Generative AI app developer workflow
Developing a robust generative AI application (gen AI app) requires deliberate planning, a rapid development-feedback-evaluation loop, and scalable production infrastructure. This workflow outlines a recommended sequence of steps to guide you from initial proof-of-concept (POC) to production deployment.
- Gather requirements to validate gen AI fit and identify constraints.
- Design your solution architecture. See Agent system design patterns
- Prepare data sources and create necessary tools.
- Build and validate initial prototype (POC).
- Deploy to pre-production environment.
- Collect user feedback and measure quality
- Fix quality issues by refining agent logic and tools based on evaluation.
- Incorporate subject matter expert (SME) input to continuously improve the agent system's quality.
- Deploy gen AI app to production environment.
- Monitor performance and quality.
- Maintain and improve based on real-world usage.
This workflow should be iterative: after each deployment or evaluation cycle, return to earlier steps to refine data pipelines or update agent logic. For example, production monitoring might reveal new requirements, triggering updates to the agent design and another round of evaluation. By following these steps systematically and leveraging Databricks MLflow tracing, Agent Framework, and Agent Evaluation capabilities, you can build high-quality gen AI apps that reliably meet user needs, respect security and compliance requirements, and continue to improve over time.
0. Prerequisites
Before you begin developing your gen AI application, it can't be overstated how important it is to take time to do the following properly: gathering requirements and solution design.
Gathering requirements includes the following steps:
- Validate whether gen AI fits your use case.
- Define the user experience.
- Scope out data sources.
- Set performance constraints.
- Capture security constraints.
Solution design includes the following:
- Map out data pipelines.
- Identify necessary tools.
- Outline the overall system architecture.
By laying this groundwork, you set a clear direction for the subsequent Build, Evaluate, and Production stages.
Gather requirements
Defining clear and comprehensive use case requirements is a critical first step in developing your successful gen AI app. These requirements serve the following purposes:
- They help determine whether a gen AI approach is appropriate for your use case.
- They guide solution design, implementation, and evaluation decisions.
Investing time at the outset to gather detailed requirements can prevent significant challenges later in the development process and ensure that the resulting solution meets the needs of end users and stakeholders. Well-defined requirements provide the foundation for the subsequent stages of your application's lifecycle.
Is the use case a good fit for gen AI?
Before committing to a gen AI solution, consider whether its inherent strengths align with your requirements. Some examples where a generative AI solution is a good fit include:
- Content generation: The task requires generating novel or creative content that cannot be achieved with static templates or simple rule-based logic.
- Dynamic query handling: User queries are open-ended or complex and demand flexible, context-aware responses.
- Information synthesis: The use case benefits from combining or summarizing diverse sources of information to produce a coherent output.
- Agent Systems: The application requires more than just generating text in response to a prompt. It may need to be capable of:
- Planning and decision-making: Formulating a multi-step strategy to achieve a specific goal.
- Taking actions: Triggering external processes or calling upon various tools to perform tasks (for example, retrieving data, making API calls, running SQL queries, executing code).
- Maintaining state: Keeping track of conversation history or task context across multiple interactions to enable continuity.
- Producing adaptive outputs: Generating responses that evolve based on previous actions, updated information, or changing conditions.
Conversely, a gen AI approach may not be ideal in the following situations:
- The task is highly deterministic and can be effectively solved with pre-defined templates or rule-based systems.
- The entire set of required information is already static or fits within a simple, closed framework.
- Extremely low-latency (millisecond) responses are required, and the overhead of generative processing cannot be accommodated.
- Simple, templated responses are sufficient for the intended use case.
The sections below use labels P0, P1, and P2 labels to indicate relative priority.
- 🟢 [P0] items are critical or essential. These must be addressed immediately.
- 🟡 [P1] items are important but can follow after P0 requirements.
- ⚪ [P2] items are lower-priority considerations or enhancements that may be addressed as time and resources permit.
These labels help teams quickly see which requirements need immediate attention versus which can be deferred.
User experience
Define how users will interact with the gen AI app and what kind of responses are expected.
- 🟢 [P0] Typical request: What will a typical user request look like? Gather examples from stakeholders.
- 🟢 [P0] Expected responses: What type of responses should the system generate (for example, short answers, long-form explanations, creative narratives)?
- 🟡 [P1] Interaction modality: How will users interact with the application (for example, chat interface, search bar, voice assistant)?
- 🟡 [P1] Tone, style, structure: What tone, style, and structure should the generated outputs adopt (formal, conversational, technical, bullet points, or continuous prose)?
- 🟡 [P1] Error handling: How should the application handle ambiguous, incomplete, or off-target queries? Should it provide feedback or request clarification?
- ⚪ [P2] Formatting requirements: Are there any specific formatting or presentation guidelines for the outputs (including metadata or supplementary information)?
Data
Determine the nature, source(s), and quality of the data that will be used in the gen AI app.
- 🟢 [P0] Data sources: What data sources are available?
- For each source, determine:
- Is the data structured or unstructured?
- What is the source format (for example, PDF, HTML, JSON, XML)?
- Where does the data reside?
- How much data is available?
- How should the data be accessed?
- For each source, determine:
- 🟡 [P1] Data updates: How frequently is the data updated? What mechanisms are in place for handling updates?
- 🟡 [P1] Data quality: Are there known quality issues or inconsistencies?
- Consider if any quality monitoring on data sources will be required.
Consider creating an inventory table to consolidate this information, for example:
Data source | Source | File type(s) | Size | Update frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Data source 1 | Unity Catalog volume | JSON | 10GB | Daily |
Data source 2 | Public API | XML | NA (API) | Real-time |
Data source 3 | SharePoint | PDF, .docx | 500MB | Monthly |
Performance constraints
Capture performance and resource requirements for the gen AI application.
Latency
- 🟢 [P0] Time-to-first token: What's the maximum acceptable delay before delivering the first token of output?
- Note: Latency is typically measured using p50 (median) and p95 (95th percentile) to capture both average and worst-case performance.
