCATION
Allows a user who is creating a foreign catalog to specify authorized paths that are covered by the external location.
The user must also have CREATE CATALOG on the Unity Catalog metastore and CREATE FOREIGN CATALOG on the connection.
CREATE FUNCTION
Applicable object types: SCHEMA
Allows a user to create a function or procedure in the schema. Because privileges are inherited, CREATE FUNCTION can also be granted on a catalog, which allows a user to create a function or procedure in any existing or future schema in the catalog.
The user must also have the USE CATALOG privilege on the parent catalog and USE SCHEMA on the parent schema.
CREATE MODEL
Applicable object types: SCHEMA
Allows a user to create an MLflow registered model (which is a type of FUNCTION) in the schema. Since privileges are inherited, CREATE MODEL can also be granted on a catalog, which allows a user to create a registered model in any existing or future schema in the catalog.
The user must also have the USE CATALOG privilege on the parent catalog and USE SCHEMA on the parent schema.
CREATE MODEL VERSION
Applicable object types: MODEL
Allows a user to register a new version of an MLflow registered model (which is a type of FUNCTION). Does not give the user permission to execute, modify, or add tags to a model version.
The user must also have the USE CATALOG privilege on the parent catalog and USE SCHEMA on the parent schema.
CREATE MANAGED STORAGE
Applicable object types: EXTERNAL LOCATION
Allows a user to specify a location for storing managed tables at the catalog or schema level, overriding the default root storage for the metastore.
CREATE SCHEMA
Applicable object types: CATALOG
Allows a user to create a schema. The user must also have the USE CATALOG privilege on the catalog.
CREATE SERVICE CREDENTIAL
Applicable object types: Unity Catalog metastore
Allows a user to create a service credential in a Unity Catalog metastore.
CREATE STORAGE CREDENTIAL
Applicable object types: Unity Catalog metastore
Allows a user to create a storage credential in a Unity Catalog metastore.
CREATE TABLE
Applicable object types: SCHEMA
Allows a user to create a table or view in the schema. Since privileges are inherited, CREATE TABLE can also be granted on a catalog, which allows a user to create a table or view in any existing or future schema in the catalog.
The user must also have the USE CATALOG privilege on its parent catalog and the USE SCHEMA privilege on its parent schema.
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW
Applicable object types: SCHEMA
Allows a user to create a materialized view in the schema. Since privileges are inherited, CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW can also be granted on a catalog, which allows a user to create a table or view in any existing or future schema in the catalog.
The user must also have the USE CATALOG privilege on its parent catalog and the USE SCHEMA privilege on its parent schema.
CREATE VOLUME
Applicable object types: SCHEMA
Allows a user to create a volume in the schema. Since privileges are inherited, CREATE VOLUME can also be granted on a catalog, which allows a user to create a volume in any existing or future schema in the catalog.
The user must also have the USE CATALOG privilege on the volume's parent catalog and the USE SCHEMA privilege on its parent schema.
EXECUTE
Applicable object types: FUNCTION, Model
Allows a user to invoke a user defined function or load a model for inference, if the user also has USE CATALOG on its parent catalog and USE SCHEMA on its parent schema. For functions, EXECUTE grants the ability to view the function definition and metadata. For registered models, EXECUTE grants the ability to view metadata for all versions of the registered model, and to download model files.
Since privileges are inherited, you can grant a user the EXECUTE privilege on a catalog or schema, which automatically grants the user the EXECUTE privilege on all current and future functions in the catalog or schema.
EXECUTE CLEAN ROOM TASK
Applicable object types: CLEAN ROOM
Allows a user to run tasks (notebooks) in a clean room. Also enables the user to view clean room details.
EXTERNAL USE LOCATION
Applicable object types: EXTERNAL LOCATION
Allows a user to be granted a temporary credential to access Unity Catalog external locations from an external processing engine using the Unity Catalog open APIs or Apache Spark.
Only users with the MANAGE privilege on the external location can grant this privilege.
To avoid accidental data exfiltration, ALL PRIVILEGES does not include the EXTERNAL USE LOCATION privilege, and external location owners do not have this privilege by default.
See Enable external data access to Unity Catalog.
EXTERNAL USE SCHEMA
This feature is in Public Preview.
Applicable object types: SCHEMA
Allows a user to be granted a temporary credential to access Unity Catalog tables from an external processing engine using the Unity Catalog open APIs or Iceberg REST APIs.
Only the catalog owner can grant this privilege.
