組み込みのLLMジャッジを使用する
概要
LLMジャッジを使用すると、 MLflow トレース を使用して GenAI アプリケーションを評価 および 監視 できます。これらのジャッジは、微妙な品質評価に大規模言語モデルを活用するMLflowスコアラーの一種で、決定論的なメトリクスを処理するコードベースのスコアラーを補完します。
:::重要 どのスコアラーをいつ使用するか: コードベースのスコアラーを使用する場合:
- 決定論的メトリクス (レイテンシ、ブラウス使用法)
- ルールベースの検証(フォーマットチェック、パターンマッチング)
- ビジネスロジック(価格計算、しきい値チェック)
LLMジャッジを使用する場合:
- 品質評価(正確性、一貫性、関連性)
- 安全性評価(毒性、有害物質含有量)
- テキスト、音声、画像、ビデオコンテンツの深い理解を必要とする複雑な評価 :::
ビルトインのLLMジャッジ
MLflow は、主要な品質ディメンション全体 にわたってトレースを評価するための、研究に裏付けられた組み込みの LLM ジャッジ を提供します。
組み込みのジャッジを使って素早く評価を開始します。ニーズの変化に応じて:
- ドメイン固有の基準に合わせてカスタム LLM ジャッジを構築する
- 決定論的なビジネス ロジック用のカスタム コード ベースのスコアラーを作成する
組み込みジャッジの仕組み
evaluate()またはモニタリング サービスによってトレースが渡されると、組み込みは次のように判断します。
traceを解析して、品質評価に使用される特定のフィールドとデータを抽出します。- 抽出されたフィールドとデータに基づいて品質評価を実行するためにLLMを呼び出します
- 品質評価を
Feedbackとして返してtraceに添付します
前提 条件
-
次のコマンドを実行して、MLflow 3.0 と OpenAI パッケージをインストールします。
Bashpip install --upgrade "mlflow[databricks]>=3.4.0" openai -
トレースの クイックスタート に従って、開発環境を MLflow エクスペリメントに接続します。
ステップ 1: 評価するサンプル アプリケーションを作成する
偽のレトリーバーを使用した単純なアプリケーションを定義します。
- OpenAI クライアントを初期化して、Databricks でホストされている LLM または OpenAI でホストされている LLM に接続します。
- Databricks-hosted LLMs
- OpenAI-hosted LLMs
MLflow を使用して、Databricks でホストされている LLM に接続する OpenAI クライアントを取得します。利用可能な基盤モデルからモデルを選択します。
import mlflow
from databricks.sdk import WorkspaceClient
# Enable MLflow's autologging to instrument your application with Tracing
mlflow.openai.autolog()
# Set up MLflow tracking to Databricks
mlflow.set_tracking_uri("databricks")
mlflow.set_experiment("/Shared/docs-demo")
# Create an OpenAI client that is connected to Databricks-hosted LLMs
w = WorkspaceClient()
client = w.serving_endpoints.get_open_ai_client()
# Select an LLM
model_name = "databricks-claude-sonnet-4"
ネイティブの OpenAI SDK を使用して、OpenAI でホストされるモデルに接続します。利用可能なOpenAIモデルからモデルを選択します。
import mlflow
import os
import openai
# Ensure your OPENAI_API_KEY is set in your environment
# os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "<YOUR_API_KEY>" # Uncomment and set if not globally configured
# Enable auto-tracing for OpenAI
mlflow.openai.autolog()
# Set up MLflow tracking to Databricks
mlflow.set_tracking_uri("databricks")
mlflow.set_experiment("/Shared/docs-demo")
# Create an OpenAI client connected to OpenAI SDKs
client = openai.OpenAI()
# Select an LLM
model_name = "gpt-4o-mini"
-
アプリケーションを定義します。
Pythonfrom mlflow.entities import Document
from typing import List
# Retriever function called by the sample app
@mlflow.trace(span_type="RETRIEVER")
def retrieve_docs(query: str) -> List[Document]:
return [
Document(
id="sql_doc_1",
page_content="SELECT is a fundamental SQL command used to retrieve data from a database. You can specify columns and use a WHERE clause to filter results.",
metadata={"doc_uri": "http://example.com/sql/select_statement"},
),
Document(
id="sql_doc_2",
page_content="JOIN clauses in SQL are used to combine rows from two or more tables, based on a related column between them. Common types include INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN, and RIGHT JOIN.",
metadata={"doc_uri": "http://example.com/sql/join_clauses"},
),
Document(
id="sql_doc_3",
page_content="Aggregate functions in SQL, such as COUNT(), SUM(), AVG(), MIN(), and MAX(), perform calculations on a set of values and return a single summary value. The most common aggregate function in SQL is COUNT().",
metadata={"doc_uri": "http://example.com/sql/aggregate_functions"},
),
]
# Sample app to evaluate
@mlflow.trace
def sample_app(query: str):
# 1. Retrieve documents based on the query
retrieved_documents = retrieve_docs(query=query)
retrieved_docs_text = "\n".join([doc.page_content for doc in retrieved_documents])