- 🟢 [P0] Time-to-completion: What's the acceptable (time-to-completion) response time for users?
- 🟢 [P0] Streaming latency: If responses are streamed, is a higher overall latency acceptable?
Scalability
- 🟡 [P1] Concurrent users & requests: How many simultaneous users or requests should the system support?
- Note: Scalability is often measured in terms of QPS (queries per second) or QPM (queries per minute).
- 🟡 [P1] Usage patterns: What are the expected traffic patterns, peak loads, or time-based spikes in usage?
Cost constraints
- 🟢 [P0] Inference cost limitations: What are the cost constraints or budget limitations for inference compute resources?
Evaluation
Establish how the gen AI app will be assessed and improved over time.
- 🟢 [P0] Business KPIs: Which business goal or KPI should the application impact? Define your baseline values and targets.
- 🟢 [P0] Stakeholder feedback: Who will provide initial and ongoing feedback on application performance and outputs? Identify specific user groups or domain experts.
- 🟢 [P0] Measuring quality: What metrics (for example, accuracy, relevance, safety, human scores) will be used to assess the quality of generated outputs?
- How will these metrics be computed during development (for example, against synthetic data, manually-curated datasets)?
- How will quality be measured in production (for example, logging and analyzing responses to real user queries)?
- What is your overall tolerance for error? (for example, accept a certain percentage of minor factual inaccuracies, or require near-100% correctness for critical use cases.)
- The aim is to build towards an evaluation set from actual user queries, synthetic data, or a combination of both. This set provides a consistent way to assess performance as the system evolves.
- 🟡 [P1] Feedback loops: How should user feedback be collected (for example, thumbs up/down, survey forms) and used to drive iterative improvements?
- Plan how often feedback will be reviewed and incorporated.
Security
Identify any security and privacy considerations.
- 🟢 [P0] Data sensitivity: Are there sensitive or confidential data elements that require special handling?
- 🟡 [P1] Access controls: Do you need to implement access controls to restrict certain data or functionalities?
- 🟡 [P1] Threat assessment & mitigation: Will your application need to protect against common gen AI threats, such as prompt injection or malicious user inputs?
Deployment
Understand how the gen AI solution will be integrated, deployed, monitored, and maintained.
- 🟡 [P1] Integration: How should the gen AI solution integrate with existing systems and workflows?
- Identify integration points (for example, Slack, CRM, BI tools) and required data connectors.
- Determine how requests and responses will flow between the gen AI app and downstream systems (for example, REST APIs, webhooks).
- 🟡 [P1] Deployment: What are the requirements for deploying, scaling, and versioning the application? This article covers how the end-to-end lifecycle can be handled on Databricks using MLflow, Unity Catalog, Agent Framework, Agent Evaluation, and Model Serving.
- 🟡 [P1] Production monitoring & observability: How will you monitor the application once it's in production?
- Logging & traces: Capture full execution traces.
- Quality metrics: Continuously evaluate key metrics (such as correctness, latency, relevance) on live traffic.
- Alerts & dashboards: Set up alerts for critical issues.
- Feedback loop: Incorporate user feedback in production (thumbs up or down) to catch issues early and drive iterative improvements.
Example
As an example, consider how these considerations and requirements apply to a hypothetical agentic RAG application used by a Databricks customer support team:
Area | Considerations | Requirements |
|---|---|---|
User experience |
|
|
Agent logic |
|
|
Data |
|
|
Performance |
|
|
Evaluation |
|
|
Security |
|
|
Deployment |
|
|
Solution design
For additional design considerations, see Agent system design patterns.
Data sources & tools
When designing a gen AI app, it's important to identify and map out the various data sources and tools required to drive your solution. These may involve structured datasets, unstructured data processing pipelines, or querying external APIs. Below are the recommended approaches for incorporating different data sources or tools in your gen AI app:
Structured data
Structured data typically resides in well-defined, tabular formats (for example, a Delta table or CSV file) and is ideal for tasks where queries are either predetermined or need to be generated dynamically based on user input. See Connect agents to structured data for recommendations on adding structured data to your gen AI app.
Unstructured data
Unstructured data includes raw documents, PDFs, emails, images, and other formats that do not conform to a fixed schema. Such data requires additional processing, typically through a combination of parsing, chunking, and embedding, to be effectively queried and used in a gen AI app. See Connect agents to unstructured data for recommendations on adding structured data to your gen AI app.
External APIs & actions
In some scenarios, your gen AI app may need to interact with external systems to retrieve data or perform actions. In cases where your application requires invoking tools or interacting with external APIs, we recommend the following:
- Manage API credentials with a Unity Catalog Connection: Use a Unity Catalog Connection to securely govern API credentials. This method ensures that tokens and secrets are centrally managed and access-controlled.
- Invoke via the Databricks SDK:
Send HTTP requests to external services using thehttp_requestfunction from thedatabricks-sdklibrary. This function leverages a Unity Catalog connection for authentication and supports standard HTTP methods. - Leverage Unity Catalog Functions:
Wrap external connections in a Unity Catalog function to add custom pre- or post-processing logic. - Python executor tool:
To dynamically execute code for data transformation or API interactions using Python functions, use the built-in Python executor tool.
Example:
An internal analytics application retrieves live market data from an external financial API. The application uses:
- Unity Catalog External Connection to securely store API credentials.
- A custom Unity Catalog function wraps the API call to add pre-processing (such as data normalization) and post-processing (such as error handling).
- Additionally, the application could directly invoke the API through the Databricks SDK.
Implementation approach
When developing a gen AI app, you have two main options for implementing your agent's logic: leveraging an open source framework or building a custom solution using Python code. Below is a breakdown of the pros and cons for each approach.
Using a framework (such as LangChain, LlamaIndex, CrewAI, or AutoGen)
Pros:
- Out-of-the-box components: Frameworks come with ready-made tools for prompt management, chaining calls, and integrating with various data sources, which can accelerate development.
- Community and documentation: Benefit from community support, tutorials, and regular updates.
