Tracing Mistral
MLflow Tracing ensures observability for your interactions with Mistral AI models.
When Mistral auto-tracing is enabled by calling the mlflow.mistral.autolog function,
usage of the Mistral SDK will automatically record generated traces during interactive development.
Note that only synchronous calls to the Text Generation API are supported, and that asynchronous API and streaming methods are not traced.
Prerequisites
Before running the examples below, make sure you have:
-
Databricks credentials configured: If running outside of Databricks, set your environment variables:
Bashexport DATABRICKS_HOST="https://your-workspace.cloud.databricks.com"
export DATABRICKS_TOKEN="your-personal-access-token"tipIf you're running inside a Databricks notebook, these are automatically set for you.
-
Mistral API key: Ensure your API key is configured. For production environments, use Mosaic AI Gateway or Databricks secrets instead of hardcoded values for secure API key management:
Bashexport MISTRAL_API_KEY="your-mistral-api-key"
Example Usage
On serverless compute clusters, autologging for genAI tracing frameworks is not automatically enabled. You must explicitly enable autologging by calling the appropriate mlflow.<library>.autolog() function for the specific integrations you want to trace.
import os
from mistralai import Mistral
import mlflow
# Turn on auto tracing for Mistral AI by calling mlflow.mistral.autolog()
mlflow.mistral.autolog()
# Set up MLflow tracking on Databricks
mlflow.set_tracking_uri("databricks")
mlflow.set_experiment("/Shared/mistral-demo")
# Configure your API key.
client = Mistral(api_key=os.environ["MISTRAL_API_KEY"])
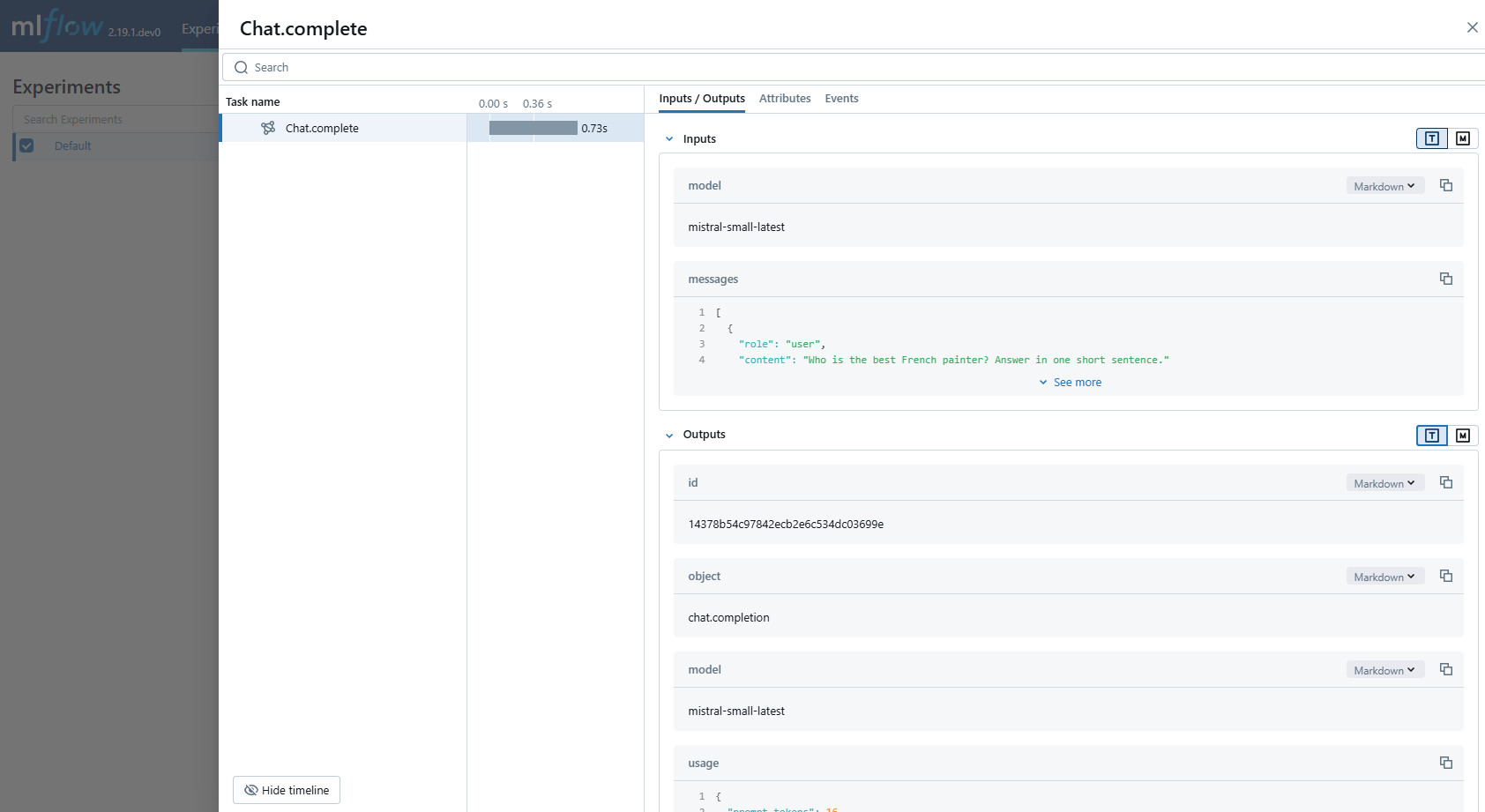
# Use the chat complete method to create new chat.
chat_response = client.chat.complete(
model="mistral-small-latest",
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Who is the best French painter? Answer in one short sentence.",
},
],
)
print(chat_response.choices[0].message)
For production environments, use Mosaic AI Gateway or Databricks secrets instead of hardcoded values for secure API key management.
Disable auto-tracing
Auto tracing for Mistral can be disabled globally by calling mlflow.mistral.autolog(disable=True) or mlflow.autolog(disable=True).
Next steps
- Understand tracing concepts - Learn how MLflow captures and organizes trace data
- Debug and observe your app - Use the Trace UI to analyze your Mistral application's behavior
- Evaluate your app's quality - Set up quality assessment for your Mistral-powered application