# 2. Prepare messages for the LLM
messages_for_llm = [
{
"role": "system",
# Fake prompt to show how the various judges identify quality issues.
"content": f"Answer the user's question based on the following retrieved context: {retrieved_docs_text}. Do not mention the fact that provided context exists in your answer. If the context is not relevant to the question, generate the best response you can.",
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": query,
},
]
# 3. Call LLM to generate the response
return client.chat.completions.create(
# Provide a valid model name for your LLM provider.
model=model_name,
messages=messages_for_llm,
)
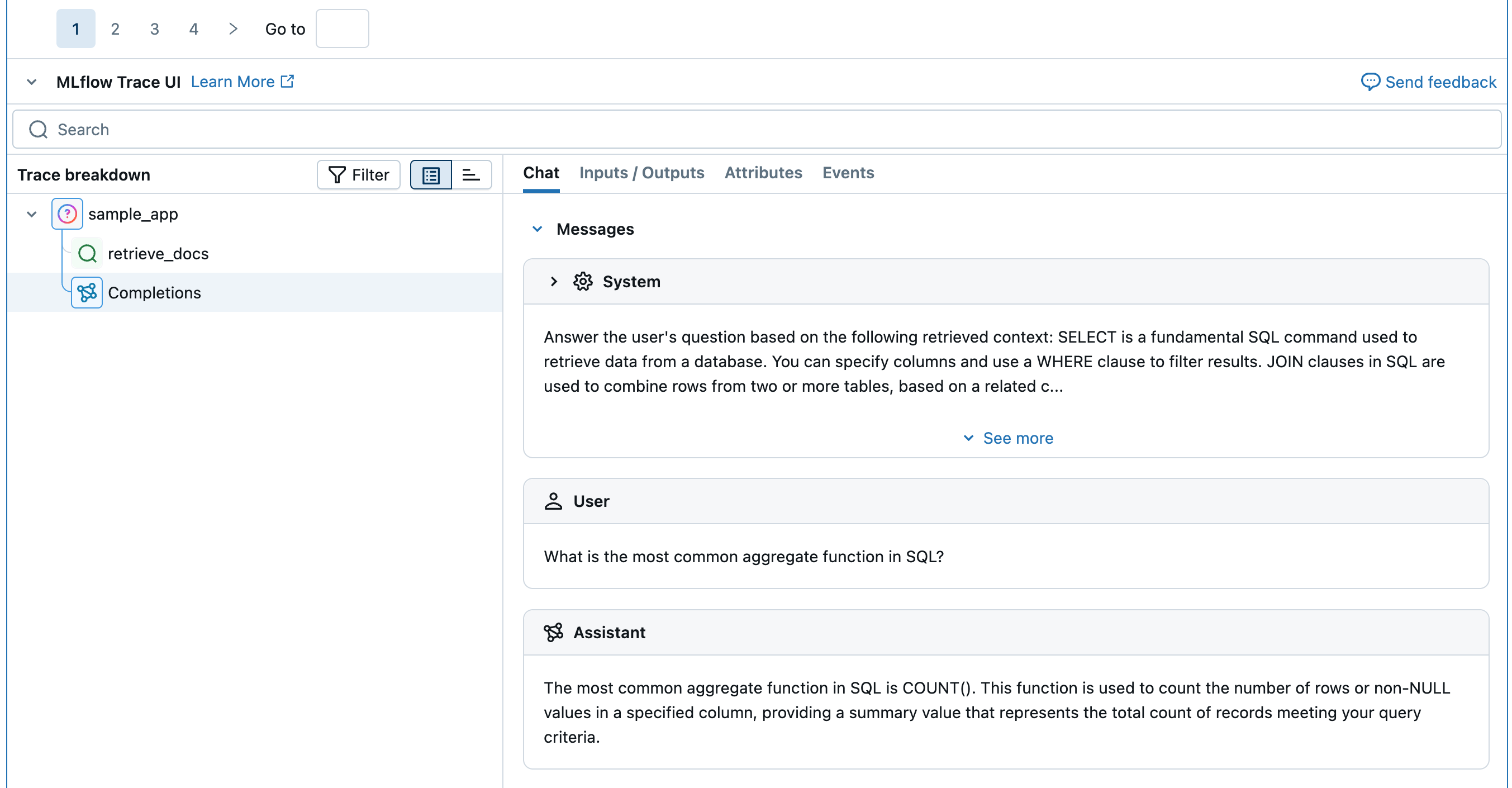
result = sample_app("what is select in sql?")
print(result)
ステップ 2: サンプル評価データセットを作成する
expected_facts グラウンドトゥルースを必要とする組み込みのジャッジを使用する場合にのみ必要です。
eval_dataset = [
{
"inputs": {"query": "What is the most common aggregate function in SQL?"},
"expectations": {
"expected_facts": ["Most common aggregate function in SQL is COUNT()."],
},
},
{