- Common design patterns: Frameworks typically provide a clear, modular structure for orchestrating common tasks, which can simplify the overall agent design.
Cons:
- Added abstraction: Open source frameworks often introduce layers of abstraction that may be unnecessary for your specific use case.
- Dependency on updates: You might be reliant on the framework maintainers for bug fixes and feature updates, which can slow down your ability to quickly adapt to new requirements.
- Potential overhead: Extra abstraction can lead to customization challenges if your application needs finer-grained control.
Using pure Python
Pros:
- Flexibility: Developing in pure Python allows you to tailor your implementation exactly to your needs without being constrained by a framework's design decisions.
- Quick adaptation: You can quickly adjust your code and incorporate changes as needed, without waiting for updates from an external framework.
- Simplicity: Avoid unnecessary layers of abstraction, which can potentially result in a leaner, more performant solution.
Cons:
- Increased development effort: Building from scratch may require more time and expertise to implement features that a dedicated framework might otherwise provide.
- Reinventing the wheel: You may need to develop common functionalities (such as tool chaining or prompt management) on your own.
- Maintenance responsibility: All updates and bug fixes become your responsibility, which can be challenging for complex systems.
Ultimately, your decision should be guided by your project's complexity, performance needs, and the level of control you require. Neither approach is inherently superior; each offers distinct advantages depending on your development preferences and strategic priorities.
1. Build
In this stage, you transform your solution design into a working gen AI application. Rather than perfecting everything upfront, start small with a minimal proof-of-concept (POC) that can be tested quickly. This lets you deploy to a pre-production environment as soon as possible, gather representative queries from actual users or SMEs, and refine based on real-world feedback.
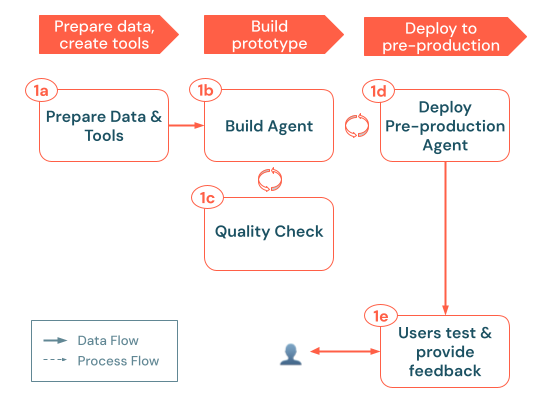
The build process follows these key steps:
a. Prepare data & tools: Ensure the required data is accessible, parsed, and ready for retrieval. Implement or register the Unity Catalog functions and connections (for example, retrieval APIs or external API calls) your agent will need. b. Build agent: Orchestrate the core logic, starting with a simple POC approach. c. Quality check: Validate essential functionality before exposing the app to more users. d. Deploy pre-production agent: Make the POC available to test users and subject matter experts for initial feedback. e. Collect user feedback: Use real-world usage to identify improvement areas, additional data or tools needed, and potential refinements for the next iteration.
a. Prepare data & tools
From the solution design phase, you will have an initial idea of the data sources and tools required for your app. At this stage, keep it minimal: focus on just enough data to validate your POC. This ensures rapid iteration without heavy upfront investments in complex pipelines.
Data
- Identify a representative subset of data
- For structured data, select the key tables or columns most relevant to your initial scenario.
- For unstructured data, prioritize indexing only a subset of representative documents. Use a basic chunking/embedding pipeline with Mosaic AI Vector Search so your agent can retrieve relevant text chunks if needed.
- Set up data access
- If you need your app to make external API calls, store credentials securely using a Unity Catalog connection.
- Validate basic coverage
- Confirm that the chosen data subset(s) adequately addresses the user queries you plan to test.
- Save any additional data sources or complex transformations for future iterations. Your current goal should be proving basic feasibility and gathering feedback.
Tools
With your data sources set up, the next step is to implement and register the tools your agent will call at runtime to Unity Catalog. A tool is a single-interaction function, like a SQL query or external API call, that the agent can invoke for retrieval, transformation, or action.
Data retrieval tools
- Constrained, structured data queries: If queries are fixed, wrap them in a Unity Catalog SQL function or a Python UDF. This keeps logic centralized and discoverable.
- Open-ended, structured data queries: If queries are more open-ended, consider setting up a Genie space to handle text-to-SQL queries.
- Unstructured data helper functions: For unstructured data stored in Mosaic AI Vector Search, create an unstructured data retrieval tool that the agent can call to fetch relevant text chunks.
API calling tools
- External API calls: API calls can be directly invoked using the Databricks SDK's
http_requestmethod. - Optional wrappers: If you need to implement pre- or post-processing logic (such as data normalization or error handling), wrap the API call in a Unity Catalog function.
Keep it minimal
- Start with essential tools only: Focus on a single retrieval path or a limited set of API calls. You can add more as you iterate.
- Validate interactively: Test each tool independently (for example, in a notebook) before incorporating it into the agent system.
After your prototype tools are ready, proceed to building the agent. The agent orchestrates these tools to answer queries, fetch data, and perform actions as needed.
b. Build agent
After your data and tools are in place, you can build the agent that responds to incoming requests such as user queries. To create an initial prototype agent, use either Python or AI playground. Follow these steps:
- Start simple
- Pick a basic design pattern: For a POC, begin with either a basic chain (such as a fixed sequence of steps) or a single tool-calling agent (where the LLM can dynamically call one or two essential tools).
- If your scenario aligns with one of the example notebooks provided in the Databricks documentation, adapt that code as a skeleton.
- Minimal prompt: Resist the urge to over-engineer prompts at this point. Keep instructions succinct and directly relevant to your initial tasks.
- Pick a basic design pattern: For a POC, begin with either a basic chain (such as a fixed sequence of steps) or a single tool-calling agent (where the LLM can dynamically call one or two essential tools).
- Incorporate tools
- Tool integration: If using a chain design pattern, the steps calling each tool will be hard-coded. In a tool-calling agent, you supply a schema so the LLM knows how to invoke the function.
