Use foundation models
In this article, you learn which options are available to write query requests for foundation models and how to send them to your model serving endpoint. You can query foundation models that are hosted by Databricks and foundation models hosted outside of Databricks.
For traditional ML or Python models query requests, see Query serving endpoints for custom models.
Mosaic AI Model Serving supports Foundation Models APIs and external models for accessing foundation models. Model Serving uses a unified OpenAI-compatible API and SDK for querying them. This makes it possible to experiment with and customize foundation models for production across supported clouds and providers.
Query options
Mosaic AI Model Serving provides the following options for sending query requests to endpoints that serve foundation models:
Method | Details |
|---|---|
OpenAI client | Query a model hosted by a Mosaic AI Model Serving endpoint using the OpenAI client. Specify the model serving endpoint name as the |
AI Functions | Invoke model inference directly from SQL using the |
Serving UI | Select Query endpoint from the Serving endpoint page. Insert JSON format model input data and click Send Request. If the model has an input example logged, use Show Example to load it. |
REST API | Call and query the model using the REST API. See POST /serving-endpoints/{name}/invocations for details. For scoring requests to endpoints serving multiple models, see Query individual models behind an endpoint. |
MLflow Deployments SDK | Use MLflow Deployments SDK's predict() function to query the model. |
Databricks Python SDK | Databricks Python SDK is a layer on top of the REST API. It handles low-level details, such as authentication, making it easier to interact with the models. |
Requirements
- A model serving endpoint.
- A Databricks workspace in a supported region.
- To send a scoring request through the OpenAI client, REST API or MLflow Deployment SDK, you must have a Databricks API token.
As a security best practice for production scenarios, Databricks recommends that you use machine-to-machine OAuth tokens for authentication during production.
For testing and development, Databricks recommends using a personal access token belonging to service principals instead of workspace users. To create tokens for service principals, see Manage tokens for a service principal.
Install packages
After you have selected a querying method, you must first install the appropriate package to your cluster.
- OpenAI client
- REST API
- MLflow Deployments SDK
- Databricks Python SDK
To use the OpenAI client, the databricks-openai package needs to be installed on your cluster. This package provides an OpenAI client with authorization automatically configured to query generative AI models. Run the following in your notebook or your local terminal:
pip install -U databricks-openai
The following is only required when installing the package on a Databricks Notebook
dbutils.library.restartPython()
Access to the Serving REST API is available in Databricks Runtime for Machine Learning.
!pip install mlflow
The following is only required when installing the package on a Databricks Notebook
dbutils.library.restartPython()
The Databricks SDK for Python is already installed on all Databricks clusters that use Databricks Runtime 13.3 LTS or above. For Databricks clusters that use Databricks Runtime 12.2 LTS and below, you must install the Databricks SDK for Python first. See Databricks SDK for Python.
Foundation model types
The following table summarizes the supported foundation models based on task type.
Meta-Llama-3.1-405B-Instruct will be retired,
- Starting February 15, 2026 for pay-per-token workloads.
- Starting May 15, 2026 for provisioned throughput workloads.
See Retired models for the recommended replacement model and guidance for how to migrate during deprecation.
Task type | Description | Supported models | When to use? Recommended use cases |
|---|---|---|---|
Models designed to understand and engage in natural, multi-turn conversations. They are fine-tuned on large datasets of human dialogue, which enables them to generate contextually relevant responses, track conversational history, and provide coherent, human-like interactions across various topics. | The following are supported Databricks-hosted foundation models:
The following are supported external models:
| Recommended for scenarios where natural, multi-turn dialogue and contextual understanding are needed:
| |
Embedding models are machine learning systems that transform complex data—such as text, images, or audio—into compact numerical vectors called embeddings. These vectors capture the essential features and relationships within the data, allowing for efficient comparison, clustering, and semantic search. | The following are supported Databricks-hosted foundation model: The following are supported external models:
| Recommended for applications where semantic understanding, similarity comparison, and efficient retrieval or clustering of complex data are essential:
| |
Models designed to process, interpret, and analyze visual data—such as images and videos so machines can "see" and understand the visual world. | The following are supported Databricks-hosted foundation models:
The following are supported external models:
| Recommended wherever automated, accurate, and scalable analysis of visual information is needed:
| |
Advanced AI systems designed to simulate human-like logical thinking. Reasoning models integrate techniques such as symbolic logic, probabilistic reasoning, and neural networks to analyze context, break down tasks, and explain their decision-making. | The following are supported Databricks-hosted foundation model:
The following are supported external models:
| Recommended wherever automated, accurate, and scalable analysis of visual information is needed:
|
Function calling
Databricks Function Calling is OpenAI-compatible and is only available during model serving as part of Foundation Model APIs and serving endpoints that serve external models. For details, see Function calling on Databricks.
Structured outputs
Structured outputs is OpenAI-compatible and is only available during model serving as part of Foundation Model APIs. For details, see Structured outputs on Databricks.
Prompt caching
Prompt caching is supported for Databricks-hosted Claude models as part of Foundation Model APIs.
You can specify the cache_control parameter in your query requests to cache the following:
- Text content messages in the
messages.contentarray. - Thinking messages content in the
messages.contentarray. - Images content blocks in the
messages.contentarray. - Tool use, results and definitions in the
toolsarray.
See Foundation model REST API reference.
- TextContent
- ReasonContent
- ImageContent
- ToolCallContent
{
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "text",
"text": "What's the date today?",
"cache_control": { "type": "ephemeral" }
}
]
}
]
}
{
"messages": [
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": [
{
"type": "reasoning",
"summary": [
{
"type": "summary_text",
"text": "Thinking...",
"signature": "[optional]"
},
{
"type": "summary_encrypted_text",
"data": "[encrypted text]"
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
Image message content must use the encoded data as its source. URLs are not supported.