"inputs": {"query": "How do I use MLflow?"},
"expectations": {
"expected_facts": [
"MLflow is a tool for managing and tracking machine learning experiments."
],
},
},
]
print(eval_dataset)
ステップ 3: 組み込みLLMジャッジによる実行評価
それでは、上で定義したジャッジによる評価を実行してみましょう。
from mlflow.genai.scorers import (
Correctness,
ExpectationsGuidelines,
Guidelines,
RelevanceToQuery,
RetrievalGroundedness,
RetrievalRelevance,
RetrievalSufficiency,
Safety,
)
# Run built-in judges that require ground truth
mlflow.genai.evaluate(
data=eval_dataset,
predict_fn=sample_app,
scorers=[
Correctness(),
# RelevanceToQuery(),
# RetrievalGroundedness(),
# RetrievalRelevance(),
RetrievalSufficiency(),
# Safety(),
],
)
# Run built-in judges that do NOT require ground truth
mlflow.genai.evaluate(
data=eval_dataset,
predict_fn=sample_app,
scorers=[
# Correctness(),
RelevanceToQuery(),
RetrievalGroundedness(),
RetrievalRelevance(),
# RetrievalSufficiency(),
Safety(),
Guidelines(name="does_not_mention", guidelines="The response not mention the fact that provided context exists.")