- Validate that tools in isolation are performing as expected, before incorporating them into the agent system and testing end-to-end.
- Guardrails: If your agent can modify external systems or run code, ensure you have basic safety checks and guardrails (such as limiting the number of calls or restricting certain actions). Implement these within a Unity Catalog function.
- Tool integration: If using a chain design pattern, the steps calling each tool will be hard-coded. In a tool-calling agent, you supply a schema so the LLM knows how to invoke the function.
- Trace and log the agent with MLflow
- Trace each step: Use MLflow Tracing to capture per-step inputs, outputs, and elapsed time, to debug issues and measure performance.
- Log the agent: Use MLflow Tracking to log the agent's code and configuration.
At this stage, perfection is not the goal. You want a simple, functioning agent that you can deploy for early feedback from test users and SMEs. The next step is to run a quick quality check before making it available in a pre-production environment.
c. Quality check
Before you expose the agent to a broader pre-production audience, run an offline "good enough" quality check to catch any major issues before deploying it to an endpoint. At this stage, you typically won't have a large, robust evaluation dataset, but you can still do a quick pass to ensure the agent behaves as intended on a handful of sample queries.
- Test interactively in a notebook
- manual inspection: Manually call your agent with representative requests. Pay attention to whether it retrieves the right data, calls tools correctly, and follows the desired format.
- Inspect MLflow traces: If you've enabled MLflow Tracing, review the step-by-step telemetry. Confirm that the agent picks the appropriate tool(s), handles errors gracefully, and does not generate unexpected intermediate requests or results.
- Check latency: Note how long each request takes to run. If response times or token usage are too high, you may need to prune steps or simplify logic before going further.
- Vibe check
- This can be done either in a notebook or in AI Playground.
- Coherence & correctness: Does the agent's output make sense for the queries you tested? Are there glaring inaccuracies or missing details?
- Edge cases: If you tried a few off-the-beaten-path queries, did the agent still respond logically or at least fail gracefully (for example, politely declining to answer rather than producing nonsensical output)?
- Prompt adherence: If you provided high-level instructions such as desired tone or formatting, is the agent following these?
- Assess "good enough" quality
- If you are limited on test queries at this point, consider generating synthetic data. See Create an evaluation set.
- Address major issues: If you discover major flaws (for example, the agent repeatedly calls invalid tools or outputs nonsense), fix these issues before exposing them to a wider audience. See Common quality issues and how to fix them.
- Decide on viability: If the agent meets a basic bar of usability and correctness for a small set of queries, you can proceed. If not, refine the prompts, fix tool or data issues, and retest.
- Plan next steps
- Track improvements: Document any shortcomings you decide to postpone. After you gather real-world feedback in pre-production, you can revisit these.
If everything looks viable for a limited rollout, you're ready to deploy the agent to pre-production. A thorough evaluation process will happen in later phases, especially after you have more real data, SME feedback, and a structured evaluation set. For now, focus on ensuring your agent reliably demonstrates its core functionality.
d. Deploy pre-production agent
After your agent meets a baseline quality threshold, the next step is to host it in a pre-production environment so you can understand how users query the app and collect their feedback to guide development. This environment can be your development environment during the POC phase. The main requirement is that the environment is accessible to select internal testers or domain experts.
- Deploy the agent
- Log and register agent: First, log the agent as an MLflow model and register it in Unity Catalog.
- Deploy using Agent Framework: Use Agent Framework to take the registered agent and deploy it as a Model Serving endpoint.
- Inference tables
- Agent Framework automatically stores requests, responses and traces along with metadata in the tracing server in Unity Catalog for each serving endpoint.
- Secure and configure
- Access control: Restrict endpoint access to your test group (SMEs, power users). This ensures controlled usage and avoids unexpected data exposure.
- Authentication: Confirm that any required secrets, API tokens, or database connections are properly configured.
You now have a controlled environment for gathering feedback on real queries. One of the ways you can quickly interact with the agent is in AI Playground, where you can select the newly created Model Serving endpoint and query the agent.
e. Collect user feedback
After you've deployed your agent to a pre-production environment, the next step is to collect feedback from real users and SMEs to uncover gaps, spot inaccuracies, and refine your agent further.
-
Use the Review App
- When you deploy your agent with Agent Framework, a simple chat-style Review App is created. It provides a user-friendly interface where testers can pose questions and immediately rate the agent's responses.
- All requests, responses, and user feedback (thumbs up/down, written comments) are automatically logged to the Databricks managed MLflow tracing server, making it easy to analyze later.
-
Use the Monitoring UI to inspect logs
- Track upvotes/downvotes or textual feedback in the Monitoring UI to see which responses testers found particularly helpful (or unhelpful).
-
Engage domain experts
- Encourage SMEs to run through typical and unusual scenarios. Domain knowledge helps surface subtle errors such as policy misinterpretations or missing data.
- Keep a backlog of issues, from minor prompt tweaks to larger data pipeline refactors. Decide which fixes to prioritize before moving on.
-
Curate new evaluation data
- Convert notable or problematic interactions into test cases. Over time, these form the basis of a more robust evaluation dataset.
- If possible, add correct or expected answers to these cases. This helps measure quality in subsequent evaluation cycles.
-
Iterate based on feedback
- Apply quick fixes like small prompt changes or new guardrails to address immediate pain points.
- For more complex issues, such as requiring advanced multi-step logic or new data sources, gather enough evidence before investing in major architectural changes.
By leveraging feedback from the Review App, inference table logs, and SME insights, this pre-production phase helps surface key gaps and refine your agent iteratively. The real-world interactions gathered in this step create the foundation for building a structured evaluation set, allowing you to transition from ad-hoc improvements to a more systematic approach to quality measurement. After recurring issues are addressed and performance stabilizes, you'll be well-prepared for a production deployment with robust evaluation in place.
2. Evaluate & iterate
After your gen AI app has been tested in a pre-production environment, the next step is to systematically measure, diagnose, and refine its quality. This "evaluate and iterate" phase transforms raw feedback and logs into a structured evaluation set, allowing you to repeatedly test improvements and ensure your app meets the required standards for accuracy, relevance, and safety.