{
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "text",
"text": "What’s in this image?"
},
{
"type": "image_url",
"image_url": {
"url": "data:image/jpeg;base64,[content]"
},
"cache_control": { "type": "ephemeral" }
}
]
}
]
}
{
"messages": [
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "Ok, let’s get the weather in New York.",
"tool_calls": [
{
"type": "function",
"id": "123",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{\"location\":\"New York, NY\"}"
},
"cache_control": { "type": "ephemeral" }
}
]
}
]
}
The Databricks REST API is OpenAI-compatible and differs from the Anthropic API. These differences also impact response objects like the following:
- Output is returned in the
choicesfield. - Streaming chunk format. All chunks adhere to the same format where
choicescontains the responsedeltaand usage is returned in every chunk. - Stop reason is returned in the
finish_reasonfield.- Anthropic uses:
end_turn,stop_sequence,max_tokens, andtool_use - Respectively, Databricks uses:
stop,stop,length, andtool_calls
- Anthropic uses:
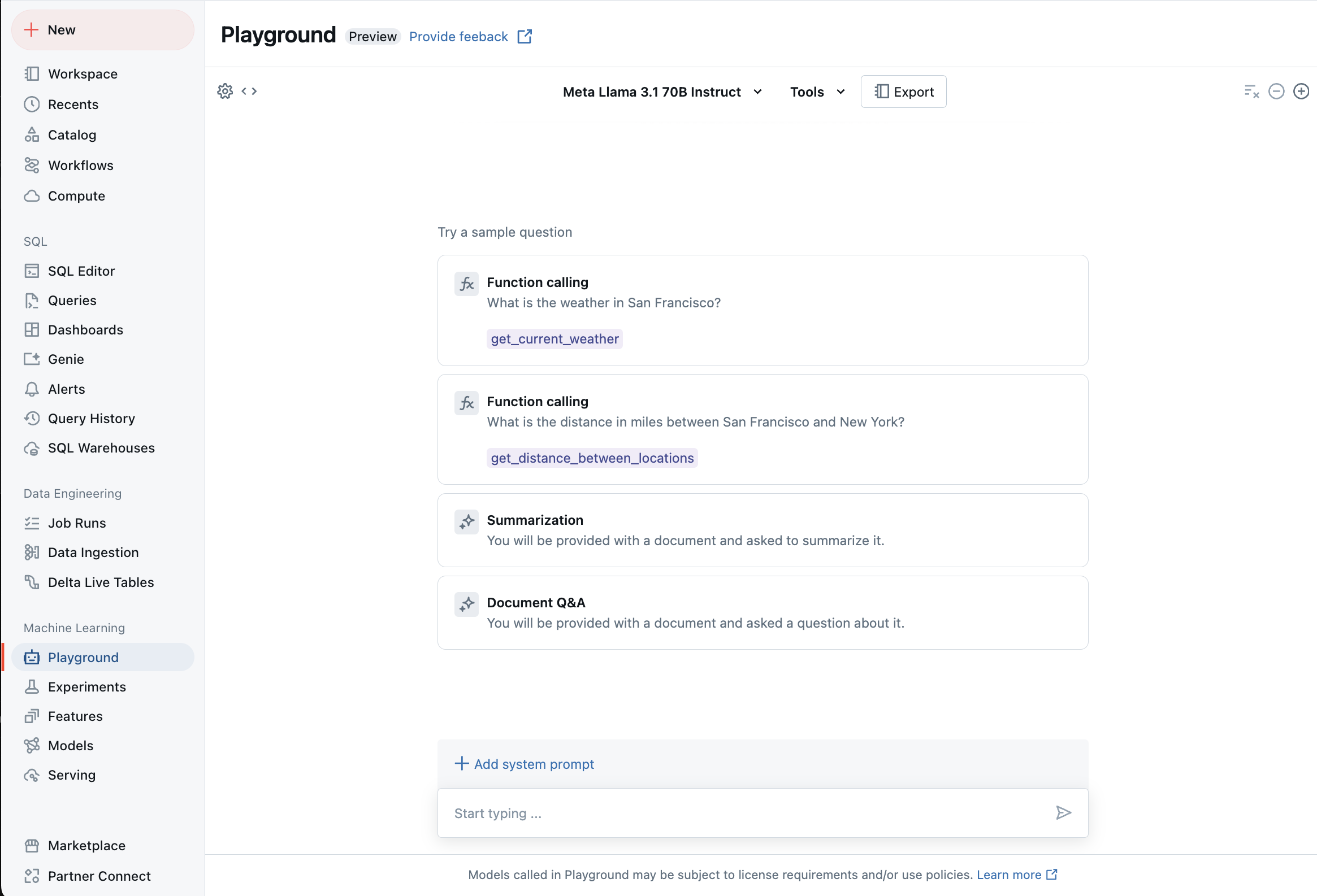
Chat with supported LLMs using AI Playground
You can interact with supported large language models using the AI Playground. The AI Playground is a chat-like environment where you can test, prompt, and compare LLMs from your Databricks workspace.
Additional resources
- Monitor served models using AI Gateway-enabled inference tables
- Deploy batch inference pipelines
- Databricks Foundation Model APIs
- External models in Mosaic AI Model Serving
- Tutorial: Create external model endpoints to query OpenAI models
- Databricks-hosted foundation models available in Foundation Model APIs
- Foundation model REST API reference