],
)
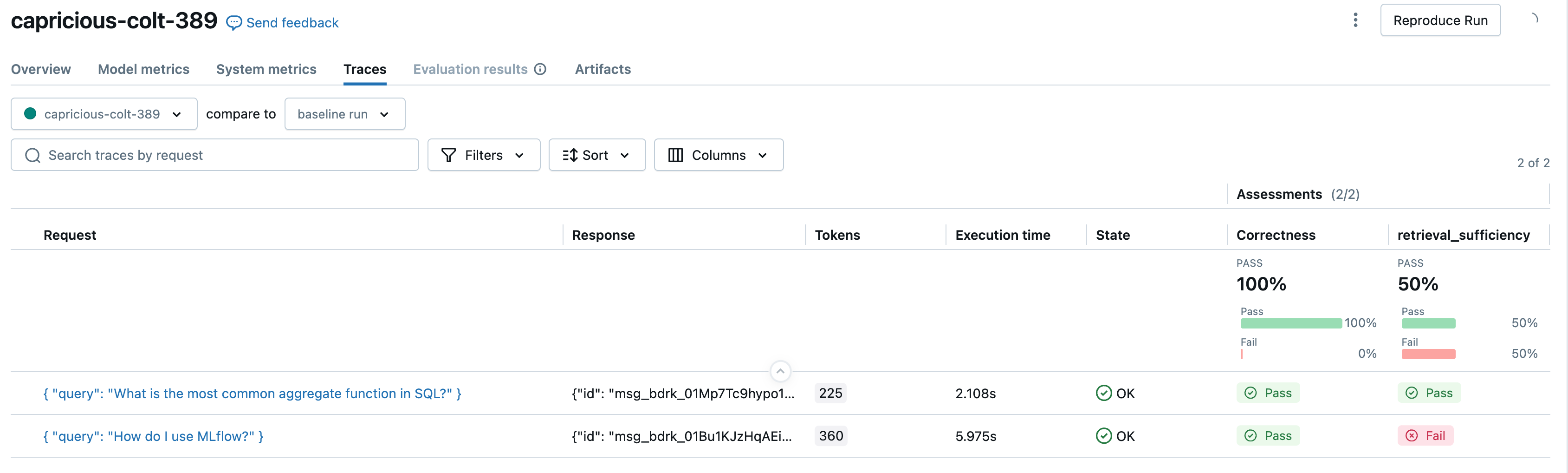
ジャッジ
デフォルトでは、各ジャッジは GenAI 品質評価を実行するために設計されたDatabricks ホスト LLMを使用します。ジャッジ定義内のmodel引数を使用してジャッジモデルを変更できます。モデルは<provider>:/<model-name>形式で指定する必要があります。例えば:
from mlflow.genai.scorers import Correctness
Correctness(model="databricks:/databricks-gpt-5-mini")
サポートされているモデルの一覧については、 MLflow のドキュメントを参照してください。
ジャッジ | 何を評価するのか? | グラウンドトゥルースが必要ですか? |
|---|---|---|
アプリのレスポンスは、ユーザーの入力に直接対応していますか? | No | |
アプリのレスポンスは、有害または有害なコンテンツを避けていますか? | No | |
アプリの応答は、取得した情報に基づいていますか? | No | |
取得したドキュメントはユーザーのリクエストに関連していますか? | No | |
アプリの応答はグラウンドトゥルースと比較して正しいですか? | Yes | |
取得したドキュメントには必要な情報がすべて含まれていますか? | Yes | |
アプリの応答は指定された条件を満たしていますか? | No | |
アプリの応答は例ごとの基準を満たしていますか? | No |
LLM ジャッジを強化するモデルに関する情報
- LLMジャッジは、Microsoftが運営するAzure OpenAIなどのサードパーティサービスを使用して生成AIアプリケーションを評価する場合があります。
- Azure OpenAIの場合、Databricksは不正行為モニタリングをオプトアウトしているため、プロンプトや応答はAzure OpenAIに保存されません。
- 欧州連合(EU)のワークスペースの場合、LLMジャッジはEUでホストされているモデルを使用します。他のすべてのリージョンでは、米国でホストされているモデルを使用します。
- パートナーを利用したAI機能を無効にすると、 LLMジャッジがパートナーを利用したモデルを呼び出すことができなくなります。 独自のモデルを提供することで、LLM ジャッジを引き続き使用できます。
- LLM ジャッジは、顧客が生成AIエージェント/アプリケーションを評価するのを支援することを目的としており、ジャッジ LLM アウトプットを LLMのトレーニング、改善、または微調整に使用すべきではありません。
次のステップ
これらの推奨アクションとチュートリアルで旅を続けてください。
- カスタムスコアラーの作成 - 特定のニーズに合わせてコードベースのメトリクスを構築します
- カスタムLLMスコアラーの作成 - LLMを使用して高度な評価基準を設計します
- アプリを評価する- 完全な例で組み込みのジャッジの動作を確認する
リファレンスガイド
このガイドで説明されている概念と機能の詳細なドキュメントをご覧ください。
- 構築済みジャッジ & スコアラーのリファレンス - 利用可能なすべてのジャッジの包括的な概要
- スコアラー - スコアラーの働き方と評価における彼らの役割を理解する
- LLM ジャッジ - 基礎となるジャッジのアーキテクチャについて学ぶ