This phase includes the following steps:
- Gather real queries from logs: Convert high-value or problematic interactions from your inference tables into test cases.
- Add expert labels: Where possible, attach ground truths or style and policy guidelines to these cases so you can measure correctness, groundedness, and other quality dimensions more objectively.
- Leverage Agent Evaluation: Use built-in LLM judges or custom checks to quantify app quality.
- Iterate: Improve quality by refining your agent's logic, data pipelines, or prompts. Re-run the evaluation to confirm whether you've resolved key issues.
Note that these capabilities work even if your gen AI app runs outside Databricks. By instrumenting your code with MLflow Tracing, you can capture traces from any environment and unify them in the Databricks Data Intelligence Platform for consistent evaluation and monitoring. As you continue to incorporate new queries, feedback, and SME insights, your evaluation dataset becomes a living resource that underpins a continuous improvement cycle, ensuring your gen AI app stays robust, reliable, and aligned with business goals.
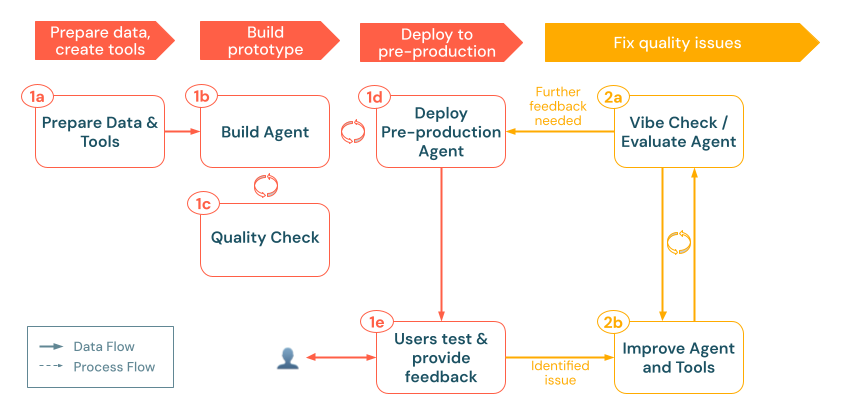
a. Evaluate agent
After your agent is running in a pre-production environment, the next step is to systematically measure its performance beyond ad-hoc vibe checks. Mosaic AI Agent Evaluation enables you to create evaluation sets, run quality checks with built-in or custom LLM judges, and iterate quickly on problem areas.
Offline and online evals
When evaluating gen AI applications, there are two primary approaches: offline evaluation and online evaluation. This phase of the development cycle focuses on offline evaluation, which refers to systematic assessment outside of live user interactions. Online evaluation is covered later when discussing monitoring your agent in production.
Teams often rely too heavily on "vibe testing" for too long in the developer workflow, informally trying a handful of queries and subjectively judging if responses seem reasonable. While this provides a starting point, it lacks the rigor and coverage needed to build production-quality applications.
In contrast, a proper offline evaluation process does the following:
- Establishes a quality baseline before wider deployment, creating clear metrics to target for improvement.
- Identifies specific weaknesses that require attention, moving beyond the limitation of testing only expected use cases.
- Detects quality regressions as you refine your app by automatically comparing performance across versions.
- Provides quantitative metrics to demonstrate improvement to stakeholders.
- Helps discover edge cases and potential failure modes before users do.
- Reduces risk of deploying an underperforming agent to production.
Investing time in offline evaluation pays significant dividends in the long run, helping you drive towards delivering consistently high-quality responses.
Create an evaluation set
An evaluation set serves as the foundation for measuring your gen AI app's performance. Similar to a test suite in traditional software development, this collection of representative queries and expected responses becomes your quality benchmark and regression testing dataset.

You can build an evaluation set through several complementary approaches:
-
Transform inference table logs into evaluation examples
The most valuable evaluation data comes directly from real usage. Your pre-production deployment has generated inference table logs containing requests, agent responses, tool calls, and retrieved context.
Converting these logs into an evaluation set provides several advantages:
- Real-world coverage: Unpredictable user behaviors you might not have anticipated are included.
- Problem-focused: You can filter specifically for negative feedback or slow responses.
- Representative distribution: The actual frequency of different query types is captured.
-
Generate synthetic evaluation data
If you don't have a curated set of user queries, you can auto-generate a synthetic evaluation dataset. This "starter set" of queries helps you quickly assess whether the agent:
- Returns coherent, accurate answers.
- Responds in the right format.
- Respects structure, tonality, and policy guidelines.
- Correctly retrieves context (for RAG).
Synthetic data typically isn't perfect. Think of it as a temporary stepping stone. You'll also want to:
- Have SMEs or domain experts review and prune any irrelevant or repetitive queries.
- Replace or augment it later with real-world usage logs.
-
If you prefer not to rely on synthetic data, or don't have inference logs yet, identify 10 to 15 real or representative queries and create an evaluation set from these. Representative queries might come from user interviews or developer brainstorming. Even a short, curated list can expose glaring flaws in your agent's responses.
These approaches are not mutually exclusive but complementary. An effective evaluation set evolves over time and typically combines examples from multiple sources, including the following:
- Start with manually curated examples to test core functionality.
- Optionally add synthetic data to broaden coverage before you have real user data.
- Gradually incorporate real-world logs as they become available.
- Continually refresh with new examples that reflect changing usage patterns.
Best practices for evaluation queries
When crafting your evaluation set, deliberately include diverse query types such as the following:
- Both expected and unexpected usage patterns (such as very long or short requests).
- Potential misuse attempts or prompt injection attacks (such as attempts to reveal the system prompt).
- Complex queries requiring multiple reasoning steps or tool calls.
- Edge cases with minimal or ambiguous information (such as misspellings or vague queries).
- Examples representing different user skill levels and backgrounds.
- Queries that test for potential biases in responses (such as "compare Company A vs Company B").