To avoid accidental data exfiltration, ALL PRIVILEGES does not include the EXTERNAL USE SCHEMA privilege, and schema owners do not have this privilege by default.
See Enable external data access to Unity Catalog.
MANAGE
Applicable object types: CATALOG, EXTERNAL LOCATION, EXTERNAL METADATA, SERVICE CREDENTIAL, STORAGE CREDENTIAL, SCHEMA, FUNCTION (including models), CONNECTION, TABLE, MATERIALIZED VIEW, VIEW, VOLUME, CLEAN ROOM
This feature is in Public Preview.
Allows a user to view and manage privileges, transfer ownership, drop, and rename an object. MANAGE is similar to object ownership, but users with the MANAGE privilege are not automatically granted all privileges on that object (however they can grant themselves privileges).
The user must also have the USE CATALOG privilege on the object's parent catalog and the USE SCHEMA privilege on its parent schema.
ALL PRIVILEGES does not include the MANAGE privilege
MANAGE ALLOWLIST
Applicable object types: Unity Catalog metastore
Allows a user to add or modify paths for init scripts, JARs, and Maven coordinates in the allowlist that governs Unity Catalog-enabled clusters with standard access mode. See Allowlist libraries and init scripts on compute with standard access mode (formerly shared access mode).
MODIFY
Applicable object types: EXTERNAL METADATA, TABLE
Allows a user to add, update, and delete data to or from the table if the user also has SELECT on the table as well as USE CATALOG on its parent catalog and USE SCHEMA on its parent schema.
Since privileges are inherited, you can grant a user the MODIFY privilege on a catalog or schema, which automatically grants the user the MODIFY privilege on all current and future tables in the catalog or schema.
MODIFY cannot be granted on a foreign table because foreign tables are read-only.
MODIFY CLEAN ROOM
Applicable object types: CLEAN ROOM
Allows a user to update a clean room, including adding and removing data assets, adding and removing notebooks, and updating comments. Also enables the user to view clean room details.
READ FILES
Applicable object types: EXTERNAL LOCATION
READ FILES allows a user to read files directly from cloud object storage configured as an external location. Databricks recommends against this practice. Instead, you should manage read access to data in cloud object storage using volumes and the READ VOLUME privilege. For more guidance, see External locations.
READ VOLUME
Applicable object types: VOLUME
Allows a user to read files and directories stored inside a volume if the user also has USE CATALOG on its parent catalog and USE SCHEMA on its parent schema.
Privileges are inherited. When you can grant a user the READ VOLUME privilege on a catalog or schema, you automatically grant the user the READ VOLUME privilege on all current and future volumes in the catalog or schema.
REFRESH
Applicable object types: MATERIALIZED VIEW
Allows a user to refresh a materialized view if the user also has USE CATALOG on its parent catalog and USE SCHEMA on its parent schema.
Privileges are inherited. When you grant the REFRESH privilege on a catalog or schema to a user, you automatically grant the user the REFRESH privilege on all current and future materialized views in the catalog or schema.
SELECT
Applicable object types: TABLE, VIEW, MATERIALIZED VIEW, SHARE
If applied to a table or view, allows a user to select from the table or view, if the user also has USE CATALOG on its parent catalog and USE SCHEMA on its parent schema. If applied to a share, allows a recipient to select from the share.
Since privileges are inherited, you can grant a user the SELECT privilege on a catalog or schema, which automatically grants the user SELECT privilege on all current and future tables, and views in the catalog or schema.
USE CATALOG
Applicable object types: CATALOG
This privilege does not grant access to the catalog itself, but is needed for a user to interact with any object within the catalog. For example, to select data from a table, users need to have the SELECT privilege on that table and USE CATALOG privileges on its parent catalog as well as USE SCHEMA privileges on its parent schema.
This is useful for allowing catalog owners to be able to limit how far individual schema and table owners can share data they produce. For example, a table owner granting SELECT to another user does not allow that user read access to the table unless they also have been granted USE CATALOG privileges on its parent catalog as well as USE SCHEMA privileges on its parent schema.
The USE CATALOG privilege on the parent catalog is not required to read an object's metadata if the user has the BROWSE privilege on that catalog.
USE CONNECTION
Applicable object types: CONNECTION
Allows a user to list and view details about connections to an external database in a Lakehouse Federation scenario. This privilege is also required to use the remote_query function to run SQL queries directly on external databases. To create foreign catalogs for a connection, you must have CREATE FOREIGN CATALOG on the connection or ownership of the connection.