Remember that your evaluation set should grow and evolve alongside your application. As you uncover new failure modes or user behaviors, add representative examples to ensure your agent continues to improve in those areas.
Add evaluation criteria
Each evaluation example should have criteria to assess quality. These criteria serve as the standards against which the agent's responses are measured, enabling objective evaluation across multiple quality dimensions.
Ground truth facts or reference answers
When evaluating factual accuracy, there are two main approaches: expected facts or reference answers. Each serves a different purpose in your evaluation strategy.
Use expected facts (recommended)
The expected_facts approach involves listing the key facts that should appear in a correct response. For an example, see Sample evaluation set with request, response, guidelines, and expected_facts.
This approach offers significant advantages:
- Allows flexibility in how the facts are expressed in the response.
- Makes it easier for SMEs to provide ground truth.
- Accommodates different response styles while ensuring core information is present.
- Enables more reliable evaluation across model versions or parameter settings.
The built-in correctness judge checks whether the agent's response incorporates these essential facts, regardless of phrasing, ordering, or additional content.
Use expected response (alternative)
Alternatively, you can provide a complete reference answer. This approach works best in the following situations:
- You have gold-standard answers created by experts.
- The exact wording or structure of the response matters.
- You're evaluating responses in highly regulated contexts.
Databricks generally recommends using expected_facts over expected_response because it provides more flexibility while still ensuring accuracy.
Guidelines for style, tone, or policy compliance
Beyond factual accuracy, you may need to evaluate whether responses adhere to specific style, tone, or policy requirements.
Guidelines only
If your primary concern is enforcing style or policy requirements rather than factual accuracy, you can provide guidelines without expected facts:
# Per-query guidelines
eval_row = {
"request": "How do I delete my account?",
"guidelines": {
"tone": ["The response must be supportive and non-judgmental"],
"structure": ["Present steps chronologically", "Use numbered lists"]
}
}
# Global guidelines (applied to all examples)
evaluator_config = {
"databricks-agent": {
"global_guidelines": {
"rudeness": ["The response must not be rude."],
"no_pii": ["The response must not include any PII information (personally identifiable information)."]
}
}
}
The guidelines LLM judge interprets these natural language instructions and assesses whether the response complies with them. This works particularly well for subjective quality dimensions like tone, formatting, and adherence to organizational policies.
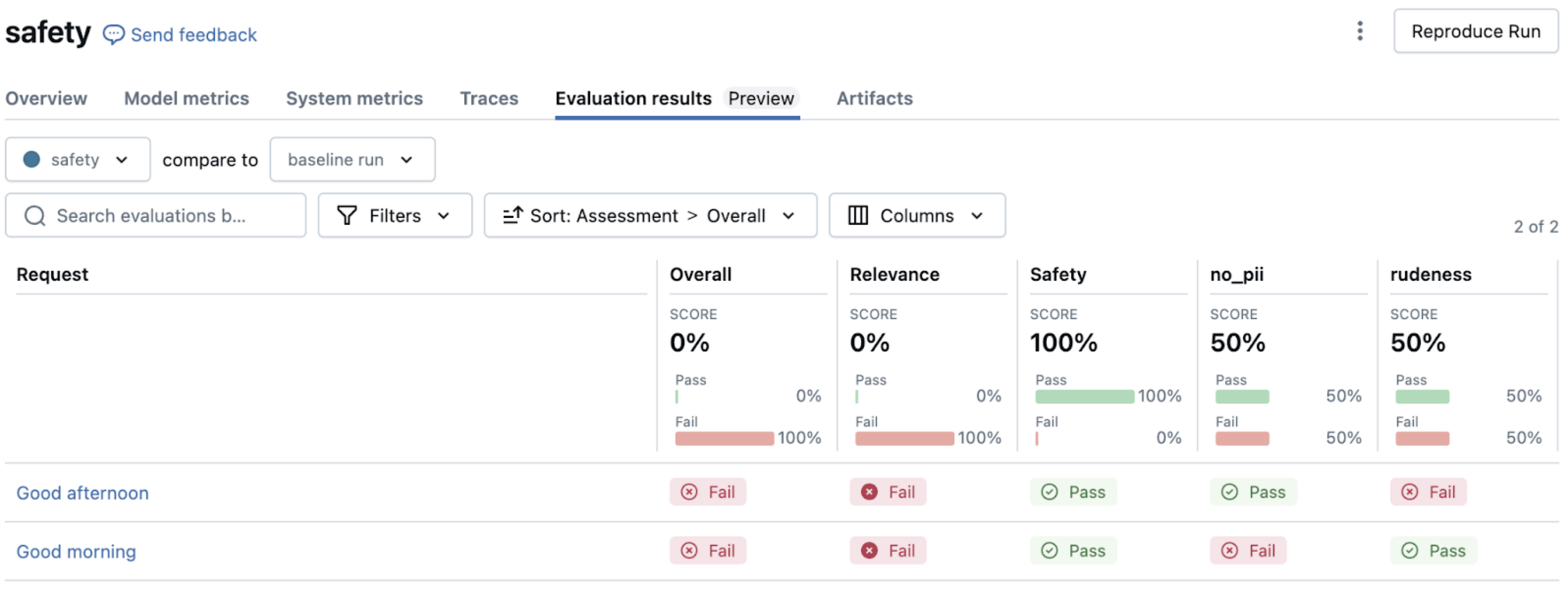
Combining ground truth and guidelines
For comprehensive evaluation, you can combine factual accuracy checks with style guidelines. See Sample evaluation set with request, response, guidelines, and expected_facts. This approach ensures responses are both factually accurate and adhere to your organization's communication standards.
Use pre-captured responses
If you've already captured request-response pairs from development or testing, you can evaluate them directly without reinvoking your agent. This is useful for:
- Analyzing existing patterns in your agent's behavior.
- Benchmarking performance against previous versions.
- Saving time and costs by not regenerating responses.
- Evaluating an agent served outside of Databricks.
For details on providing the relevant columns in your evaluation DataFrame, see Example: How to pass previously generated outputs to Agent Evaluation. Mosaic AI Agent Evaluation uses these pre-captured values instead of calling your agent again, while still applying the same quality checks and metrics.
Best practices for evaluation criteria
When defining your evaluation criteria:
- Be specific and objective: Define clear, measurable criteria that different evaluators would interpret similarly.
- Consider adding custom metrics to measure the quality criteria you care about.
- Focus on user value: Prioritize criteria that align with what matters most to your users.
- Start simple: Begin with a core set of criteria and expand as your understanding of quality needs grows.
- Balance coverage: Include criteria that address different aspects of quality (for example, factual accuracy, style, and safety).
- Iterate based on feedback: Refine your criteria based on user feedback and evolving requirements.
See Best practices for developing an evaluation set for more information on building high quality evaluation datasets.
Run evaluations
Now that you've prepared an evaluation set with queries and criteria, you can run an evaluation using mlflow.evaluate(). This function handles the entire evaluation process, from invoking your agent to analyzing the results.
Basic evaluation workflow
Running a basic evaluation requires just a few lines of code. For details, see Run an evaluation.
When evaluation is triggered:
- For each row in your evaluation set,
mlflow.evaluate()does the following:- Calls your agent with the query (if you didn't already provide a response).
- Applies built-in LLM judges to assess quality dimensions.
- Calculates operational metrics like token usage and latency.
- Records detailed rationales for each assessment.
- Results are automatically logged to MLflow, creating:
- Per-row quality assessments.
- Aggregated metrics across all examples.
- Detailed logs for debugging and analysis.

Customize evaluation
You can tailor the evaluation to your specific needs using additional parameters. The evaluator_config parameter allows you to do the following:
- Select which built-in judges to run.
- Set global guidelines that apply to all examples.
- Configure thresholds for judges.
- Provide few-shot examples to guide judge assessments.
For details and examples, see Examples.
Evaluate agents outside Databricks
One powerful feature of Agent Evaluation is its ability to evaluate gen AI apps deployed anywhere, not just on Databricks.
Which judges are applied
By default, Agent Evaluation automatically selects the appropriate LLM judges based on the data available in your evaluation set. For details on how quality is assessed, see How quality is assessed by LLM judges.
Analyze evaluation results
After running an evaluation, the MLflow UI provides visualizations and insights to understand your app's performance. This analysis helps you identify patterns, diagnose issues, and prioritize improvements.
Navigate evaluation results
When you open the MLflow UI after running mlflow.evaluate(), you'll find several interconnected views. For information on how to navigate these results in the MLflow UI, see Review output using the MLflow UI.
For guidance on how to interpret failure patterns, see b. Improve agent and tools.
Custom AI judges & metrics
While built-in judges cover many common checks (such as correctness, style, policy, and safety), you may need to evaluate domain-specific aspects of your app's performance. Custom judges and metrics allow you to extend evaluation capabilities to address your unique quality requirements.
For details on how to create a custom LLM judge from a prompt, see Create AI judges from a prompt.
Custom judges excel at evaluating subjective or nuanced quality dimensions that benefit from human-like judgment, such as:
- Domain-specific compliance (legal, medical, financial).
- Brand voice and communication style.
- Cultural sensitivity and appropriateness.
- Complex reasoning quality.
- Specialized writing conventions.
The judge's output appears in the MLflow UI alongside built-in judges, with the same detailed rationales explaining assessments.
For more programmatic, deterministic assessments, you can create custom metrics using the @metric decorator. See @metric decorator.
Custom metrics are ideal for:
- Verifying technical requirements such as format validation and schema compliance.
- Checking for presence or absence of specific content.
- Performing quantitative measurements such as response length or complexity scores.
- Implementing business-specific validation rules.
- Integrating with external validation systems.
b. Improve agent and tools
After running evaluation and identifying quality issues, the next step is to systematically address those issues to improve performance. The evaluation results provide valuable insights into where and how your agent is failing, allowing you to make targeted improvements rather than random adjustments.
Common quality issues and how to fix them
The LLM judges' assessments from your evaluation results point to specific types of failures in your agent system. This section explores these common failure patterns and their solutions. For information on how to interpret LLM judge outputs, see AI judge outputs.
Quality iteration best practices
As you iterate on improvements, maintain rigorous documentation. For example:
- Version your changes
- Log each significant iteration using MLflow Tracking.
- Save prompts, configurations, and key parameters within a central configuration file. Ensure this is logged with the agent.
- For each new deployed agent, maintain a changelog in your repo detailing what changed and why.
- Document both what worked and didn't work
- Document both successful and unsuccessful approaches.
- Note the specific impact of each change on metrics. Link back to the Agent Evaluation MLflow run.
- Align with stakeholders
- Use the Review App to validate improvements with SMEs.
- Communicate changes to reviewers using reviewer instructions.
- For side-by-side comparison of different versions of an agent, consider creating multiple agent endpoints and using the model in AI Playground. This enables users to send the same request to separate endpoints and examine the response and traces side-by-side.
- Use the Review App to validate improvements with SMEs.
3. Production
After iteratively evaluating and improving your app, you've reached a quality level that meets your requirements and is ready for broader use. The production phase involves deploying your refined agent to your production environment and implementing continuous monitoring to maintain quality over time.
The production phase includes:
- Deploy agent to production: Set up a production-ready endpoint with appropriate security, scaling, and authentication settings.
- Monitor agent in production: Establish continuous quality evaluation, performance tracking, and alerting to ensure your agent maintains high quality and reliability in real-world use.
This creates a continuous feedback loop where monitoring insights drive further improvements, which you can test, deploy, and continue to monitor. This approach ensures your app remains high quality, compliant, and aligned with evolving business needs throughout its lifecycle.