USE SCHEMA
Applicable object types: SCHEMA
This privilege does not grant access to the schema itself, but is needed for a user to interact with any object within the schema. For example, to select data from a table, users need to have the SELECT privilege on that table and USE SCHEMA on its parent schema as well as USE CATALOG on its parent catalog.
Since privileges are inherited, you can grant a user the USE SCHEMA privilege on a catalog, which automatically grants the user the USE SCHEMA privilege on all current and future schemas in the catalog.
This is useful for allowing schema owners to limit how far individual table owners can share data they produce. For example, a table owner granting SELECT to another user does not allow that user read access to the table unless they also have been granted USE SCHEMA privileges on its parent schema and USE CATALOG privileges on its parent catalog.
The USE SCHEMA privilege on the parent schema is not required to read an object's metadata if the user has the BROWSE privilege on that schema's parent catalog.
WRITE FILES
Applicable object types: EXTERNAL LOCATION
Databricks recommends managing write access to data in cloud object storage using volumes and the WRITE VOLUME privilege.
WRITE FILES allows a user to write files directly to your cloud object storage configured as an external location. For more guidance, see Managed and external volumes.
WRITE VOLUME
Applicable object types: VOLUME
Allows a user to add, remove, or modify files and directories stored inside a volume if the user also has USE CATALOG on its parent catalog and USE SCHEMA on its parent schema.
Privileges are inherited. When you can grant a user the WRITE VOLUME privilege on a catalog or schema, you automatically grant the user the WRITE VOLUME privilege on all current and future volumes in the catalog or schema.
Privilege types that apply only to Delta Sharing or Databricks Marketplace
This section provides details about the privilege types that apply only to Delta Sharing.
CREATE PROVIDER
Applicable object types: Unity Catalog metastore
Allows a user to create a Delta Sharing provider object in the metastore. A provider identifies an organization or group of users that have shared data using Delta Sharing. Provider creation is performed by a user in the recipient's Databricks account. See What is Delta Sharing?.
CREATE RECIPIENT
Applicable object types: Unity Catalog metastore
Allows a user to create a Delta Sharing recipient object in the metastore. A recipient identifies an organization or group of users that can have data shared with them using Delta Sharing. Recipient creation is performed by a user in the provider's Databricks account. See What is Delta Sharing?.
CREATE SHARE
Applicable object types: Unity Catalog metastore
Allows a user to create a share in the metastore. A share is a logical grouping for the tables you intend to share using Delta Sharing
SET SHARE PERMISSION
Applicable object types: Unity Catalog metastore
In Delta Sharing, this privilege, combined with USE SHARE and USE RECIPIENT (or recipient ownership), gives a provider user the ability to grant a recipient access to a share. Combined with USE SHARE, it gives the ability to transfer ownership of a share to another user, group, or service principal.
USE MARKETPLACE ASSETS
Applicable object types: Unity Catalog metastore
Enabled by default for all Unity Catalog metastores. In Databricks Marketplace, this privilege gives a user the ability to get instant access or request access for data products shared in a Marketplace listing. It also allows a user to access the read-only catalog that is created when a provider shares a data product. Without this privilege, the user would require the CREATE CATALOG and USE PROVIDER privileges or the metastore admin role. This enables you to limit the number of users with those powerful permissions.
USE PROVIDER
Applicable object types: Unity Catalog metastore
In Delta Sharing, gives a recipient user read-only access to all providers in a recipient metastore and their shares. Combined with the CREATE CATALOG privilege, this privilege allows a recipient user who is not a metastore admin to mount a share as a catalog. This enables you to limit the number of users with the powerful metastore admin role.
USE RECIPIENT
Applicable object types: Unity Catalog metastore
In Delta Sharing, gives a provider user read-only access to all recipients in a provider metastore and their shares. This allows a provider user who is not a metastore admin to view recipient details, recipient authentication status, and the list of shares that the provider has shared with the recipient.
In Databricks Marketplace, this gives provider users the ability to view listings and consumer requests in the Provider console.
USE SHARE
Applicable object types: Unity Catalog metastore
In Delta Sharing, gives a provider user read-only access to all shares defined in a provider metastore. This allows a provider user who is not a metastore admin to list shares and list the assets (tables and notebooks) in a share, along with the share's recipients.
In Databricks Marketplace, this gives provider users the ability to view details about the data shared in a listing.