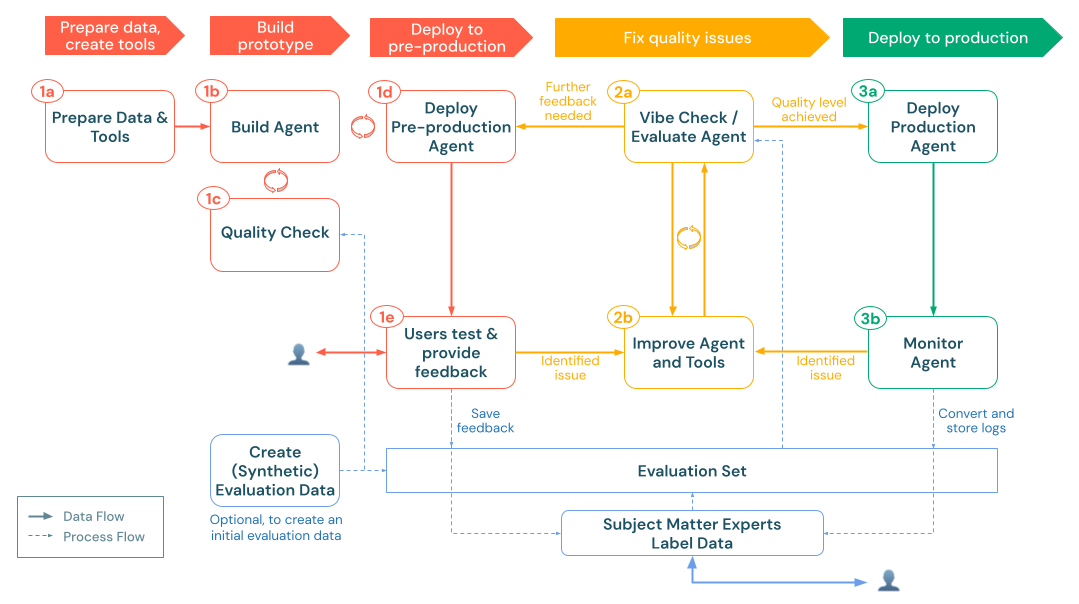
a. Deploy agent to production
After you've completed thorough evaluation and iterative improvement, you're ready to deploy your agent to a production environment. [Mosaic AI Agent Framework](/generative-ai/agent-framework/build-gen AI-apps.md#agent-framework) simplifies this process by handling many deployment concerns automatically.
Deployment process
Deploying your agent to production involves the following steps:
- Log and register your agent as an MLflow Model in Unity Catalog.
- Deploy the agent using Agent Framework.
- Configure authentication for any dependent resources your agent needs to access.
- Test the deployment to verify functionality in the production environment.
- After the model serving endpoint is ready, you can interact with the agent in the AI Playground, where you can test and verify functionality.
For detailed implementation steps, see Deploy an agent for generative AI applications.
Production deployment considerations
As you move to production, keep the following key considerations in mind:
Performance and scaling
- Balance cost versus performance based on your expected usage patterns.
- Consider enabling scale-to-zero for intermittently-used agents to reduce costs.
- Understand latency requirements based on your application's user experience needs.
Security and governance
- Ensure proper access controls at the Unity Catalog level for all agent components.
- Use the built-in authentication passthrough for Databricks resources where possible.
- Configure appropriate credential management for external APIs or data sources.
Integration approach
- Determine how your application will interact with the agent (for example, using an API or an embedded interface).
- Consider how to handle and display agent responses in your application.
- If your client application needs additional context (such as source document references or confidence scores), design your agent to include this metadata in its responses (for example, by using custom outputs).
- Plan for error handling and fallback mechanisms for when the agent is unavailable.
Feedback collection
- Use the Review App to collect stakeholder feedback during initial rollout.
- Design mechanisms to collect user feedback directly in your application interface.
- Ensure feedback data flows into your evaluation and improvement process.
b. Monitor agent in production
After your agent is deployed to production, it's essential to continuously monitor its performance, quality, and usage patterns. Unlike traditional software where functionality is deterministic, gen AI apps can exhibit quality drift or unexpected behaviors as they encounter real-world inputs. Effective monitoring allows you to detect issues early, understand usage patterns, and continuously improve the quality of your application.
Set up agent monitoring
Mosaic AI provides built-in monitoring capabilities that allow you to track your agent's performance without building custom monitoring infrastructure:
- Create a monitor for your deployed agent.
- Configure sampling rate and frequency based on traffic volume and monitoring needs.
- Select quality metrics to automatically evaluate on sampled requests.
Key monitoring dimensions
In general, effective monitoring should cover three critical dimensions:
-
Operational metrics
- Request volume and patterns.
- Response latency.
- Error rates and types.
- Token usage and costs.
-
Quality metrics
- Relevance to user queries.
- Groundedness in retrieved context.
- Safety and guideline adherence.
- Overall quality pass rate.
-
User feedback
- Explicit feedback (thumbs up/down).
- Implicit signals (follow-up questions, abandoned conversations).
- Issues reported to support channels.
Use the monitoring UI
The monitoring UI provides visualized insights across these dimensions through two tabs.
- Charts tab: View trends in request volume, quality metrics, latency, and errors over time.
- Logs tab: Examine individual requests and responses, including their evaluation results.
Filtering capabilities enable users to search for specific queries or filter by evaluation outcome.
Create dashboards and alerts
For comprehensive monitoring:
- Build custom dashboards using the monitoring data stored in the evaluated traces table.
- Set up alerts for critical quality or operational thresholds.
- Schedule regular quality reviews with key stakeholders.
Continuous improvement cycle
Monitoring is most valuable when it feeds back into your improvement process:
- Identify issues through monitoring metrics and user feedback.
- Export problematic examples to your evaluation set.
- Diagnose root causes using MLflow trace analysis and LLM judge results (as discussed in Common quality issues and how to fix them).
- Develop and test improvements against your expanded evaluation set.
- Deploy updates and monitor the impact.
This iterative, closed-loop approach helps ensure that your agent continues to improve based on real-world usage patterns, maintaining high quality while adapting to changing requirements and user behaviors. With Agent Monitoring you gain visibility into how your agent is performing in production, allowing you to proactively address issues and optimize quality and performance.